The Human Brain Worksheets
The Human Brain Worksheets are a helpful resource that provide a comprehensive and engaging way for students to learn about this fascinating organ. Whether you are a teacher looking for supplementary materials or a parent seeking additional activities for your child, these worksheets are designed to enhance understanding of the subject matter and promote critical thinking skills.
Table of Images 👆
More Other Worksheets
Kindergarten Worksheet My RoomSpanish Verb Worksheets
Healthy Eating Plate Printable Worksheet
Cooking Vocabulary Worksheet
My Shadow Worksheet
Large Printable Blank Pyramid Worksheet
Relationship Circles Worksheet
DNA Code Worksheet
Meiosis Worksheet Answer Key
Rosa Parks Worksheet Grade 1
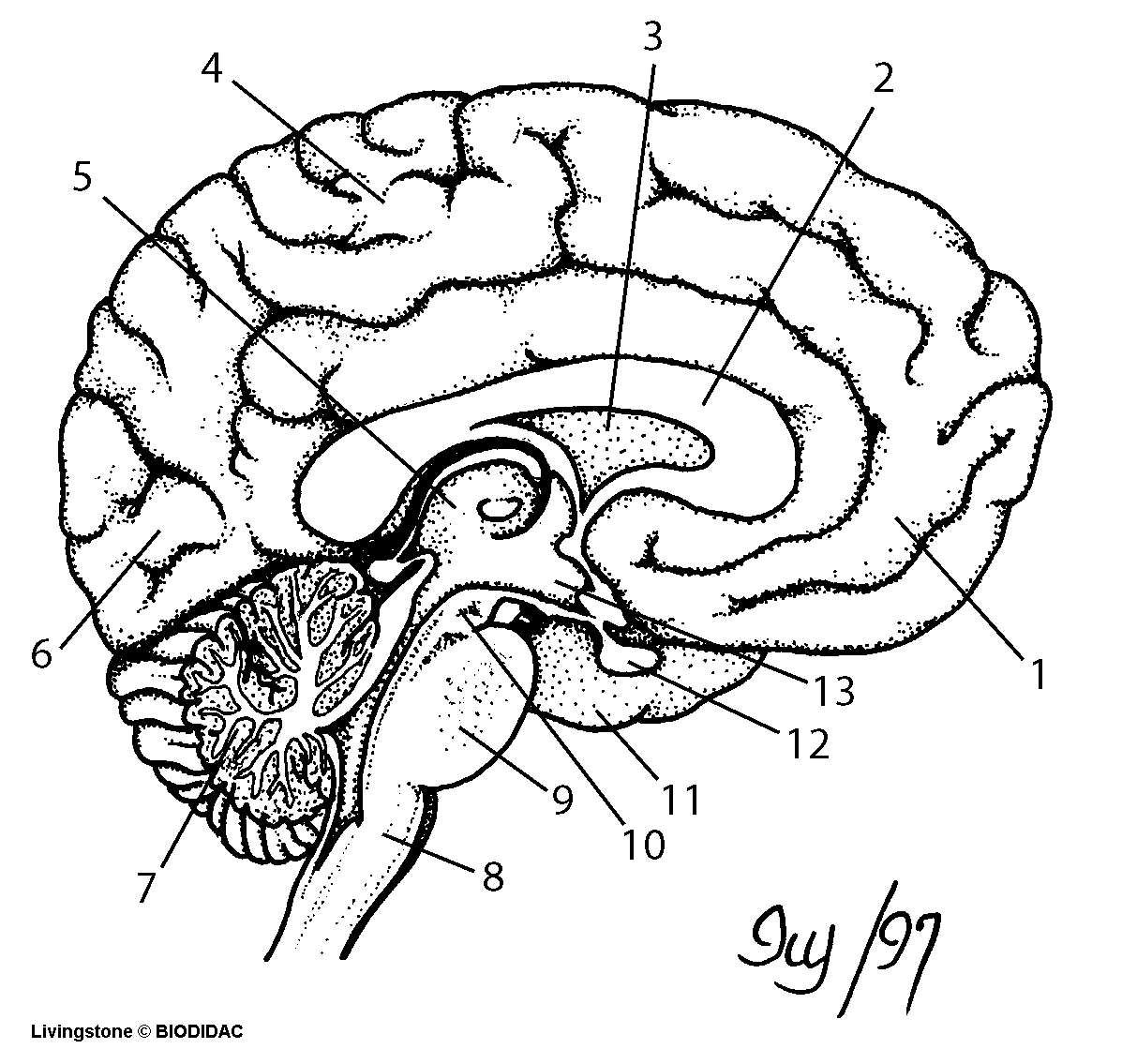
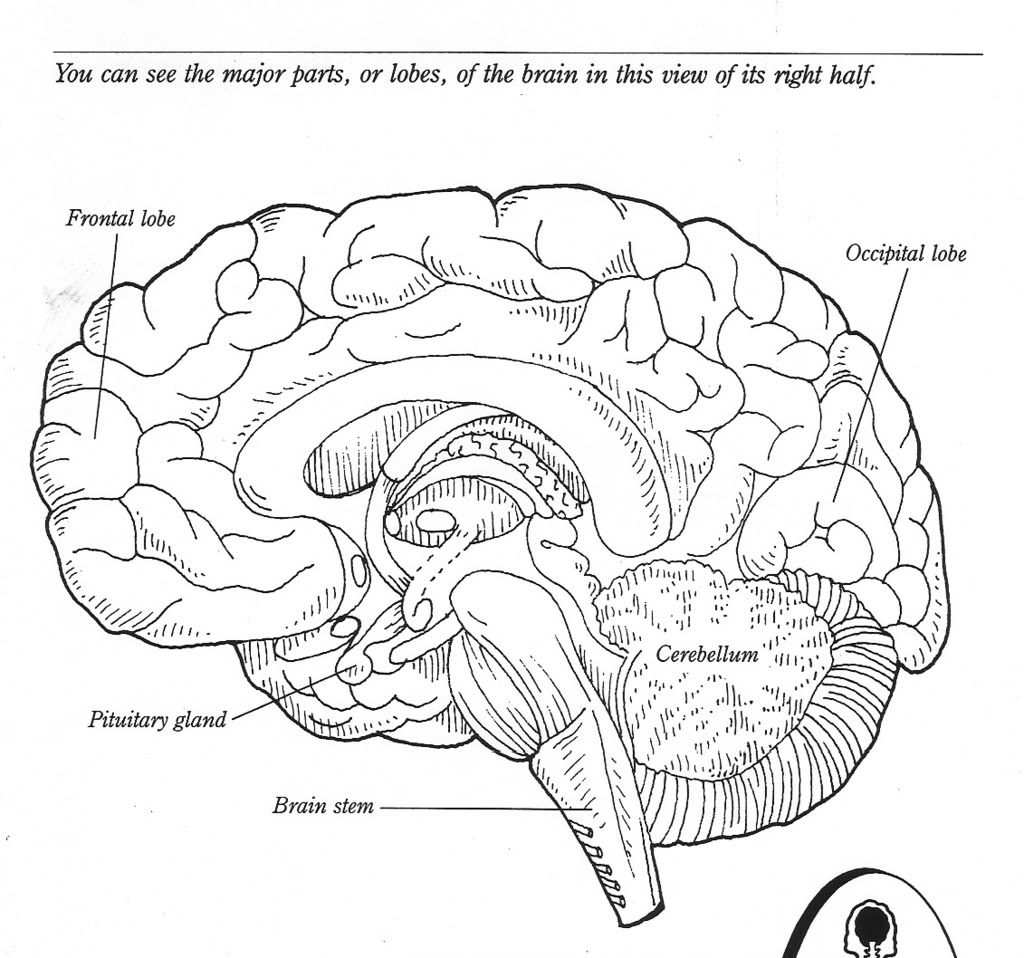
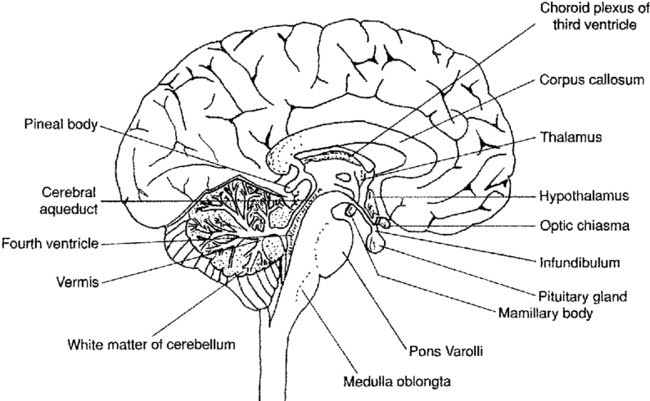
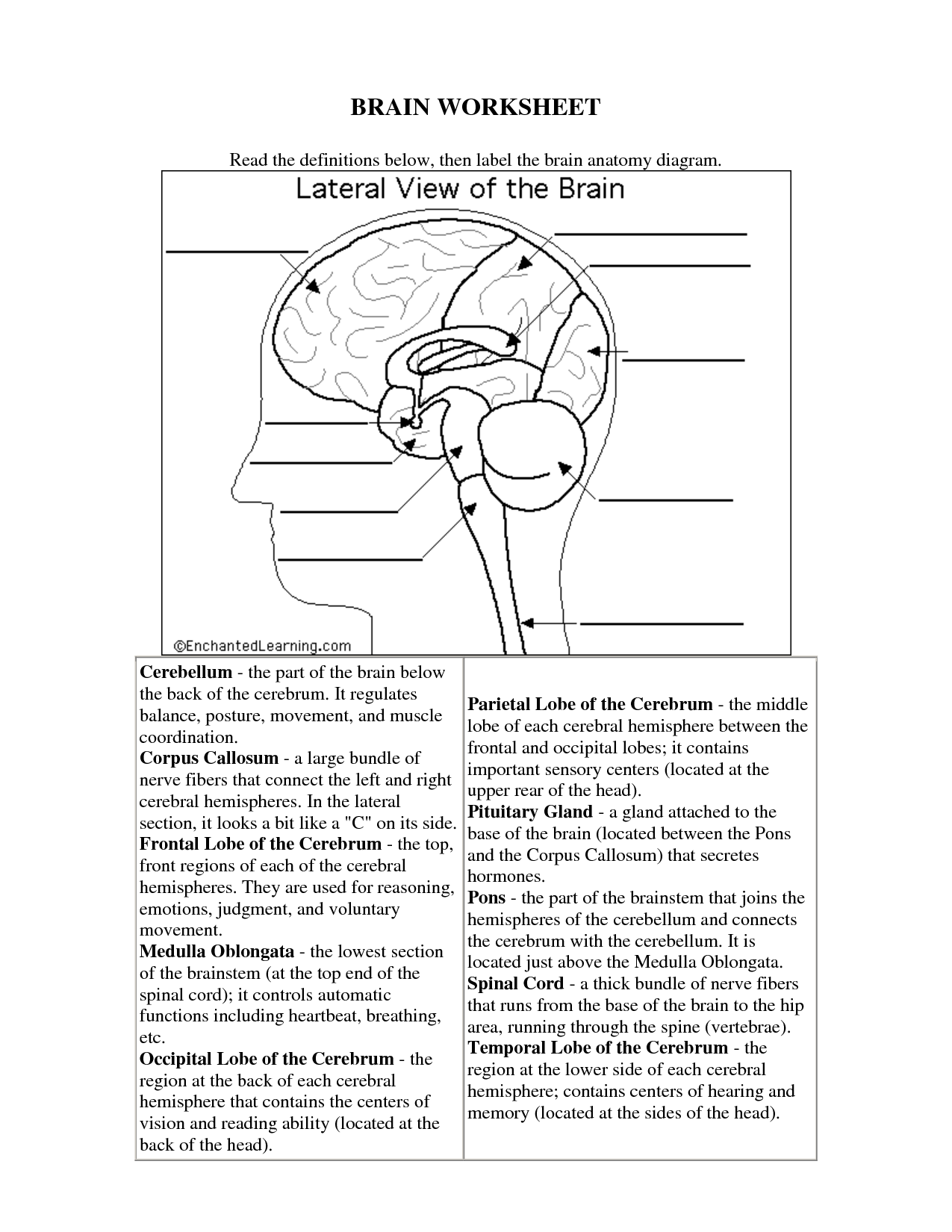
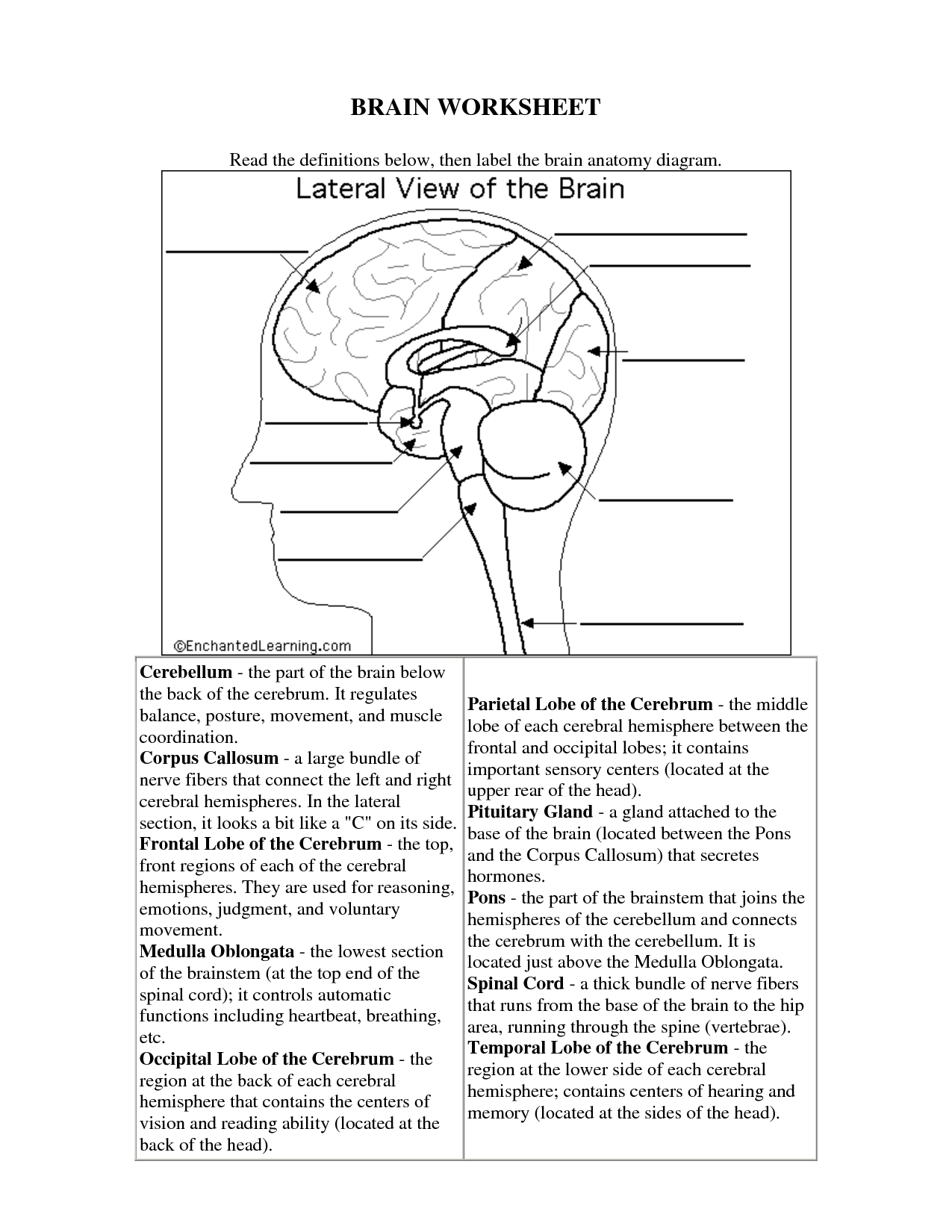
What is the purpose of the cerebral cortex in the brain?
The purpose of the cerebral cortex in the brain is to process sensory information, control voluntary movements, regulate thoughts, reasoning, and emotions, as well as to facilitate higher cognitive functions such as language, problem-solving, and decision-making. Additionally, it plays a crucial role in memory formation and storage, attention, and consciousness.
Describe the function of the hippocampus.
The hippocampus is a vital region of the brain responsible for memory formation and retention, particularly for converting short-term memories into long-term memories. It also plays a crucial role in spatial navigation, which is why damage to the hippocampus can result in memory loss and difficulties with spatial awareness. Additionally, the hippocampus is involved in regulating emotions and is important for learning and cognitive functions.
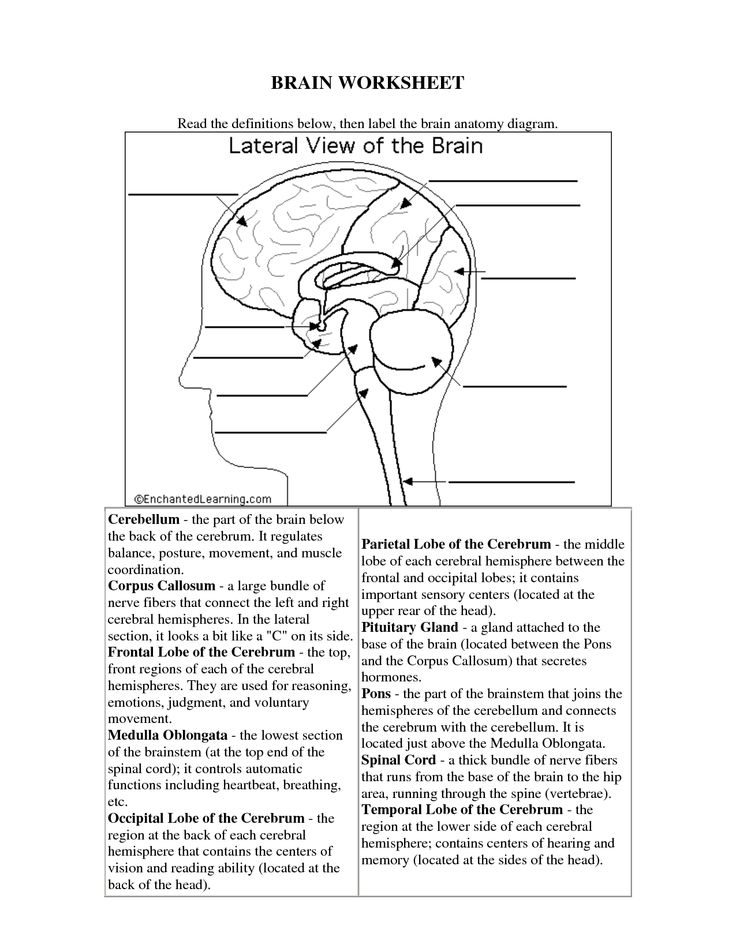
What is the role of the frontal lobe in cognitive processes?
The frontal lobe is responsible for a variety of cognitive processes, including executive functions such as decision-making, problem-solving, planning, and judgment. Additionally, it plays a crucial role in impulse control, emotional regulation, attention, and working memory. This area of the brain is essential for higher-level thinking and complex behavior, making it a key player in shaping our interactions with the world around us.
Explain the function of the cerebellum in motor control and coordination.
The cerebellum plays a crucial role in motor control and coordination by fine-tuning movements, maintaining posture, and ensuring smooth and balanced muscle coordination. It receives input from the sensory systems and the cerebral cortex to help coordinate voluntary movements, adjust motor activities based on sensory information, and regulate muscle tone. Damage to the cerebellum can result in issues such as ataxia, tremors, and difficulties with balance and coordination, underscoring its significance in motor control and coordination.
Describe how the brain processes and stores information through synaptic connections.
The brain processes and stores information through synaptic connections, where neurons communicate with each other through connections called synapses. When a neuron is activated, it releases neurotransmitters that travel across the synapse and bind to receptors on the receiving neuron, triggering an electrical signal. This process strengthens the connection between the two neurons, known as synaptic plasticity, which is fundamental for learning and memory. Through repeated activation, long-lasting changes in the strength of synaptic connections occur, facilitating the encoding and storage of information in the brain.
What is the role of the amygdala in emotional processing?
The amygdala plays a crucial role in emotional processing by regulating emotions such as fear, pleasure, and aggression. It is involved in the processing and memory of emotional reactions, particularly fear-related memories, and also helps to prioritize emotional information for faster response to potential threats or rewards. Additionally, the amygdala is responsible for coordinating physiological responses to emotional stimuli, such as the release of stress hormones in response to a perceived threat.
Explain how the brain controls voluntary movements through the motor cortex.
The motor cortex, located in the brain's frontal lobe, plays a crucial role in controlling voluntary movements. It receives signals from other parts of the brain and sends commands to the spinal cord, which then directs muscles to move. Neurons in the motor cortex are organized in a somatotopic manner, meaning that different areas of the cortex correspond to specific body parts. When a movement is initiated, the motor cortex activates the appropriate neurons which then send signals down the spinal cord to the muscles, ultimately resulting in the desired movement. This process allows the brain to finely control and coordinate voluntary movements.
Describe the function of the hypothalamus in regulating basic bodily functions.
The hypothalamus plays a crucial role in regulating basic bodily functions such as hunger, thirst, body temperature, and sleep-wake cycles. It helps to maintain homeostasis by monitoring and controlling hormone production, autonomic functions, and the circadian rhythm. Additionally, the hypothalamus is involved in emotional responses, stress reactions, and the regulation of the pituitary gland, impacting various physiological processes throughout the body.
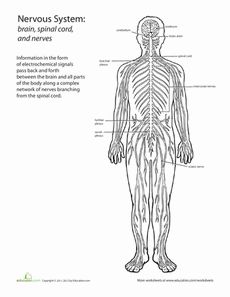
What role does the brain stem play in controlling vital functions such as breathing and heart rate?
The brain stem plays a crucial role in controlling vital functions such as breathing and heart rate. It contains centers that regulate these functions, including the respiratory center, which controls breathing, and the cardiovascular center, which regulates heart rate and blood pressure. Through a network of neurons, the brain stem receives sensory information and sends out signals to coordinate these essential bodily processes, ensuring that oxygen is delivered to the tissues and organs effectively. Damage to the brain stem can disrupt these functions, leading to serious consequences for overall health and well-being.
Explain the significance of neural plasticity in the brain's ability to adapt and learn.
Neural plasticity, or the brain's ability to change and reorganize itself throughout life, is crucial for adaptation and learning. This flexibility allows the brain to form new neural connections, strengthen existing ones, and even reassign functions to different areas, enabling us to acquire new skills, store memories, and adjust to changes in our environment. In essence, neural plasticity is the foundation of our ability to learn, adapt, and continuously evolve in response to experiences and challenges.
Have something to share?
Who is Worksheeto?
At Worksheeto, we are committed to delivering an extensive and varied portfolio of superior quality worksheets, designed to address the educational demands of students, educators, and parents.


















Comments