The Genetic Code Worksheet Answers
Are you a biology student seeking a comprehensive resource to test your understanding of the genetic code? Look no further than the Genetic Code Worksheet Answers. This informative document provides detailed answers to a variety of worksheet questions, allowing you to check your knowledge and ensure mastery of this essential topic. Whether you're reviewing for an exam or simply looking to deepen your understanding, these answers provide a valuable tool for biology students at any level.
Table of Images 👆
- Breaking the Code Worksheet Answers
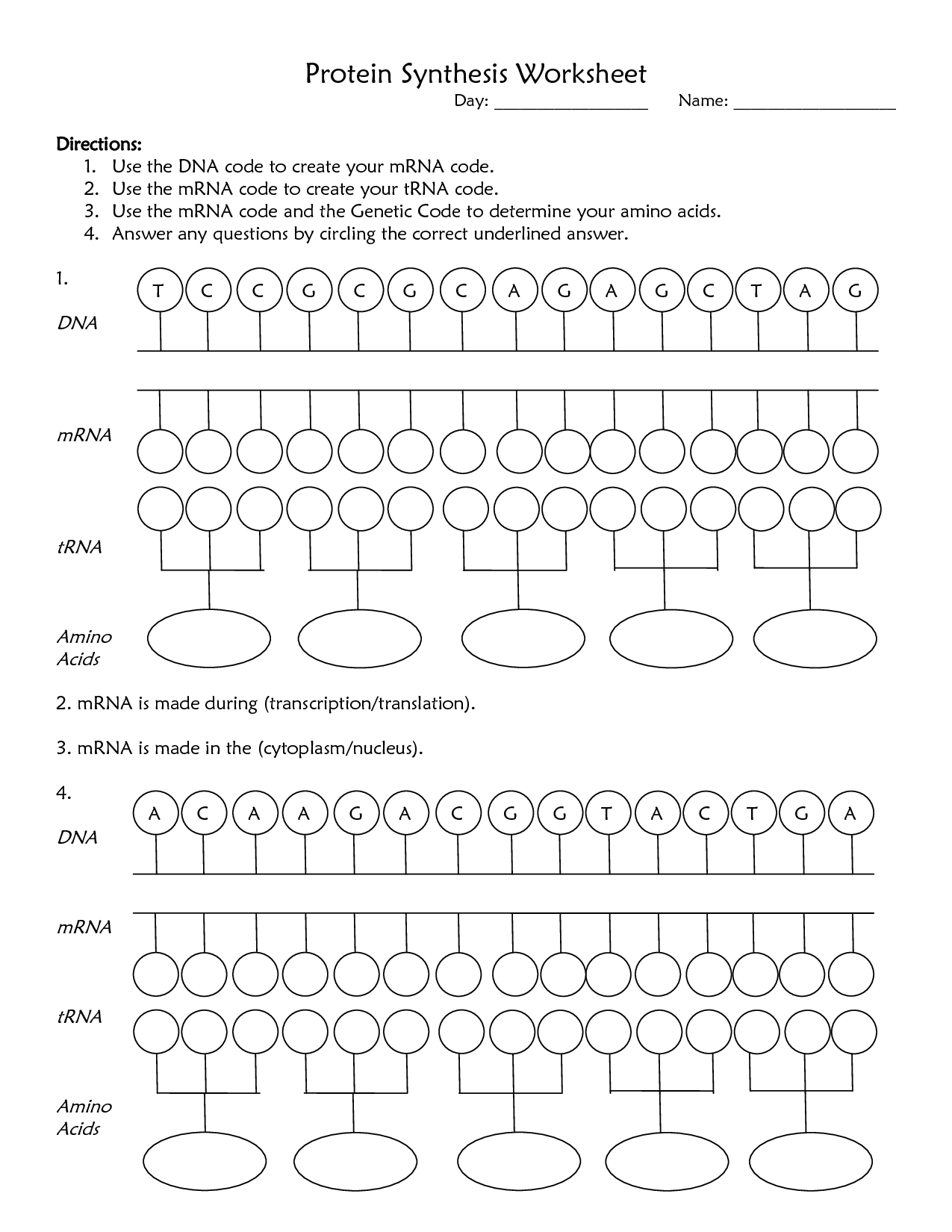
- Protein Synthesis Worksheet Answer Key
- DNA Mutations Practice Worksheet Answer Key
- Simple Genetics Practice Problems Worksheet Answers
- Genetic Mutation Worksheet Answers
- Genetics Monohybrid Crosses Worksheet Answer Key
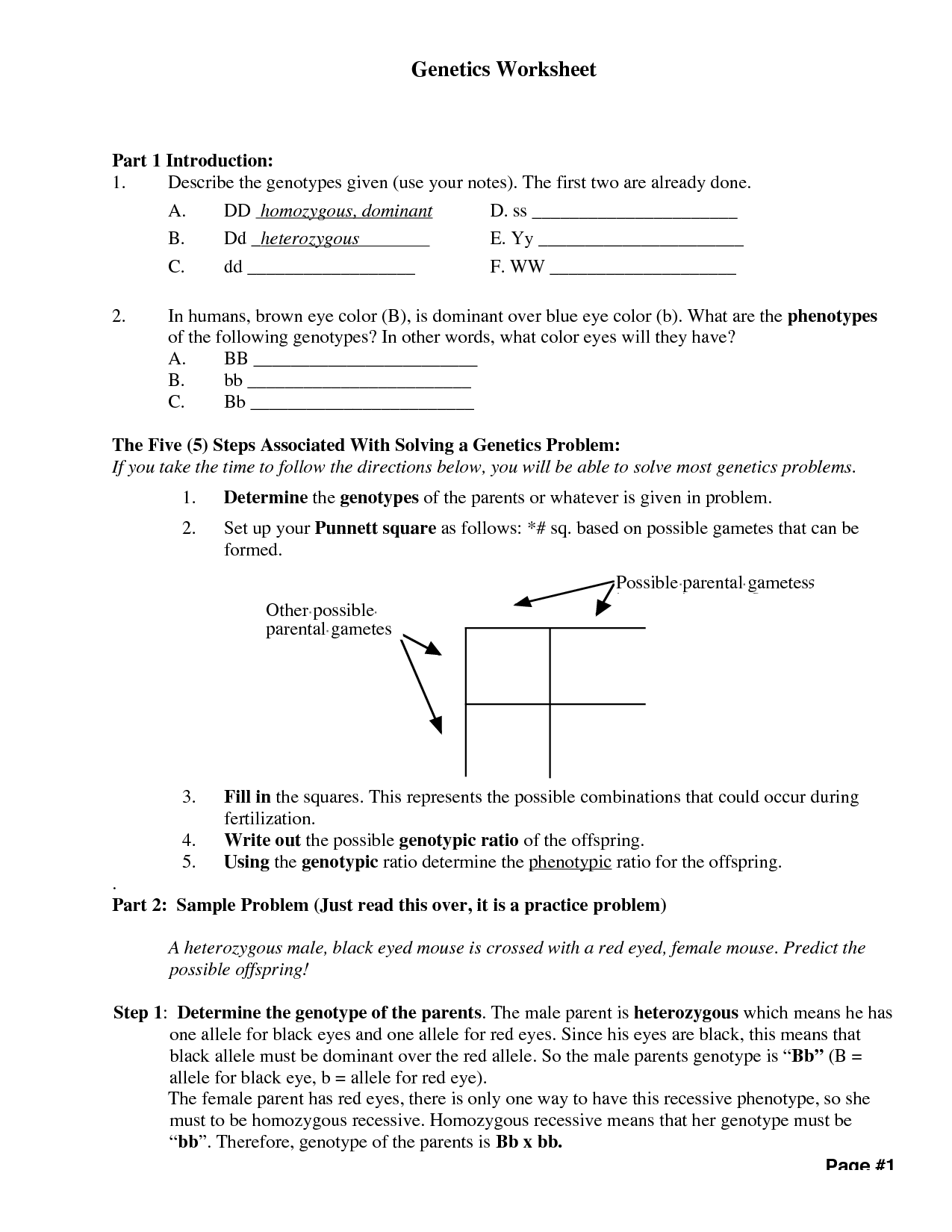
- Genetics Worksheet Answer Key
- Genetics Worksheet Answer Key
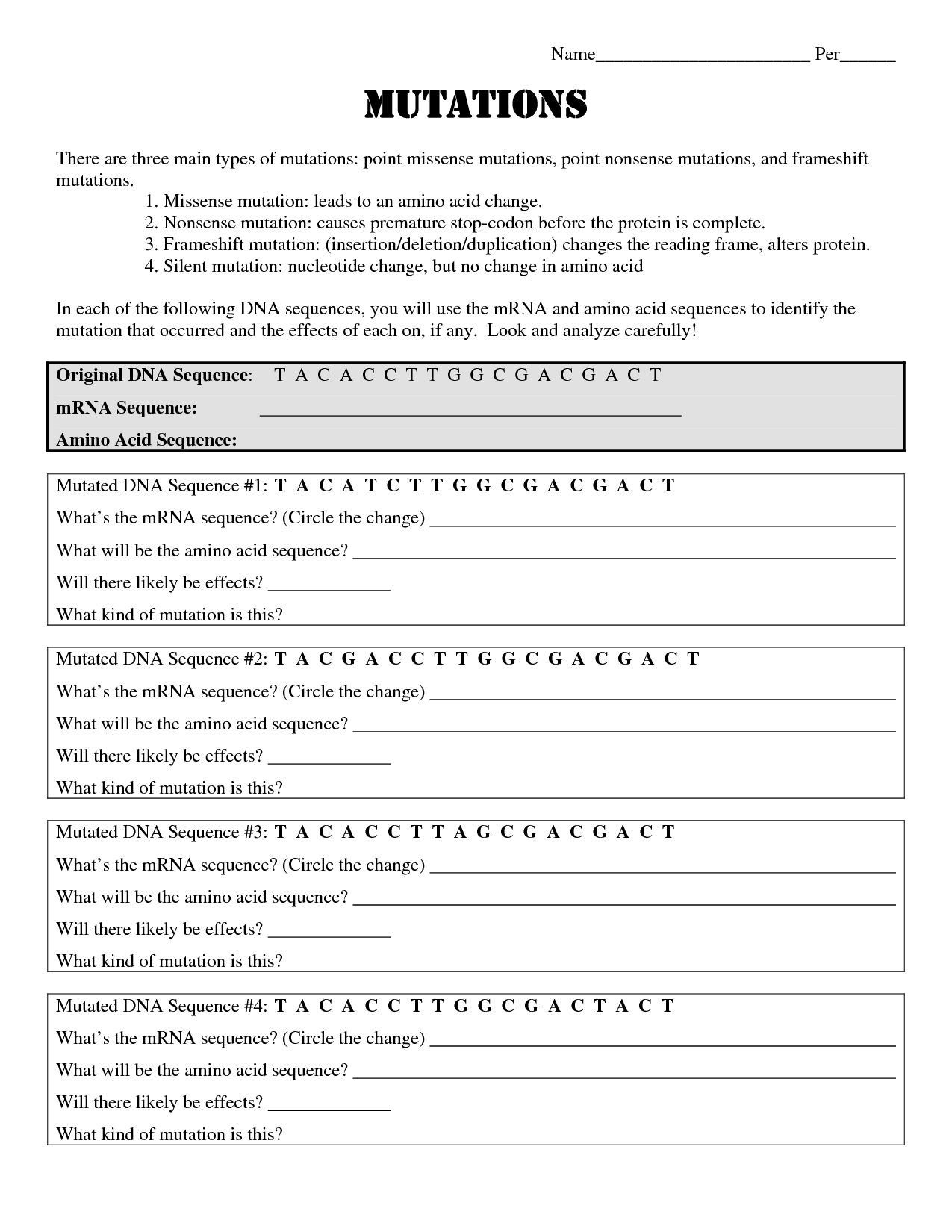
- Mutations Worksheet Answer Key
- Genetics Review Worksheet Answers
- Human Genetic Disorders Worksheet
- Genetic Engineering Worksheet Answers
- Mutations Worksheet Answer Key
- Gene Mutations Worksheet Answer Key
- Mutations Worksheet Answer Key
- Simple Genetics Practice Problems Worksheet Answers
- Genetic Variation Worksheet Answers
- AP Biology Genetics Worksheet
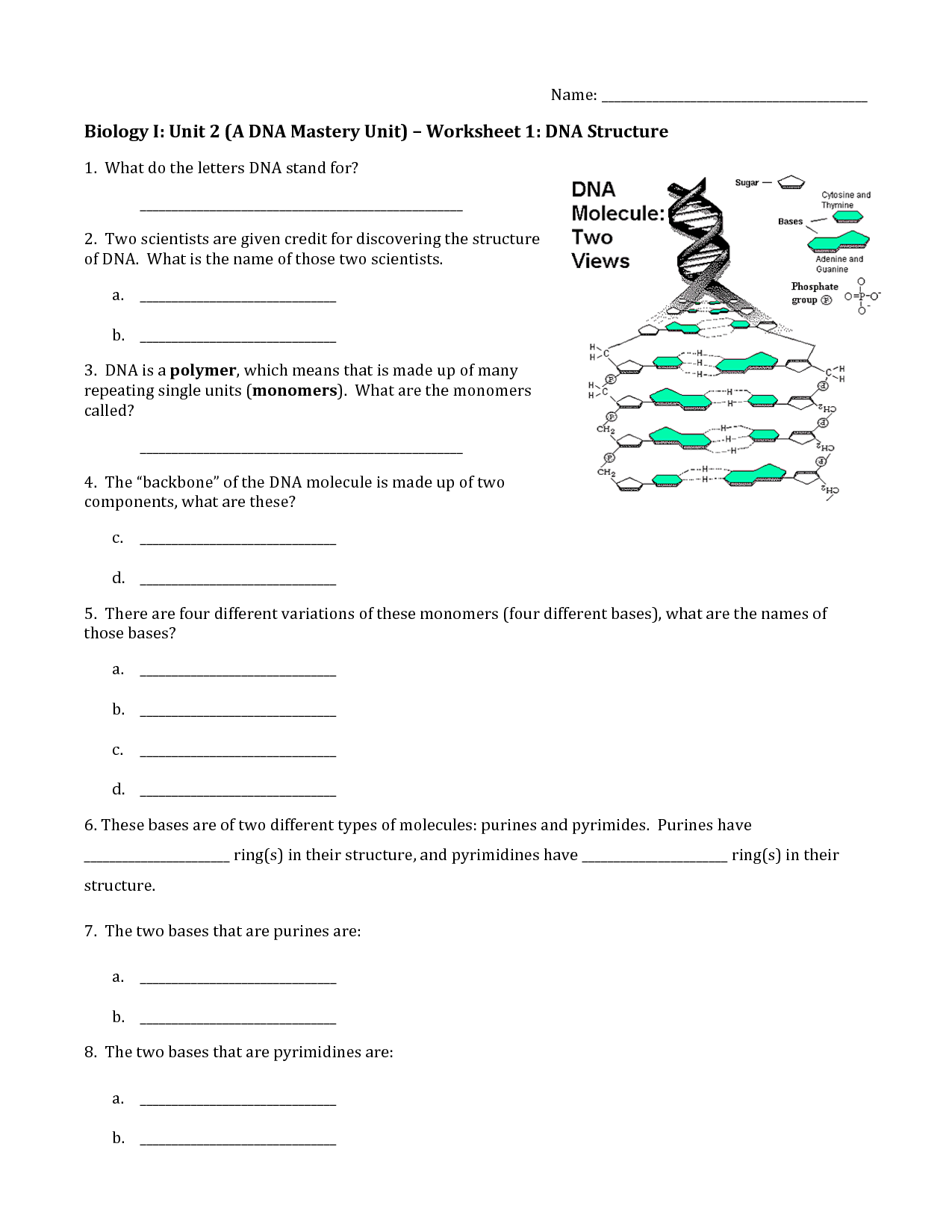
- DNA Structure Worksheet Answers
More Other Worksheets
Kindergarten Worksheet My RoomSpanish Verb Worksheets
Cooking Vocabulary Worksheet
My Shadow Worksheet
Large Printable Blank Pyramid Worksheet
Relationship Circles Worksheet
DNA Code Worksheet
Meiosis Worksheet Answer Key
Art Handouts and Worksheets
7 Elements of Art Worksheets
What is the Genetic Code?
The Genetic Code is the set of rules by which information encoded within the genetic material, usually in the form of DNA or RNA, is translated into proteins. This code consists of a specific sequence of nucleotides that dictate the sequence of amino acids in a protein. Each set of three nucleotides, known as a codon, corresponds to a specific amino acid or a specific signal for the beginning or end of protein synthesis.
How is genetic information stored in DNA?
Genetic information is stored in DNA through a series of nucleotide bases, which are arranged in a particular sequence to form genes. These genes contain the instructions for making proteins, the building blocks of cells and tissues. The sequence of nucleotide bases in DNA is like a code that directs the activities of the cell, such as cell growth, division, and function. This genetic information is passed on from one generation to the next through the process of DNA replication and cell division.
What are the building blocks of DNA?
The building blocks of DNA are nucleotides, which consist of a phosphate group, a sugar molecule (deoxyribose in DNA), and one of four nitrogenous bases: adenine (A), cytosine (C), guanine (G), or thymine (T). These nucleotides pair up to form the double helix structure of DNA, with A always pairing with T and C always pairing with G.
How many letters in the genetic code specify an amino acid?
There are 64 letters in the genetic code, also known as codons, of which 61 specify amino acids.
How many nucleotides are typically present in a codon?
A codon typically consists of three nucleotides.
How many codons code for a stop signal?
There are three codons that code for a stop signal in the genetic code: UAA, UAG, and UGA. These codons signal the termination of protein synthesis during translation.
What is the start codon that initiates protein synthesis?
The start codon that initiates protein synthesis is AUG, which codes for the amino acid methionine.
What is the role of transfer RNA (tRNA) in the genetic code?
Transfer RNA (tRNA) plays a crucial role in the genetic code by bringing amino acids to the ribosome during protein synthesis according to the mRNA template. Each tRNA molecule carries a specific amino acid and has an anticodon sequence that pairs with the codon on the mRNA. By matching the correct amino acid with the corresponding codon, tRNA ensures that the protein being synthesized is accurate and functional.
How does the genetic code ensure that each amino acid is specified by a specific codon?
The genetic code ensures that each amino acid is specified by a specific codon through the principle of codon-anticodon recognition during translation. Each codon in the mRNA sequence corresponds to a specific anticodon on the tRNA molecule, which carries the corresponding amino acid. This specific pairing between codons and anticodons ensures that the correct amino acid is incorporated into the growing polypeptide chain during protein synthesis, thereby maintaining the fidelity of protein translation in the cell.
Can multiple codons code for the same amino acid?
Yes, multiple codons can code for the same amino acid. This redundancy is due to the degenerate nature of the genetic code, where most amino acids are specified by more than one codon. For example, the amino acid leucine can be encoded by six different codons: UUA, UUG, CUU, CUC, CUA, and CUG. This redundancy helps to protect against errors during protein synthesis and allows for greater flexibility in the genetic code.
Have something to share?
Who is Worksheeto?
At Worksheeto, we are committed to delivering an extensive and varied portfolio of superior quality worksheets, designed to address the educational demands of students, educators, and parents.

































Comments