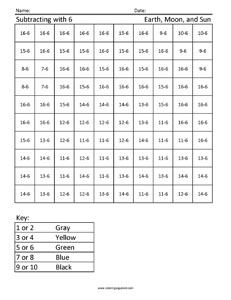
Sun Worksheets Addition
Need some engaging and informative worksheets to help reinforce addition skills? Look no further! Our Sun Worksheets Addition collection is designed specifically for elementary school students who are learning the basics of addition. These worksheets offer a variety of activities and exercises that focus on developing their understanding of adding numbers. Whether it's counting suns and adding them together or solving simple addition problems, these worksheets provide a fun and effective way for students to practice their math skills.
Table of Images 👆
More Other Worksheets
Kindergarten Worksheet My RoomSpanish Verb Worksheets
Cooking Vocabulary Worksheet
My Shadow Worksheet
Large Printable Blank Pyramid Worksheet
Relationship Circles Worksheet
DNA Code Worksheet
Meiosis Worksheet Answer Key
Art Handouts and Worksheets
7 Elements of Art Worksheets
What is the Sun?
The Sun is a yellow dwarf star located at the center of our solar system, consisting mostly of hydrogen and helium. It is a powerful source of energy, emitting heat and light that sustain life on Earth. The Sun's gravity holds the planets in orbit around it, and its nuclear fusion reactions create the energy that powers the star.
How does the Sun produce energy?
The Sun produces energy through a process called nuclear fusion, where hydrogen atoms fuse together to form helium. This reaction releases an immense amount of energy in the form of light and heat. The high pressure and temperature in the Sun's core allow for these fusion reactions to occur, sustaining the Sun's energy output.
How far is the Sun from Earth?
The average distance from the Sun to Earth is approximately 93 million miles (150 million kilometers), which is known as an astronomical unit (AU).
What is the temperature of the Sun's surface?
The temperature of the Sun's surface is approximately 5,500 degrees Celsius (9,932 degrees Fahrenheit).
What are sunspots and how do they form?
Sunspots are dark areas on the sun's surface caused by magnetic activity. They form when the sun's magnetic field lines become twisted, inhibiting the normal flow of heat from the sun's interior to its surface. This disruption results in cooler spots on the sun's surface, which appear dark in contrast to the surrounding hotter areas. Sunspots are often accompanied by solar flares and coronal mass ejections, which can affect space weather and communication systems on Earth.
What is the Sun made of?
The Sun is primarily made up of hydrogen and helium, with small amounts of other elements like oxygen, carbon, neon, and iron. These elements undergo nuclear fusion in the Sun's core, where immense pressure and temperature create the conditions for hydrogen atoms to fuse together and release energy in the form of light and heat.
How long does it take for sunlight to reach Earth?
It takes approximately 8 minutes and 20 seconds for sunlight to travel from the Sun to reach Earth.
How does the Sun's gravity affect the planets in our solar system?
The Sun's gravity affects the planets in our solar system by keeping them in orbit around it. This gravitational force is what causes the planets to move in elliptical paths and to remain in a stable configuration relative to the Sun. The strength of the Sun's gravity decreases with distance, so planets closer to the Sun experience a stronger pull compared to those farther away. This gravitational interaction is essential for maintaining the stability and structure of our solar system.
What is a solar flare and how does it impact Earth?
A solar flare is a sudden and intense burst of energy and radiation emitted from the sun's surface. These solar flares can release massive amounts of solar particles into space, which can impact Earth's magnetosphere and potentially lead to disturbances in communication and navigation systems, power grids, and even cause auroras. Additionally, exposure to high levels of radiation from solar flares can pose risks to astronauts in space and airline passengers at high altitudes.
How does the Sun's activity change over time, and what are the implications for Earth?
The Sun's activity changes over time in an approximately 11-year cycle known as the solar cycle. During this cycle, the Sun goes through periods of increased and decreased solar activity, including sunspots, solar flares, and solar storms. These changes can impact Earth in various ways, such as affecting satellites and communication systems, causing geomagnetic storms, and influencing our climate. Understanding the Sun's activity is crucial for predicting and mitigating potential risks to our planet.
Have something to share?
Who is Worksheeto?
At Worksheeto, we are committed to delivering an extensive and varied portfolio of superior quality worksheets, designed to address the educational demands of students, educators, and parents.









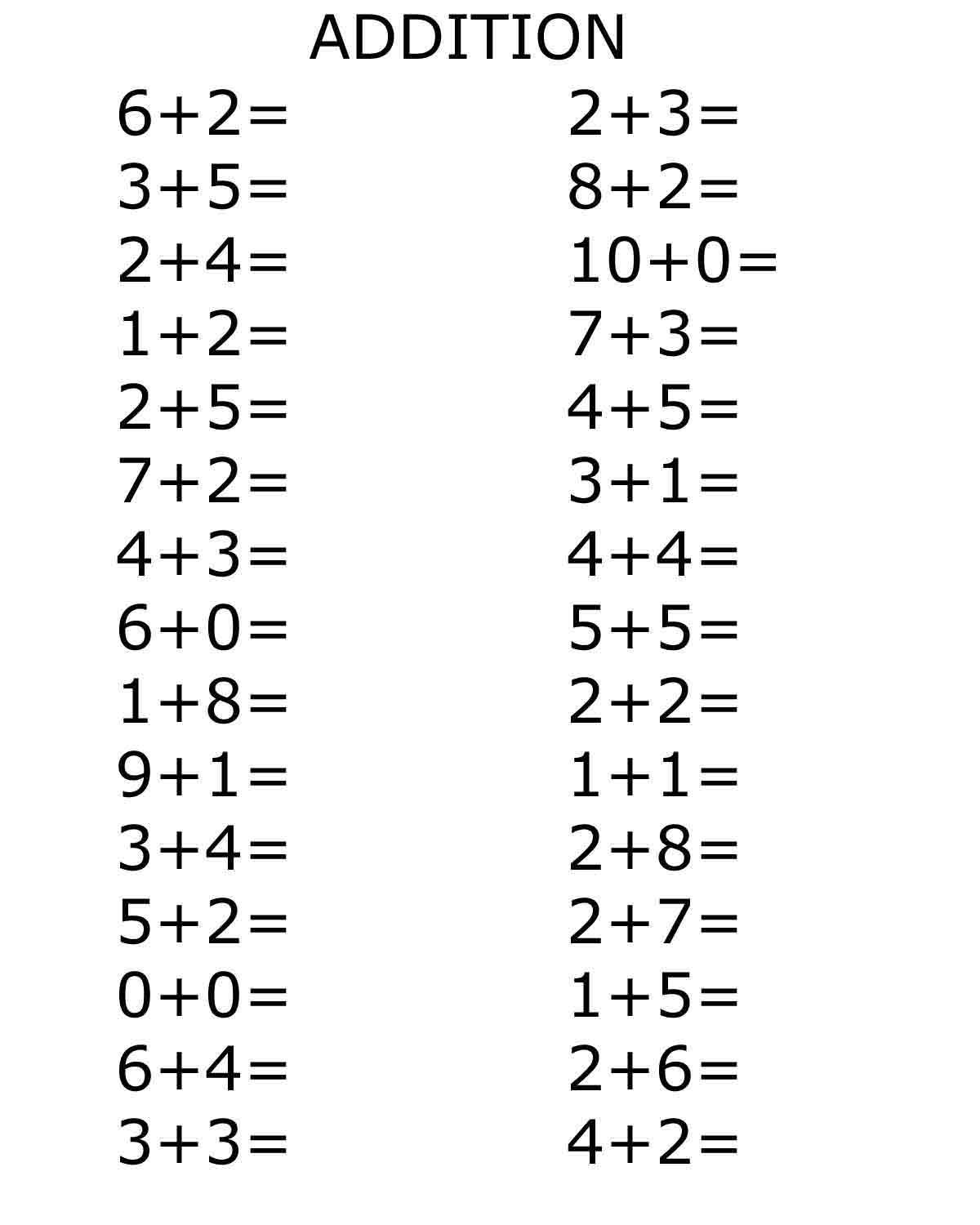














Comments