Speed Velocity and Acceleration Worksheets
In the world of physics, studying the concepts of speed, velocity, and acceleration is essential. Whether you are a student wanting to reinforce your understanding or a teacher searching for supplemental resources, worksheets can be a valuable tool. These worksheets provide a structured way to practice and solidify your knowledge of these fundamental concepts in physics.
Table of Images 👆
- Force and Acceleration Worksheet
- Speed Velocity Acceleration Worksheet Answers
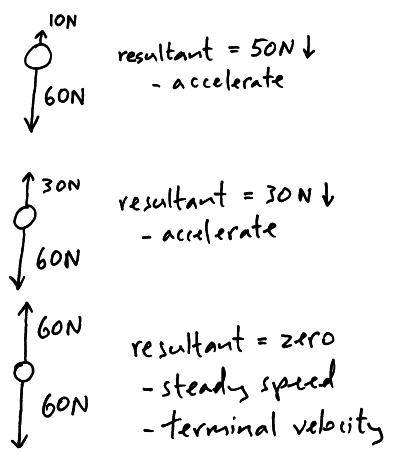
- Terminal Velocity Physics
- Speed and Acceleration Worksheets
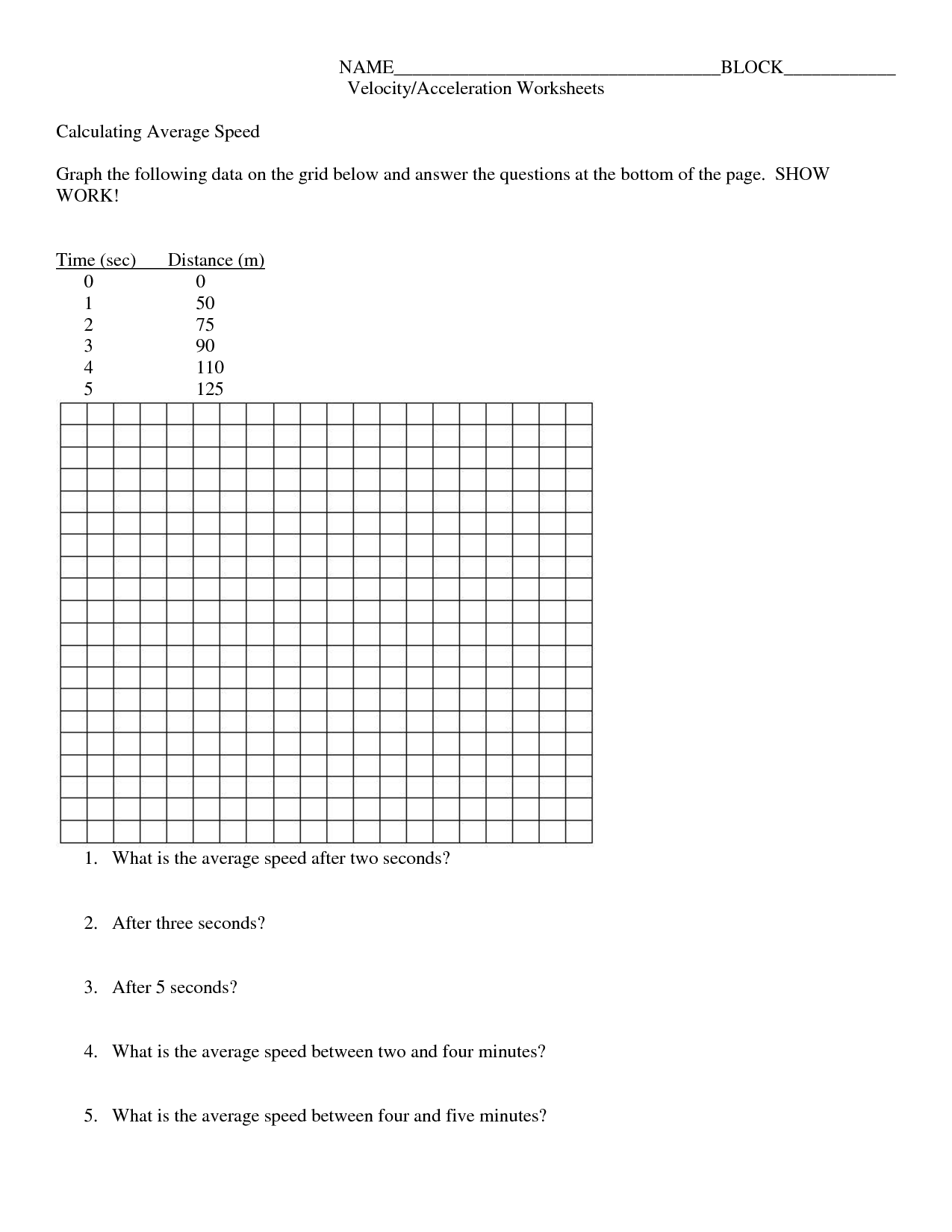
- Speed and Velocity Graphing Worksheets
- Force and Acceleration Worksheet Answers
- Motion Graphs Worksheet Answers
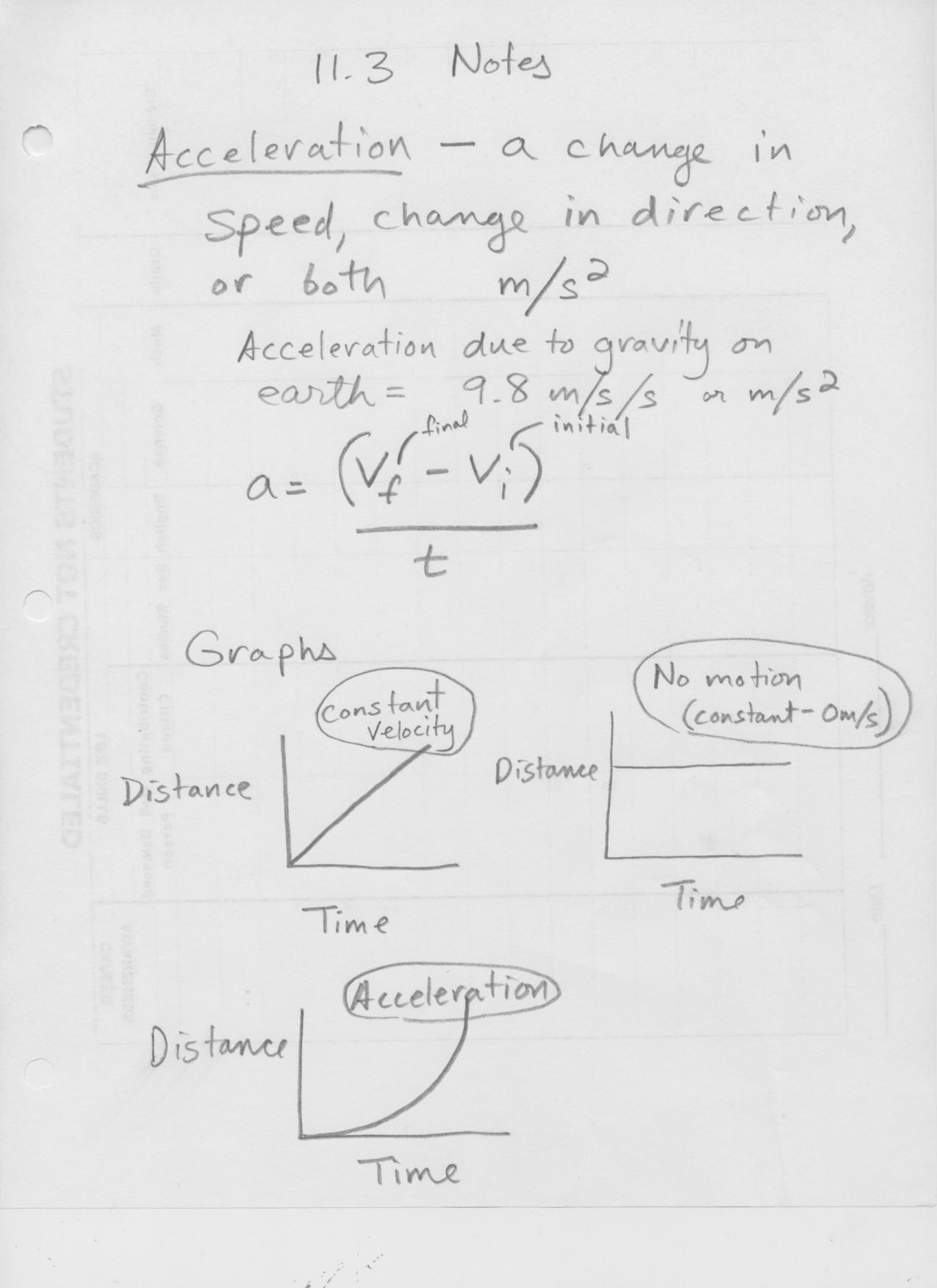
- Uniform Acceleration
- Examples of Non Linear-Motion
- Bill Nye Video Worksheet Answer Key
- Force and Momentum Problems Worksheet Answers
- Force and Momentum Problems Worksheet Answers
- Force and Momentum Problems Worksheet Answers
- Force and Momentum Problems Worksheet Answers
- Force and Momentum Problems Worksheet Answers
- Force and Momentum Problems Worksheet Answers
More Other Worksheets
Kindergarten Worksheet My RoomSpanish Verb Worksheets
Healthy Eating Plate Printable Worksheet
Cooking Vocabulary Worksheet
My Shadow Worksheet
Large Printable Blank Pyramid Worksheet
Relationship Circles Worksheet
DNA Code Worksheet
Meiosis Worksheet Answer Key
Art Handouts and Worksheets
What is speed?
Speed is a measure of how fast an object is moving, calculated as the distance traveled per unit of time. It is a scalar quantity, meaning it only has magnitude (how fast an object is moving) and not direction. Speed is commonly measured in units such as meters per second (m/s) or kilometers per hour (km/h).
How is speed different from velocity?
Speed is a scalar quantity that represents the rate at which an object moves, while velocity is a vector quantity that includes both the speed of an object and its direction of motion. This means that velocity not only tells us how fast an object is moving but also in which direction it is moving. Speed is just a numerical value without any directional information, whereas velocity combines speed and direction into a single quantity.
What is the formula for calculating speed?
The formula for calculating speed is speed = distance / time.
What are the units of speed?
The units of speed are typically measured in meters per second (m/s), kilometers per hour (km/h), miles per hour (mph), or knots (nautical miles per hour).
Define velocity.
Velocity is a vector quantity that describes the rate of change of an object's position with respect to time. It includes both the speed of the object and the direction in which it is moving, making it a more comprehensive measure of motion than speed alone. Velocity is typically measured in units such as meters per second (m/s) or kilometers per hour (km/h).
How is velocity different from speed?
Velocity and speed both describe how fast an object is moving, but velocity also includes the direction in which the object is moving whereas speed does not. In other words, speed is a scalar quantity, only representing the magnitude of the object's movement, while velocity is a vector quantity that includes both the object's speed and direction.
What is the formula for calculating velocity?
The formula for calculating velocity is velocity = distance / time.
What are the units of velocity?
The units of velocity are meters per second (m/s) in the International System of Units (SI).
Define acceleration.
Acceleration is a vector quantity that measures the rate of change of an object's velocity with respect to time. It can either be an increase in speed, a decrease in speed, or a change in direction. Mathematically, acceleration is calculated as the change in velocity divided by the time taken for that change to occur, and its SI unit is meters per second squared (m/s^2).
How is acceleration related to velocity and time?
Acceleration is the rate of change of velocity over time, meaning it is directly related to both velocity and time. A higher acceleration means a faster change in velocity over a given period of time, while a lower acceleration means a slower change in velocity. Acceleration can be positive (speeding up), negative (slowing down), or zero (constant velocity). This relationship is described by the equation: acceleration = (change in velocity)/(time taken).
Have something to share?
Who is Worksheeto?
At Worksheeto, we are committed to delivering an extensive and varied portfolio of superior quality worksheets, designed to address the educational demands of students, educators, and parents.































Comments