Skin Coloring Worksheet
Are you searching for an engaging and educational activity to help your children learn about the different layers of the skin and the importance of skin coloring? Look no further! Our skin coloring worksheet is the perfect resource for parents and educators looking to teach kids about this fascinating subject.
Table of Images 👆
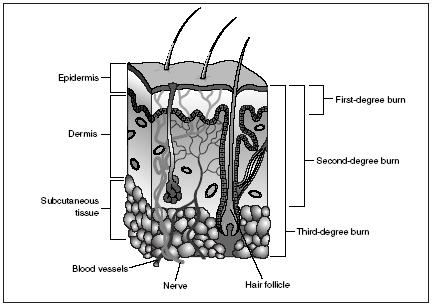
- Black and White Integumentary System Diagram
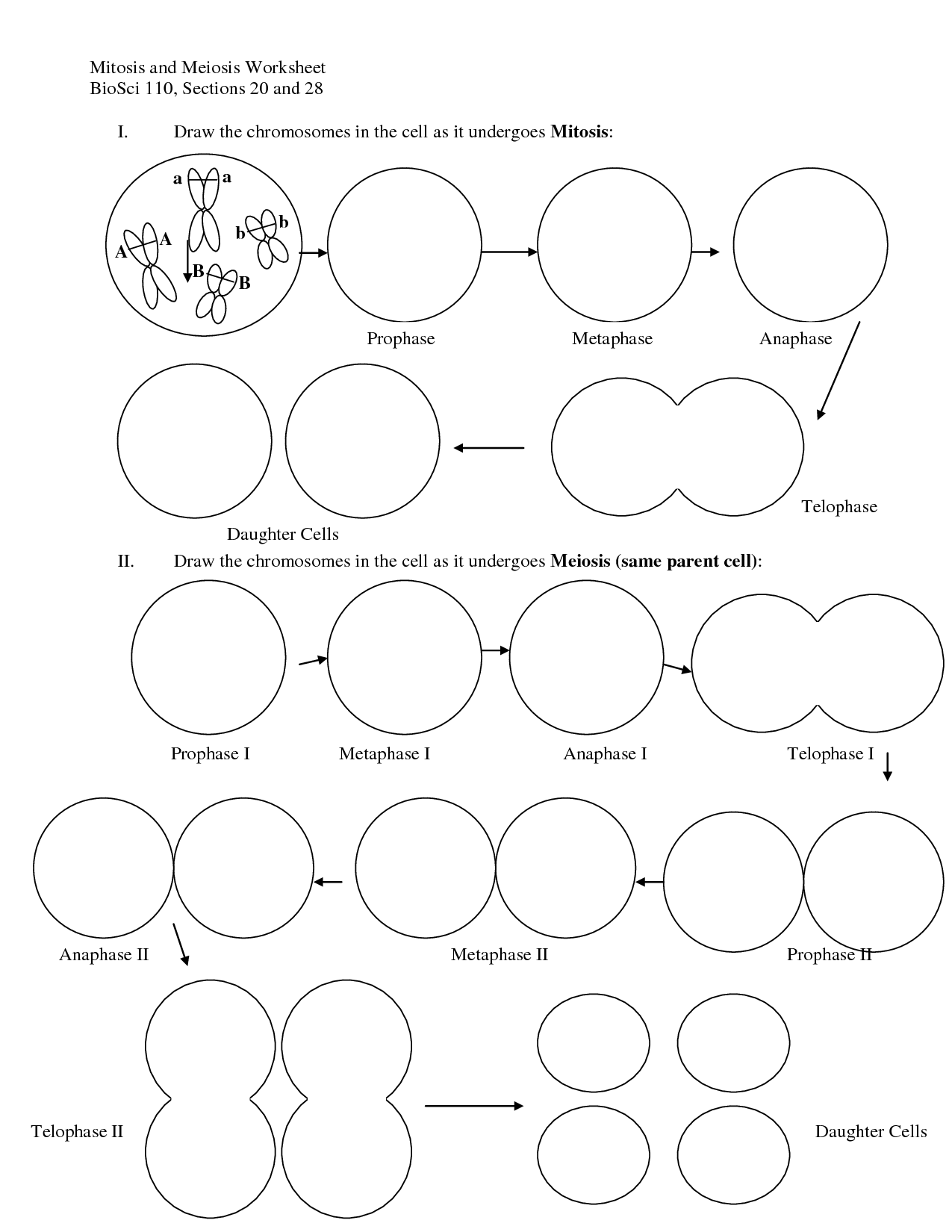
- Meiosis and Mitosis Worksheet Answers
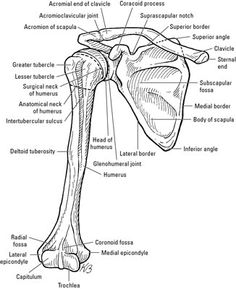
- Shoulder Girdle Anatomy
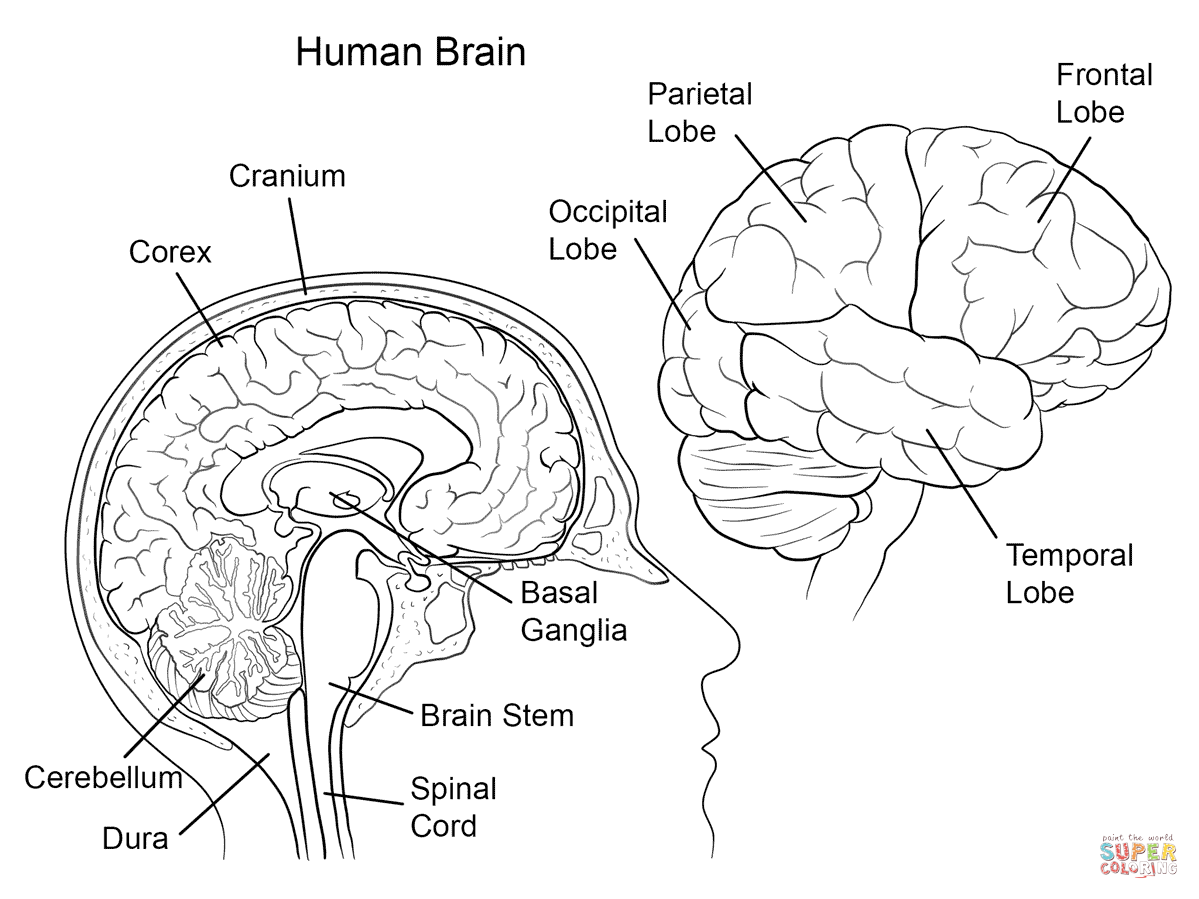
- Human Brain Anatomy Coloring Page
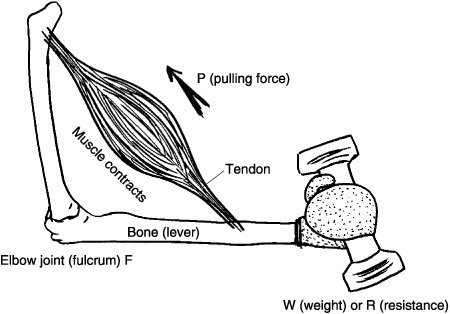
- Muscle Lever System
- Native American Buffalo Uses
- Free Printable Coloring Pages Animals
- Native American Symbols Dictionary
- Internal Organs Coloring Page
- Human Cell Structure
More Other Worksheets
Kindergarten Worksheet My RoomSpanish Verb Worksheets
Cooking Vocabulary Worksheet
My Shadow Worksheet
Large Printable Blank Pyramid Worksheet
Relationship Circles Worksheet
DNA Code Worksheet
Meiosis Worksheet Answer Key
Art Handouts and Worksheets
7 Elements of Art Worksheets
What is skin coloring?
Skin coloring refers to the natural pigmentation or tone of an individual's skin, which is determined by the amount and distribution of melanin in the skin. Melanin, a pigment produced by specialized cells called melanocytes, helps protect the skin from the damaging effects of ultraviolet (UV) radiation. Skin coloring can vary widely among individuals, ranging from very light to very dark, and is influenced by genetic, environmental, and hormonal factors.
What are the factors that influence skin color?
Skin color is primarily influenced by genetics, specifically the amount and type of melanin produced by melanocytes in the skin. Additional factors that can impact skin color include sun exposure, which can stimulate melanin production and lead to tanning, as well as environmental factors such as pollution and lifestyle choices like smoking. Other factors like age, hormonal changes, and certain medical conditions can also affect skin color by influencing melanin production or distribution.
What is melanin and how does it contribute to skin color?
Melanin is a pigment produced by specialized cells called melanocytes in the skin. It contributes to skin color by absorbing harmful UV radiation from the sun, protecting the skin from damage. The amount and type of melanin produced by melanocytes determine an individual's skin color, with higher levels of melanin resulting in darker skin tones.
How does sun exposure affect skin coloring?
Sun exposure can darken the skin by stimulating the production of melanin, a pigment that gives skin its color. When the skin is exposed to the ultraviolet (UV) rays from the sun, melanocytes produce more melanin to protect the skin from UV damage. This can result in a suntan or a darker skin tone. However, excessive sun exposure can also lead to sunburn, skin damage, premature aging, and an increased risk of skin cancer. It is important to wear sunscreen and practice sun protection measures to maintain healthy skin.
What are the different types of skin tones?
There is a wide range of skin tones, varying from very fair to very dark, with numerous intermediate shades in between. Some common classifications include fair, light, medium, olive, tan, dark, and deep. Skin tones can also be influenced by undertones, such as cool (pink or red undertones), warm (yellow or golden undertones), or neutral (a mix of cool and warm undertones). It's important to remember that each person's skin is unique and can fall within a combination of these categories.
How does skin color vary among different ethnicities?
Skin color varies among different ethnicities due to differences in the amount of melanin, a pigment that gives skin its color. Darker skin tones have more melanin, which helps protect against harmful UV rays, while lighter skin tones have less melanin. Genetics play a significant role in determining an individual's skin color, with factors such as ancestry, location, and environmental factors contributing to the wide range of skin tones seen across different ethnic groups.
How does skin color change with age?
As people age, their skin color can change due to a variety of factors such as sun exposure, decreased production of melanin, or changes in blood circulation. Sun exposure can lead to the darkening of skin spots known as age spots or liver spots. Additionally, as melanin production decreases with age, skin may appear lighter or become more prone to pigmentation changes. Changes in blood circulation can also affect skin color, with elderly individuals often experiencing thinner skin that may appear more translucent or paler. Nevertheless, these changes in skin color are a natural part of the aging process and vary from person to person.
What role does genetics play in determining skin color?
Genetics play a fundamental role in determining skin color by influencing the amount of melanin produced by melanocytes in the skin. Variations in genes that control melanin production can lead to differences in skin pigmentation among individuals. People with more melanin have darker skin tones, while those with less melanin have lighter skin tones. Additionally, genetic factors can also influence how skin responds to sunlight and other environmental factors, further impacting skin color.
How does skin color affect the risk of certain skin conditions?
Skin color can affect the risk of certain skin conditions due to differences in melanin production. People with darker skin have more melanin, providing some protection against UV damage and reducing the risk of sunburn and skin cancer. However, they may still be at risk for hyperpigmentation disorders like melasma and post-inflammatory hyperpigmentation. On the other hand, those with lighter skin are more prone to sunburn, skin cancer, and conditions like eczema and actinic keratosis due to lower levels of melanin providing less natural protection from UV radiation. Regular sun protection and appropriate skincare are essential for all skin tones to minimize the risk of skin conditions.
How has society historically viewed and valued different skin colors?
Throughout history, society has often associated lighter skin with beauty, purity, and higher social status, while darker skin has been associated with lower status, labor-intensive work, and inferiority. This Eurocentric view has manifested in discrimination, colorism, and systemic inequalities that favor lighter-skinned individuals in various aspects of life, such as employment opportunities, education, and media representation. However, there is a growing awareness and movement towards promoting diversity, inclusivity, and the celebration of all skin colors in society to challenge these harmful biases and promote equality.
Have something to share?
Who is Worksheeto?
At Worksheeto, we are committed to delivering an extensive and varied portfolio of superior quality worksheets, designed to address the educational demands of students, educators, and parents.























Comments