Skeletal System Worksheets Answers
The skeletal system worksheets provide a comprehensive and interactive way for students to learn about the human body's structure and function. By focusing on the entity of the skeletal system and its various subjects such as bones, joints, and muscles, these worksheets are designed to engage students in a meaningful way. With clear and concise answers, these worksheets ensure that students can confidently grasp the concepts related to the skeletal system.
Table of Images 👆
- Skeletal System Worksheets
- Skeletal System Worksheets
- Skeletal System Study Guide Answers
- Hand Tool Safety Worksheet
- Skeletal System Worksheet Human Body
- Skeletal System Crossword Puzzle Answers
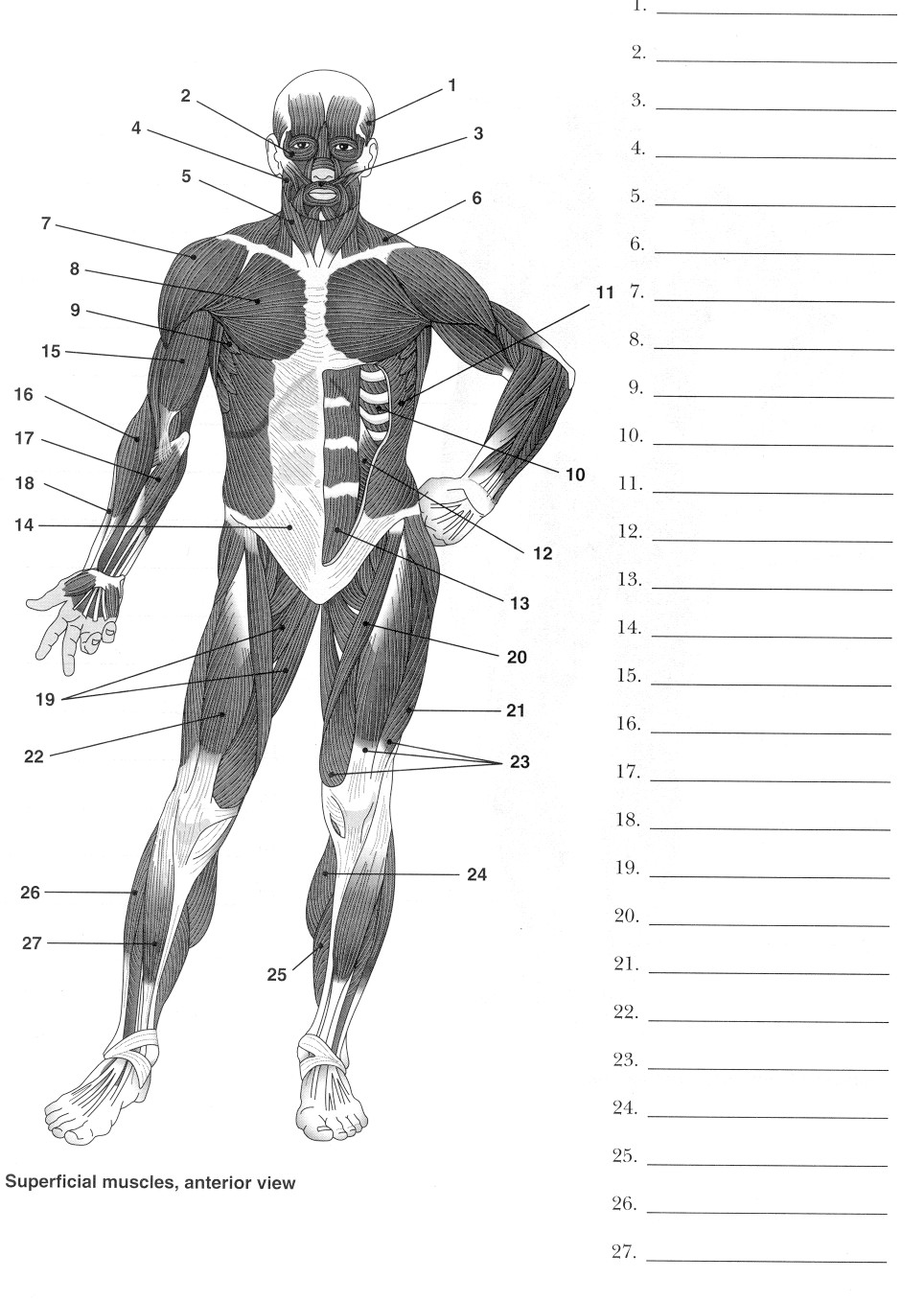
- Blank Muscle Diagram Worksheet
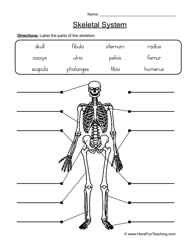
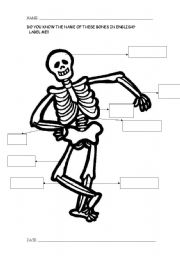
- Skeleton Label Bones Worksheet
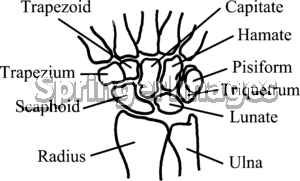
- Skull Bones Diagram Worksheet
- Pig Digestive System Diagram Labeled
- Anatomy and Physiology Worksheet Answer Key
- Label Heart Diagram Worksheet
- The Skeletal System Anatomy Chapter 5 Answers
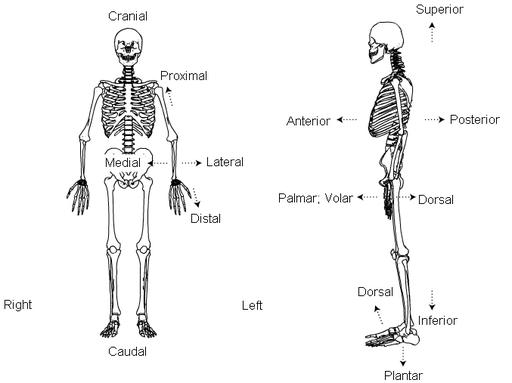
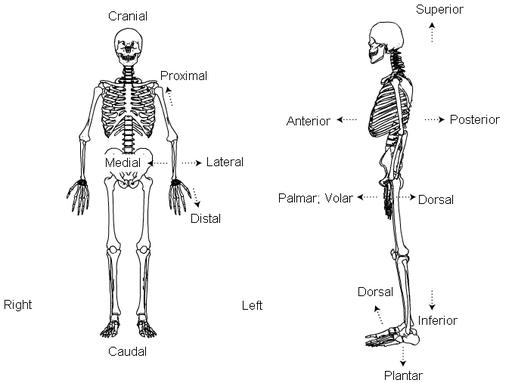
- Standard Anatomical Position
- Standard Anatomical Position
- Standard Anatomical Position
More Other Worksheets
Kindergarten Worksheet My RoomSpanish Verb Worksheets
Cooking Vocabulary Worksheet
My Shadow Worksheet
Large Printable Blank Pyramid Worksheet
Relationship Circles Worksheet
DNA Code Worksheet
Meiosis Worksheet Answer Key
Art Handouts and Worksheets
7 Elements of Art Worksheets
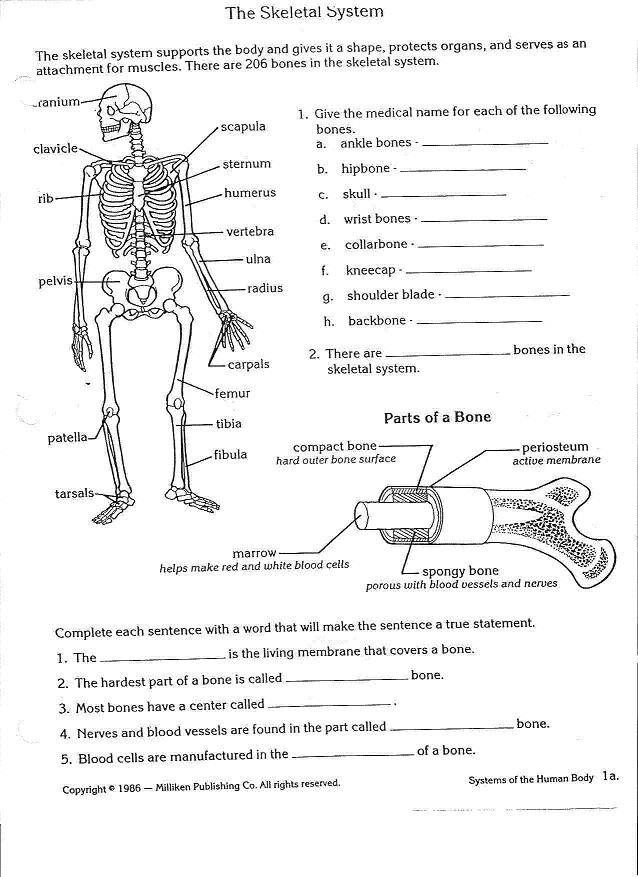
What is the main function of the skeletal system?
The main function of the skeletal system is to provide structural support for the body, protect internal organs, facilitate movement, and produce blood cells.
How many bones are there in the adult human body?
There are 206 bones in the adult human body.
What are the five main types of bones?
The five main types of bones in the human body are long bones, short bones, flat bones, irregular bones, and sesamoid bones.
How do bones provide support for the body?
Bones provide support for the body by serving as the framework that holds up and shapes the body. They also help in allowing movement by providing points for muscles to attach to, allowing for joints that enable mobility. Additionally, bones protect vital organs, such as the brain, heart, and lungs, by acting as a protective shield. Moreover, bones play a crucial role in producing blood cells and storing minerals like calcium, which are essential for various bodily functions.
What is the difference between compact bone and spongy bone?
Compact bone is dense and smooth outer layer of bone that provides strength and protection, while spongy bone is a porous inner layer that contains bone marrow and helps to reduce the overall weight of the bone. Compact bone is more solid and has a higher mineral content, making it more rigid, while spongy bone has a honeycomb-like structure that allows for better flexibility and shock absorption. Ultimately, compact bone is found in the shafts of long bones and the exterior of all bones, while spongy bone is found at the ends of long bones and in the interior of flat and irregular bones.
What are the two main minerals stored in bones?
The two main minerals stored in bones are calcium and phosphorus. Calcium provides strength and rigidity to the bones, while phosphorus helps in the formation and maintenance of the bone structure. These minerals play crucial roles in various bodily functions and are essential for maintaining overall bone health and strength.
How do bones assist in movement?
Bones provide structure and support for the body, allowing muscles to attach to them and create movement. When muscles contract, they pull on the bones, causing them to move at the joints. The shape and arrangement of bones also determine the range of motion at each joint, influencing the types of movements that are possible. Additionally, bones protect vital organs and act as levers to amplify the force generated by muscles, ultimately enabling smooth and coordinated movement in the body.
What is the purpose of bone marrow?
Bone marrow serves the essential function of producing blood cells, including red blood cells that carry oxygen, white blood cells that fight infection, and platelets that help with blood clotting. It is a vital component of the body's hematopoietic system and plays a critical role in maintaining overall health and immune function.
How does the skeletal system protect vital organs?
The skeletal system protects vital organs by providing a framework of bones that surround and support them. For example, the rib cage protects the heart and lungs, while the skull safeguards the brain. Additionally, the skeletal system acts as a barrier that absorbs impact and helps distribute forces away from vital organs, reducing the risk of injury.
How does the skeletal system contribute to the production of red blood cells?
The skeletal system contributes to the production of red blood cells through a process called hematopoiesis, which occurs in the bone marrow. The bone marrow, found within the cavities of certain bones, is responsible for producing red blood cells, white blood cells, and platelets. Stem cells within the bone marrow differentiate into specialized blood cells, including red blood cells, which are essential for transporting oxygen throughout the body.
Have something to share?
Who is Worksheeto?
At Worksheeto, we are committed to delivering an extensive and varied portfolio of superior quality worksheets, designed to address the educational demands of students, educators, and parents.























Comments