Situational Graph Worksheet
Are you searching for a helpful and engaging tool to strengthen your understanding of entity and subject in English language learning? Look no further, as we have just the solution for you! Introducing the Situational Graph Worksheet, a comprehensive resource designed to enhance your grasp on entity and subject concepts through practical and interactive exercises.
Table of Images 👆
More Other Worksheets
Kindergarten Worksheet My RoomSpanish Verb Worksheets
Healthy Eating Plate Printable Worksheet
Cooking Vocabulary Worksheet
My Shadow Worksheet
Large Printable Blank Pyramid Worksheet
Relationship Circles Worksheet
DNA Code Worksheet
Meiosis Worksheet Answer Key
Rosa Parks Worksheet Grade 1
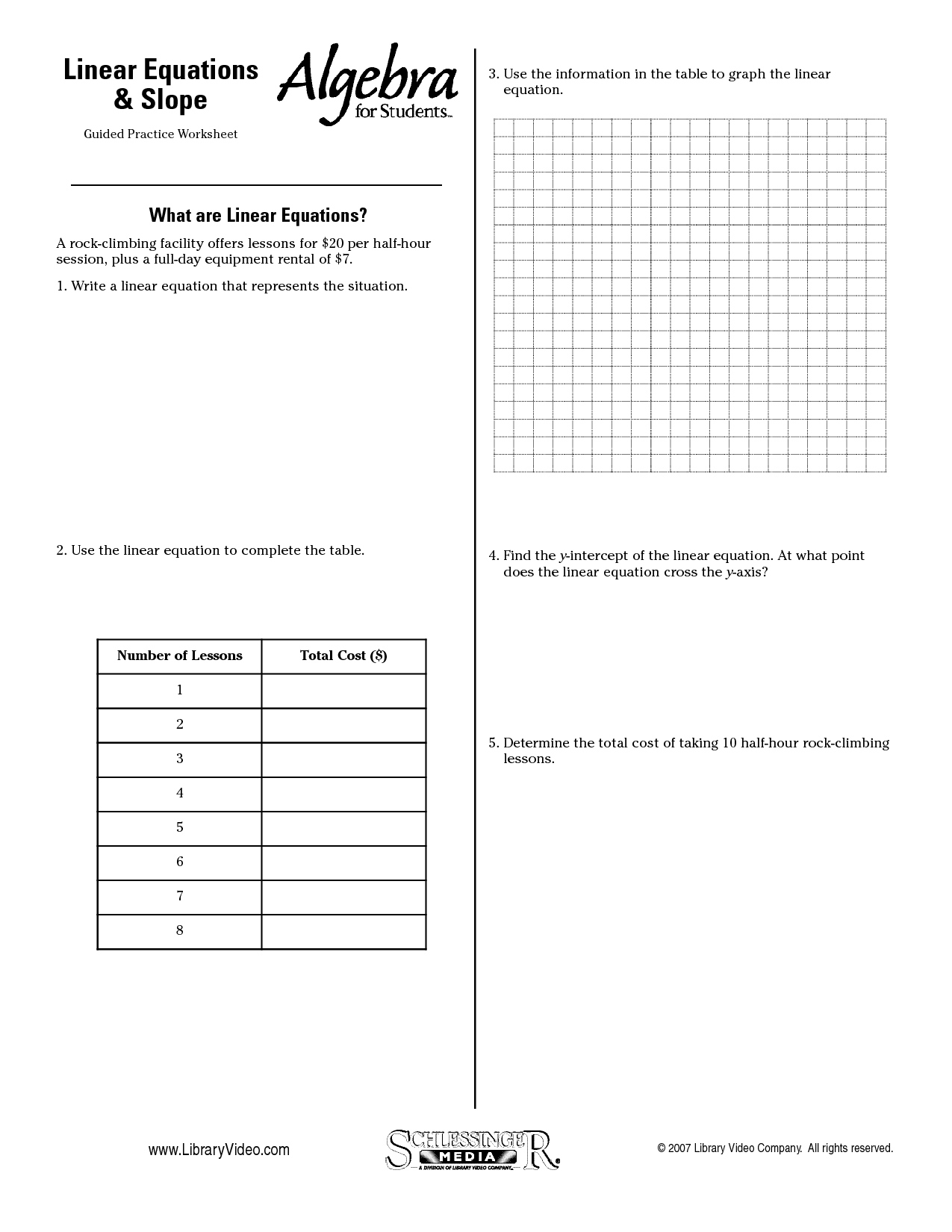
What is a situational graph?
A situational graph is a type of visual representation that illustrates how different variables or factors interact with each other in a particular situation or scenario. It helps to visualize the relationships between the elements involved and how they influence each other within a specific context, making it easier to analyze and understand complex situations.
What types of data can be represented in a situational graph?
A situational graph can represent various types of data, including numerical data such as quantities, measurements, or values; categorical data such as types or categories; and temporal data such as time-related information. Additionally, situational graphs can also represent relationships between entities, events, or variables, making them a versatile tool for visualizing and analyzing complex situations or scenarios.
How is a situational graph different from other types of graphs?
A situational graph differs from other types of graphs in that it represents specific situations or scenarios rather than general trends or relationships. It is used to visually organize and analyze information related to a particular context, helping to understand complex relationships or sequences within that specific situation. Situational graphs are dynamic and can change based on different variables or inputs, making them especially useful in decision-making processes and problem-solving situations.
What are the main components of a situational graph?
The main components of a situational graph include nodes, which represent entities or objects, and edges, which represent relationships or connections between these entities. Nodes can have labels to provide more information, and edges can be directed or undirected to show the nature of the relationship. Additionally, weights or properties can be assigned to nodes or edges to convey additional details or constraints within the situational graph.
What is the purpose of a situational graph?
A situational graph is used to visually represent and analyze the relationships and dependencies between different variables or elements within a specific situation or system. It helps in identifying patterns, trends, and potential outcomes based on different scenarios, making it an important tool for decision-making, problem-solving, and strategic planning in various fields such as business, engineering, and social sciences.
How is the x-axis typically labeled in a situational graph?
The x-axis in a situational graph is typically labeled with the independent variable, which is the variable being manipulated or controlled in the experiment or situation being represented in the graph. This could be time, distance, temperature, or any other measurable quantity that is being varied or observed in the context of the graph.
How is the y-axis typically labeled in a situational graph?
The y-axis in a situational graph is typically labeled with the dependent variable, which represents the outcome or response that is being measured or studied in relation to the independent variable on the x-axis. This labeling helps viewers understand the data being depicted and the relationship between the variables being analyzed in the graph.
What are some common shapes or patterns that can be observed in a situational graph?
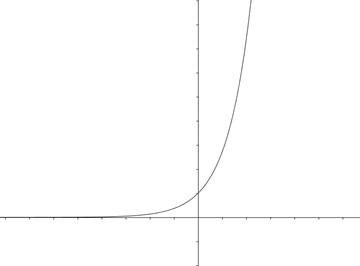
Some common shapes or patterns that can be observed in a situational graph include linear relationships (straight lines), exponential growth or decay (curved lines), periodic patterns (repetitive waves or cycles), and clustering or grouping of data points (concentrations of points in specific regions). These shapes and patterns can provide insights into the underlying relationships or trends in the data and help in making informed decisions or predictions.
How can a situational graph be used to analyze trends or relationships?
A situational graph can be used to analyze trends or relationships by visually representing data points over time or across different variables. By plotting the data on the graph, patterns, correlations, or fluctuations can be identified more easily, aiding in understanding trends or relationships within the data set. This visual representation allows for a more intuitive and comprehensive analysis of the information, helping to draw insights and make informed decisions based on the identified trends or relationships in the data.
What are some potential limitations or considerations when interpreting a situational graph?
When interpreting a situational graph, some potential limitations and considerations to keep in mind include the need to ensure the accuracy and reliability of the data presented, the possibility of oversimplification leading to incomplete understanding of the situation, the potential for biases in graph design or data selection, and the importance of considering context and external factors that may influence the interpretation of the graph. Additionally, one must be cautious of extrapolating trends too far into the future or making assumptions without sufficient supporting evidence.
Have something to share?
Who is Worksheeto?
At Worksheeto, we are committed to delivering an extensive and varied portfolio of superior quality worksheets, designed to address the educational demands of students, educators, and parents.























Comments