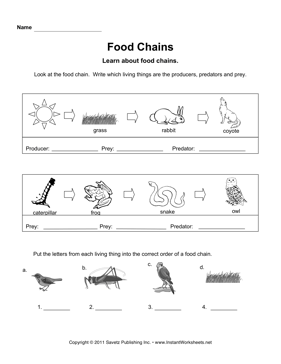
Simple Food Chain Worksheets
Food chains are an essential concept for young learners to understand the flow of energy in ecosystems. By introducing worksheets as a learning tool, educators can effectively engage students in exploring the relationships between different organisms. These simple food chain worksheets provide an interactive approach for students to grasp the concept and identify the entities and subjects involved in various food chains.
Table of Images 👆
- Food Chain Worksheets Free
- Food Chain Worksheets
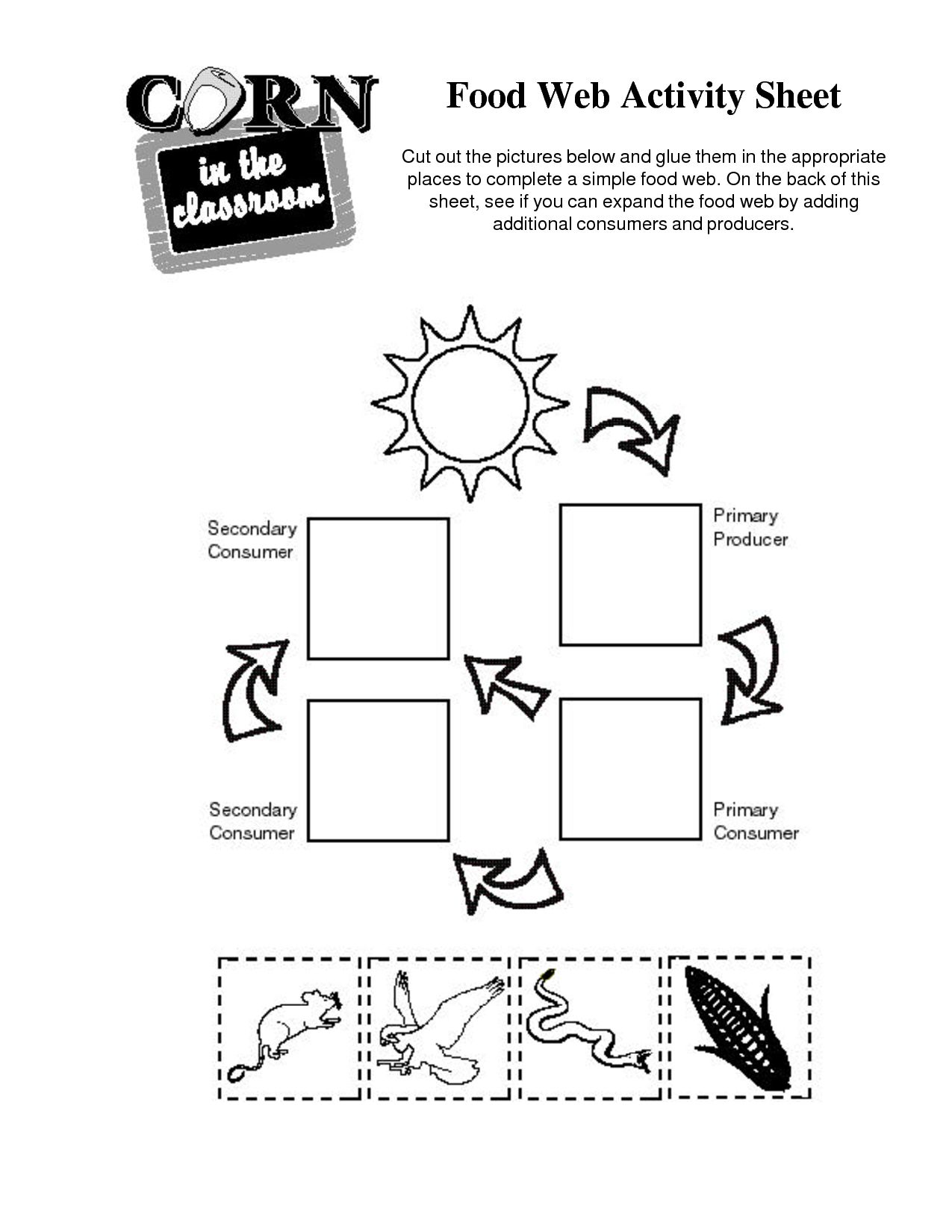
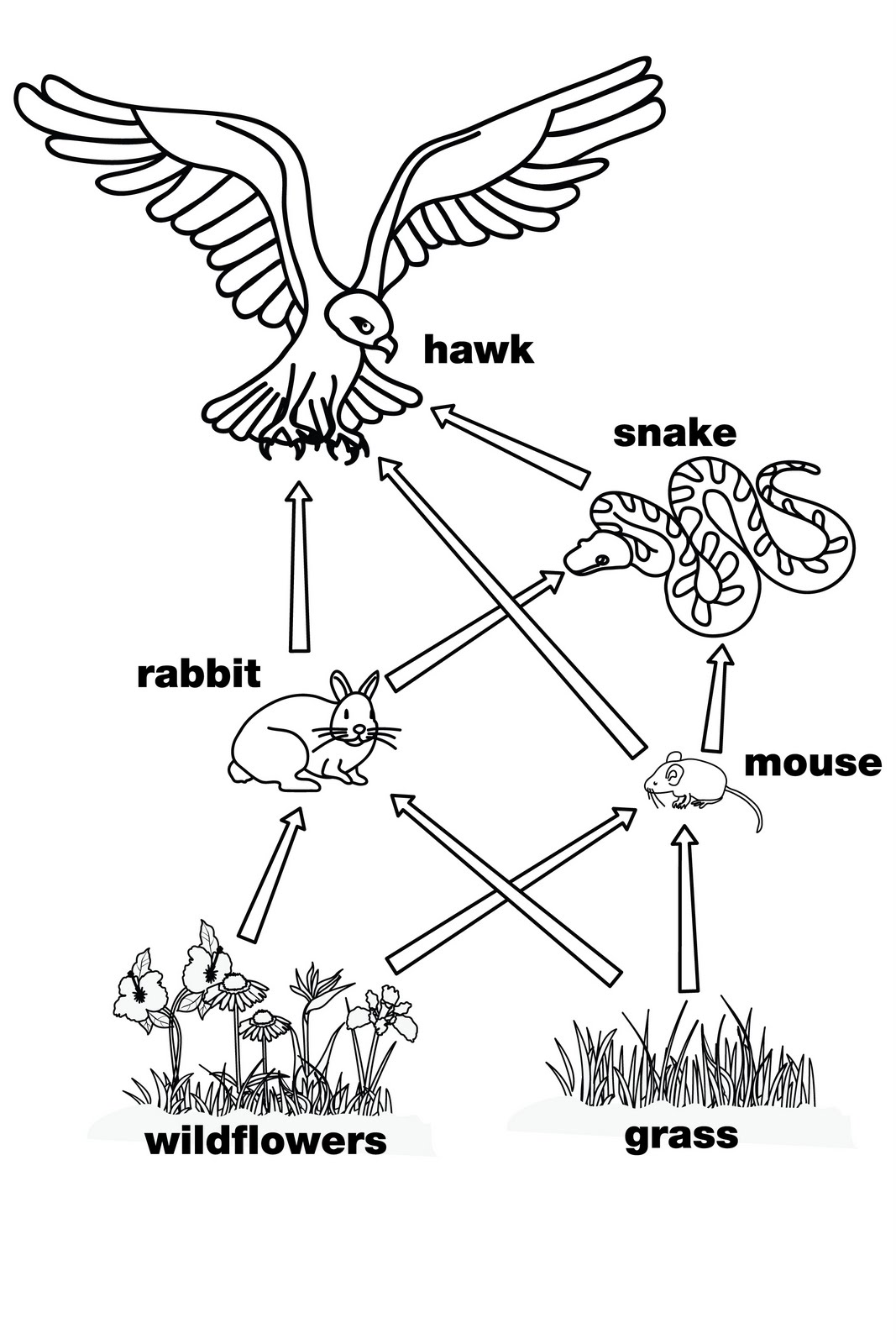
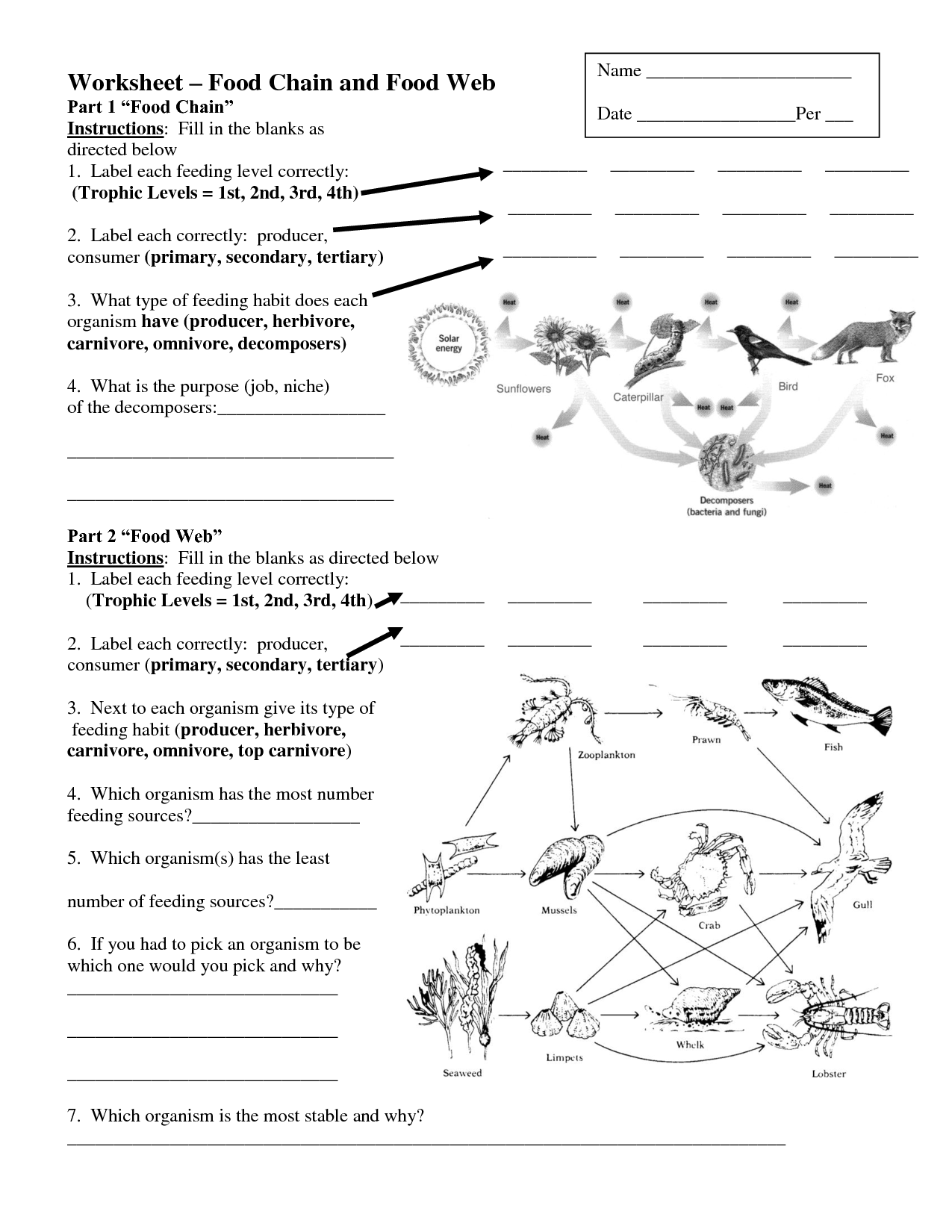
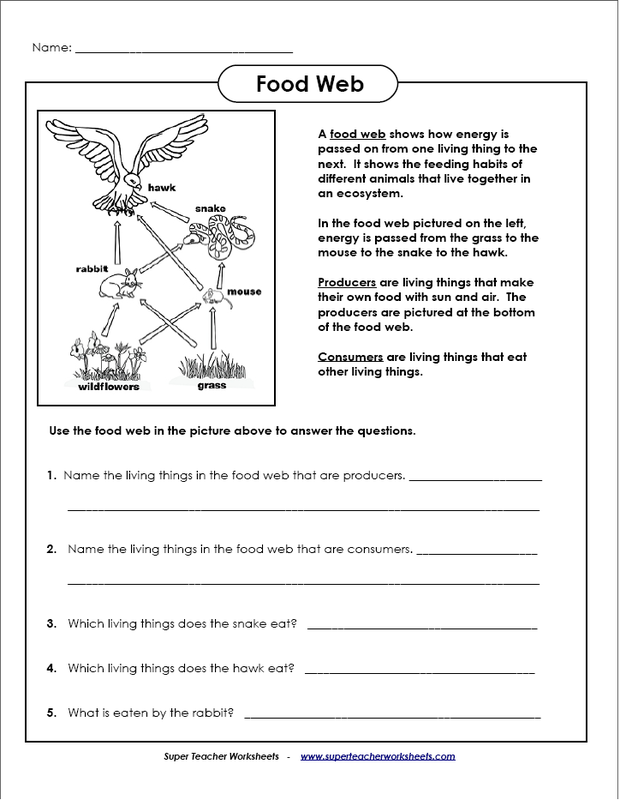
- Food Web Worksheet
- Food Chain Worksheets Free
- Free Printable Food Chain Worksheets
- How to Draw Food Web
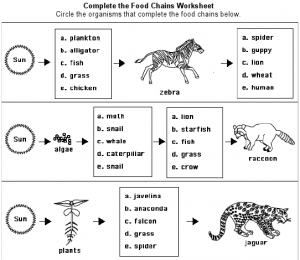
- Food Chain Worksheets
- Food Chain Activity
- Food Web Coloring Pages
- Food Web Worksheet
- Food Chain Worksheets
- Ecosystem Worksheet Food Chain
- Food Web Energy Pyramid Worksheet
- Food Chain Printable Worksheets
More Food Worksheets
Printable Worksheets for French FoodDaily Food Intake Worksheet
5 Food Groups Worksheet
Food Production Worksheet Template
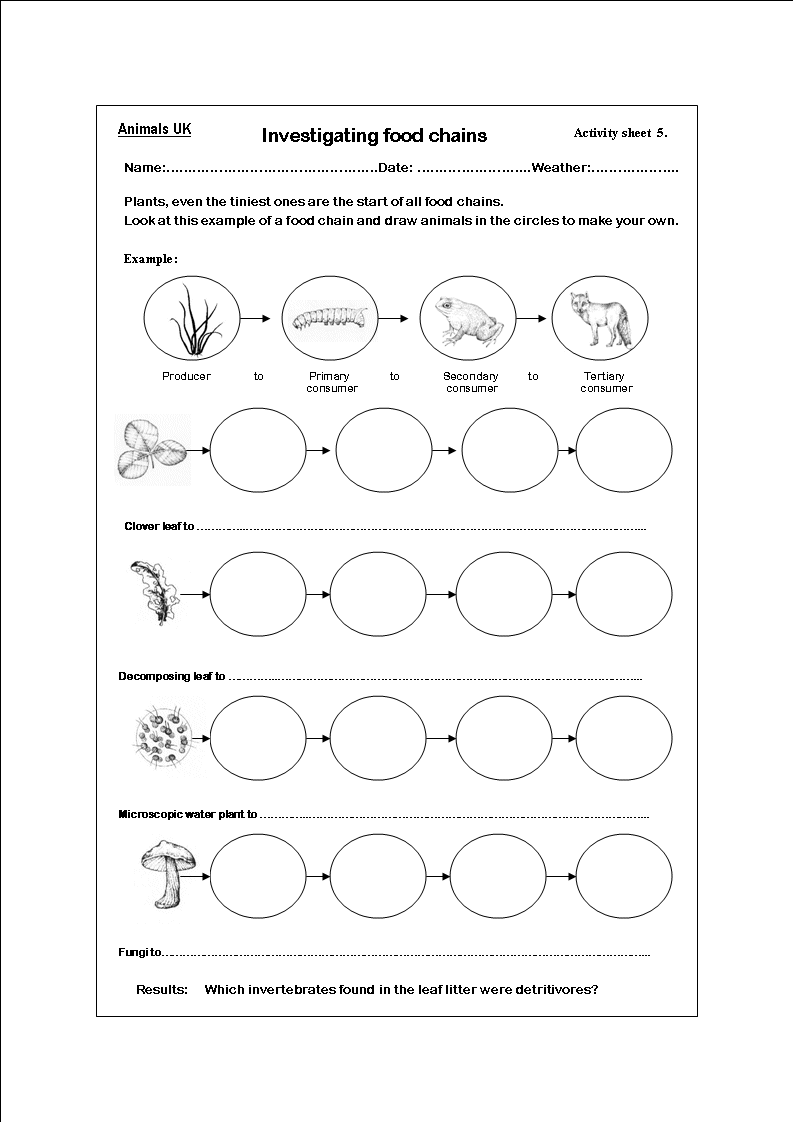
What is a simple food chain?
A simple food chain is a linear sequence of organisms where each organism serves as a source of food for the next organism in the chain. For example, a plant is eaten by a herbivore, which is then eaten by a carnivore. This basic interaction demonstrates the transfer of energy and nutrients from one organism to another in an ecosystem.
What is the primary producer in a simple food chain?
The primary producer in a simple food chain is typically a plant or an organism that is capable of producing its own food through photosynthesis, such as green plants or algae. These primary producers are essential for the food chain as they convert sunlight into energy, which is then passed on to primary consumers such as herbivores.
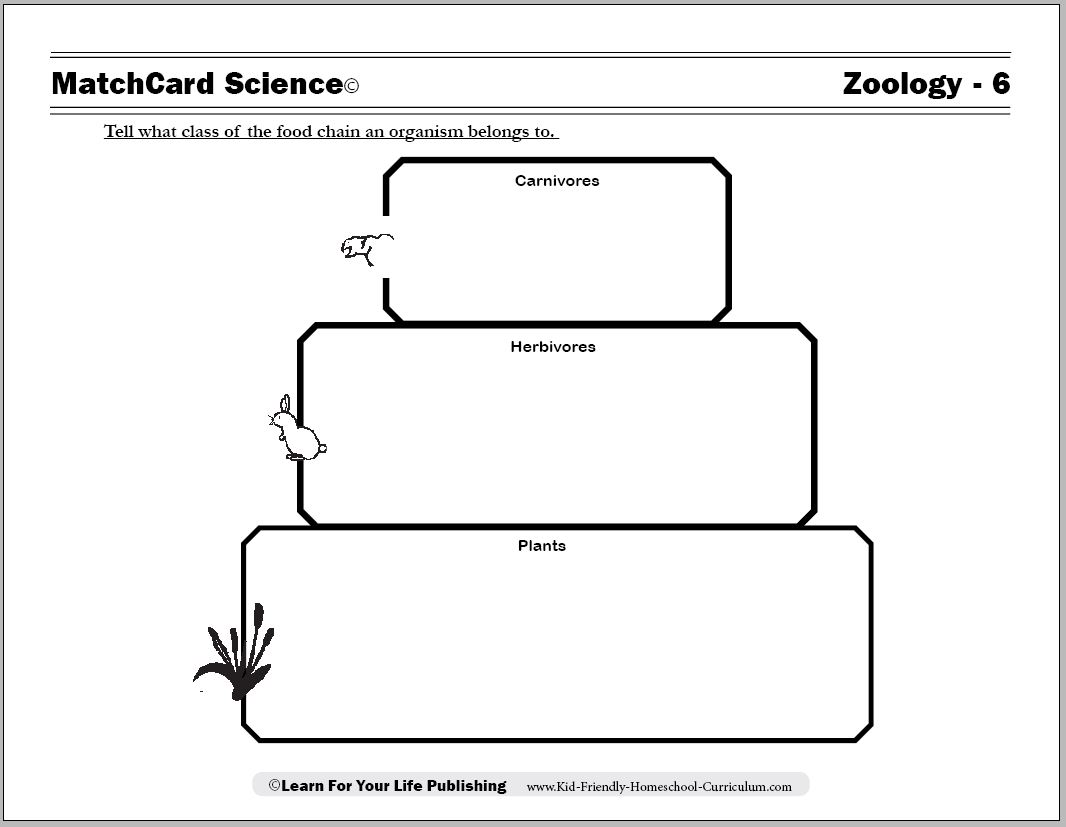
What is a primary consumer in a simple food chain?
A primary consumer is an organism that feeds directly on producers in a food chain. These organisms usually include herbivores that consume plant material as their main source of energy, such as deer eating grass or rabbits munching on plants. This is the second trophic level in a food chain, following the producers, and serves as a crucial link in transferring energy from plants to higher levels of the food chain.
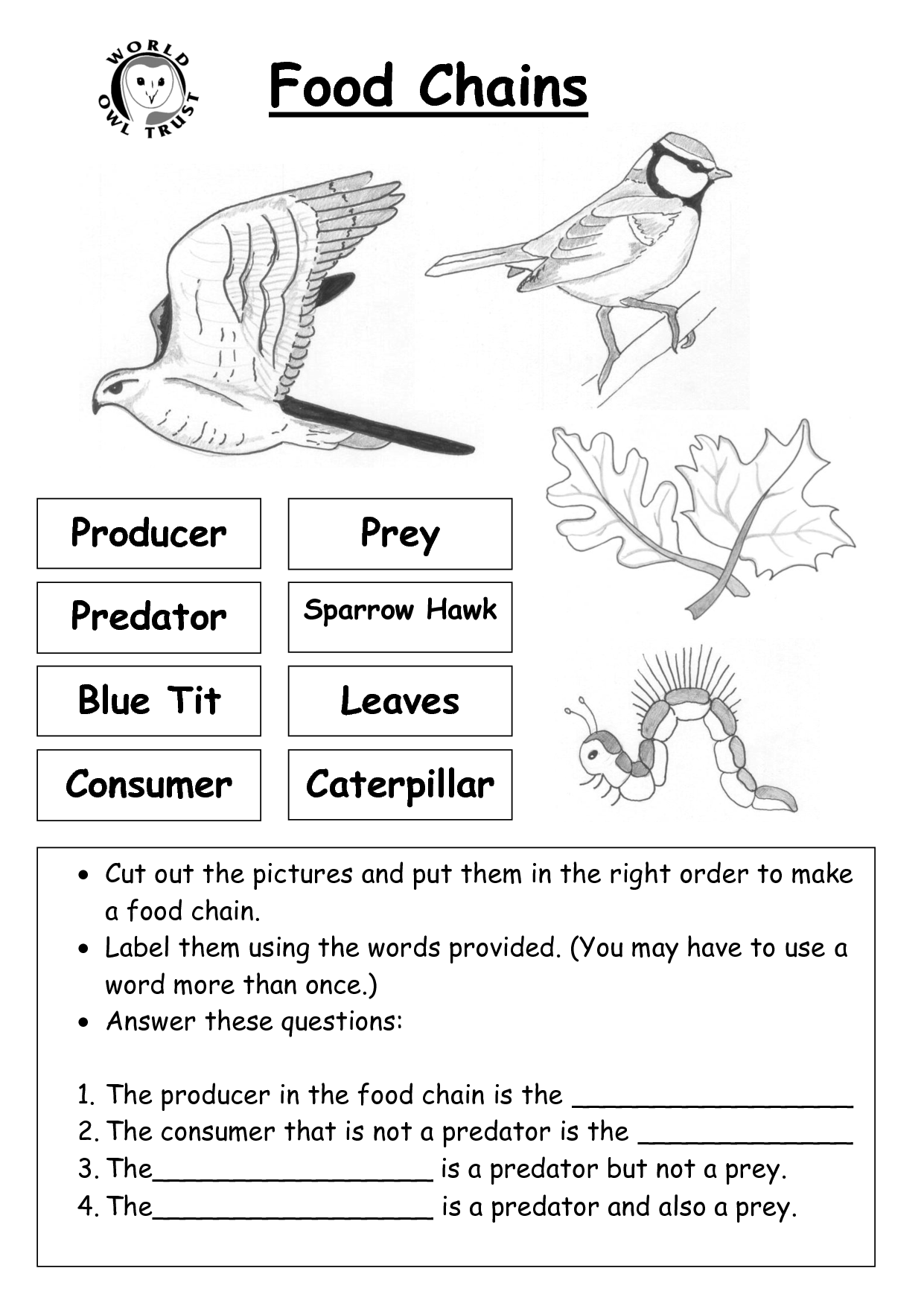
What is a secondary consumer in a simple food chain?
A secondary consumer in a simple food chain is an organism that feeds on primary consumers, which are herbivores or plant-eating animals. They are typically predators that hunt and consume animals that are lower in the food chain, and they are a crucial part of maintaining the balance of ecosystems by controlling the populations of other organisms.
Describe the role of decomposers in a simple food chain.
Decomposers play a crucial role in a food chain by breaking down dead plant and animal matter into simpler compounds. They help recycle nutrients back into the ecosystem, making them available for producers like plants to use for growth. In this way, decomposers act as nature's recyclers, ensuring the continuous flow of energy and nutrients through the food chain.
Explain how energy flows through a simple food chain.
Energy in a simple food chain flows from producers, such as plants, that convert sunlight into energy through photosynthesis. Herbivores then consume the plants, transferring this energy up the chain. Next, carnivores eat the herbivores, absorbing the energy. At each step, energy is lost as heat through respiration, and only a fraction is passed on to the next trophic level. This process continues until decomposers break down the remains of organisms, releasing nutrients back into the ecosystem to be used by producers, thus completing the energy flow cycle in the food chain.
Describe a complete food chain, including all trophic levels.
In a complete food chain, starting with the primary producer, we have grass as the first trophic level being consumed by the primary consumer, a grasshopper, at the second trophic level. The grasshopper is then eaten by a secondary consumer, a frog, at the third trophic level. Moving on, the frog is consumed by a tertiary consumer, a snake, at the fourth trophic level. Finally, a quaternary consumer, such as a hawk, preys on the snake at the fifth trophic level, completing the food chain.
What happens if one species in a simple food chain becomes extinct?
If one species in a simple food chain becomes extinct, it can disrupt the entire ecosystem. This can lead to a cascade effect where other species that depended on the extinct species for food or other resources are impacted. It can ultimately lead to imbalances in populations, changes in species interactions, and potential decline in biodiversity. Ultimately, the extinction of one species can have far-reaching consequences on the ecosystem as a whole.
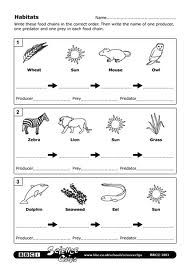
Give an example of a simple food chain found in a terrestrial ecosystem.
An example of a simple food chain found in a terrestrial ecosystem is grass (producer) being eaten by a grasshopper (primary consumer), which is then consumed by a bird (secondary consumer).
Provide an example of a simple food chain found in an aquatic ecosystem.
An example of a simple food chain in an aquatic ecosystem could be algae being consumed by zooplankton, which are then eaten by small fish, and finally those small fish are preyed upon by larger fish.
Have something to share?
Who is Worksheeto?
At Worksheeto, we are committed to delivering an extensive and varied portfolio of superior quality worksheets, designed to address the educational demands of students, educators, and parents.



















Comments