Series Parallel Circuit Worksheet
Are you a student or an aspiring electrical engineer looking to sharpen your understanding of series and parallel circuits? Look no further as we present to you a series parallel circuit worksheet designed specifically to help you grasp the core concepts of this fundamental topic. This worksheet will provide you with a structured set of questions and exercises to reinforce your understanding of how series and parallel circuits work, with a focus on identifying entities and subjects within these circuits.
Table of Images 👆
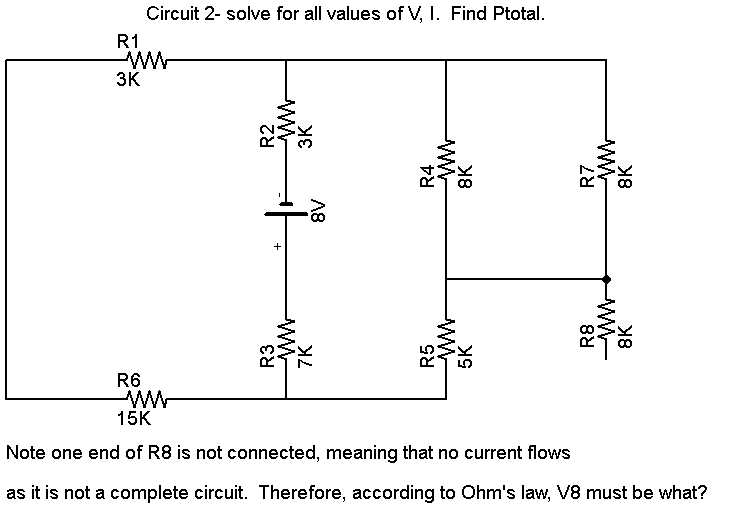
- Series and Parallel Circuits Worksheets
- Series and Parallel Circuits Worksheets
- Series and Parallel Circuits Worksheets
- Series and Parallel Circuits Worksheets
- Series and Parallel Circuits Worksheets
- Series and Parallel Circuits Worksheets
- Series and Parallel Circuits Worksheets
- Series and Parallel Circuits Worksheets
- Series and Parallel Circuits Worksheets
- Series and Parallel Circuits Worksheets
- Series and Parallel Circuits Worksheets
- Series Parallel Circuit Worksheet Answers
- Series Parallel Circuit Problems Worksheet
More Other Worksheets
Kindergarten Worksheet My RoomSpanish Verb Worksheets
Healthy Eating Plate Printable Worksheet
Cooking Vocabulary Worksheet
My Shadow Worksheet
Large Printable Blank Pyramid Worksheet
Relationship Circles Worksheet
DNA Code Worksheet
Meiosis Worksheet Answer Key
Rosa Parks Worksheet Grade 1
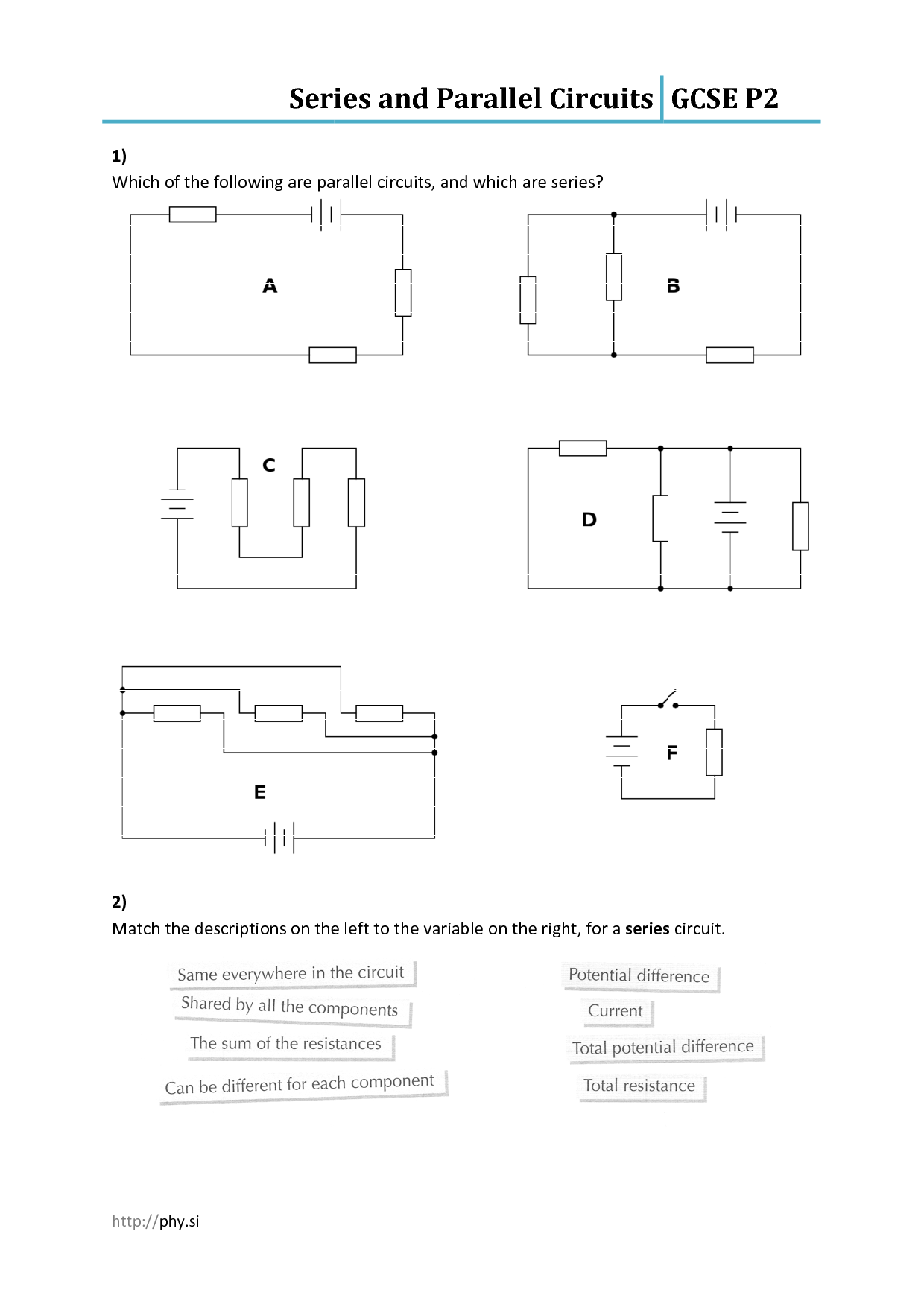
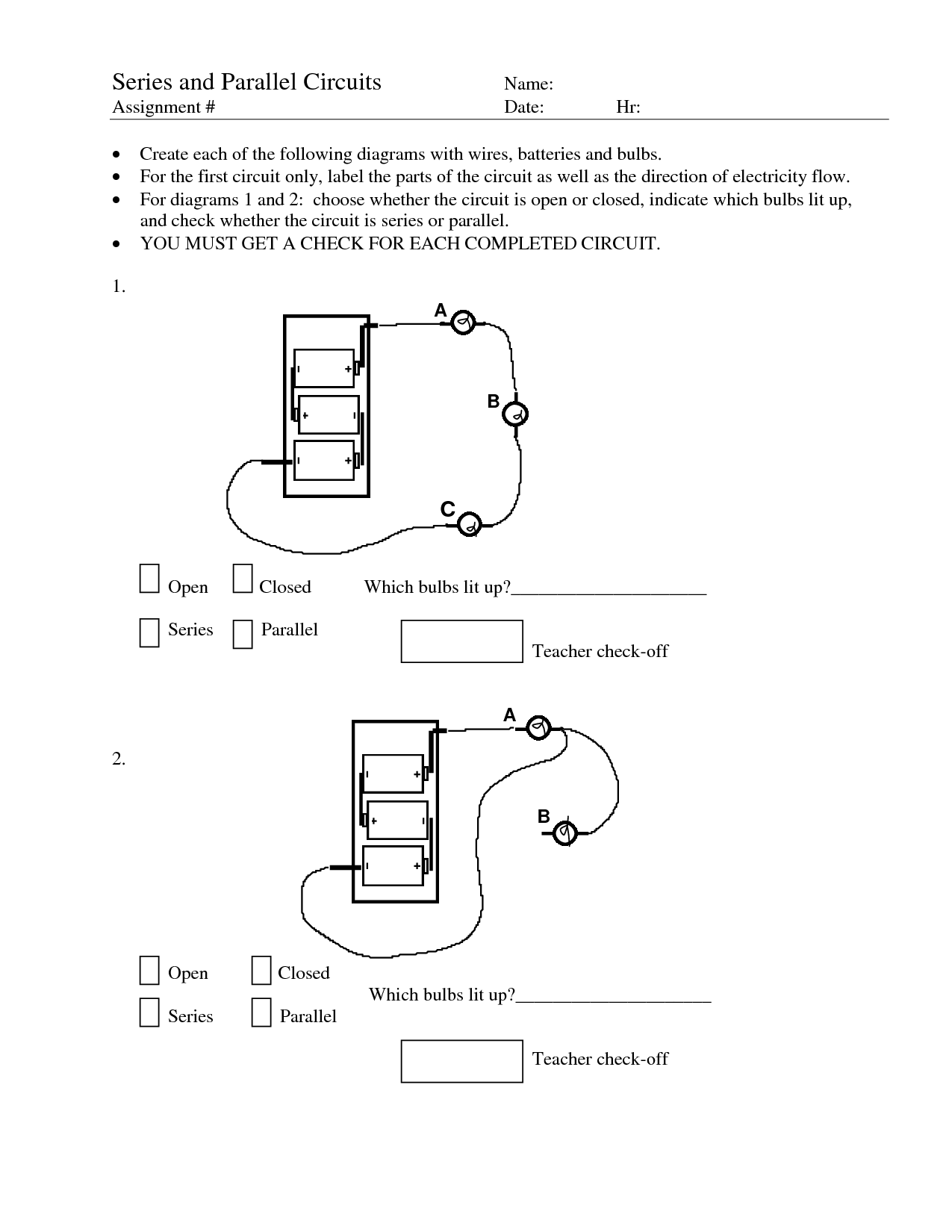
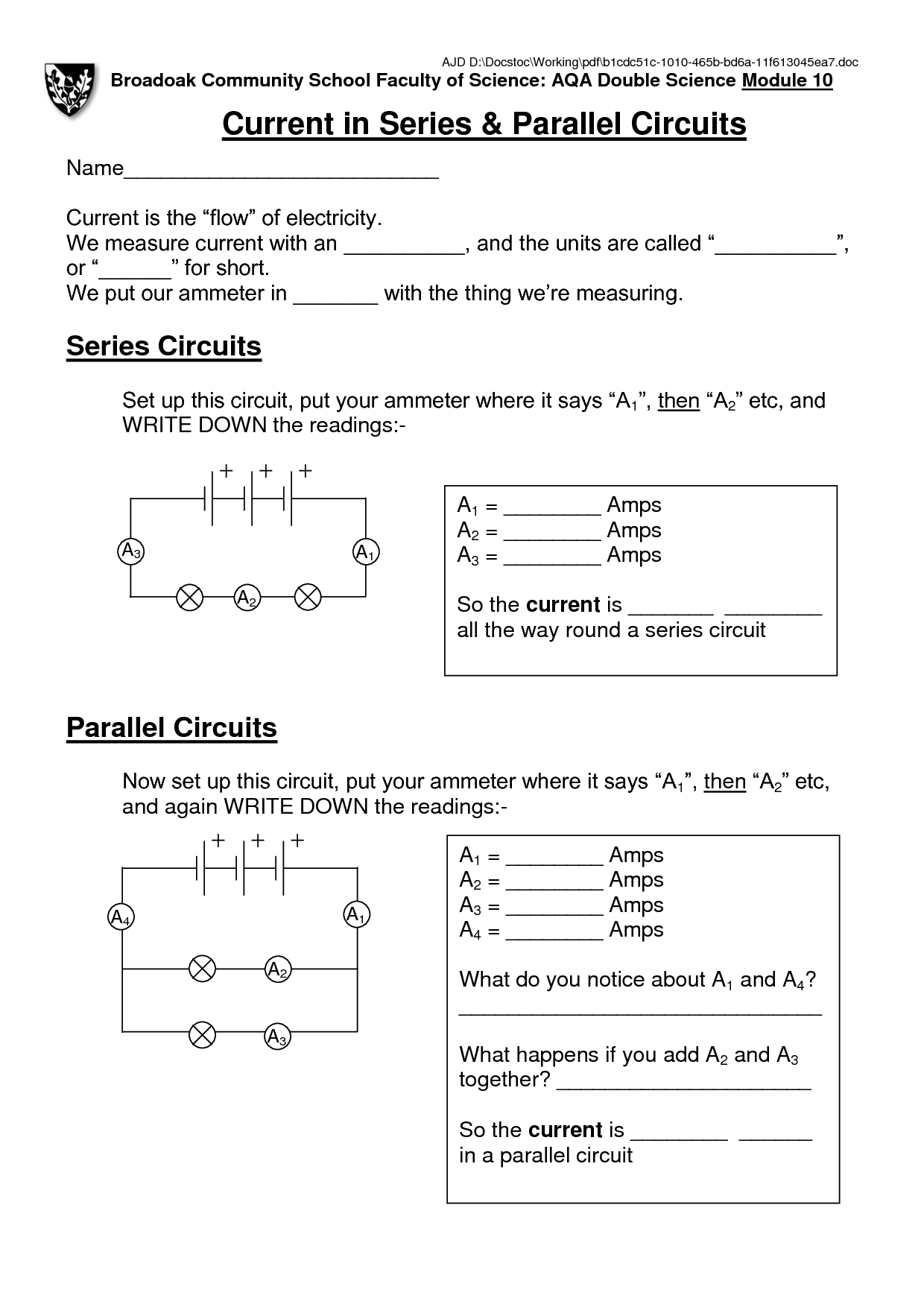
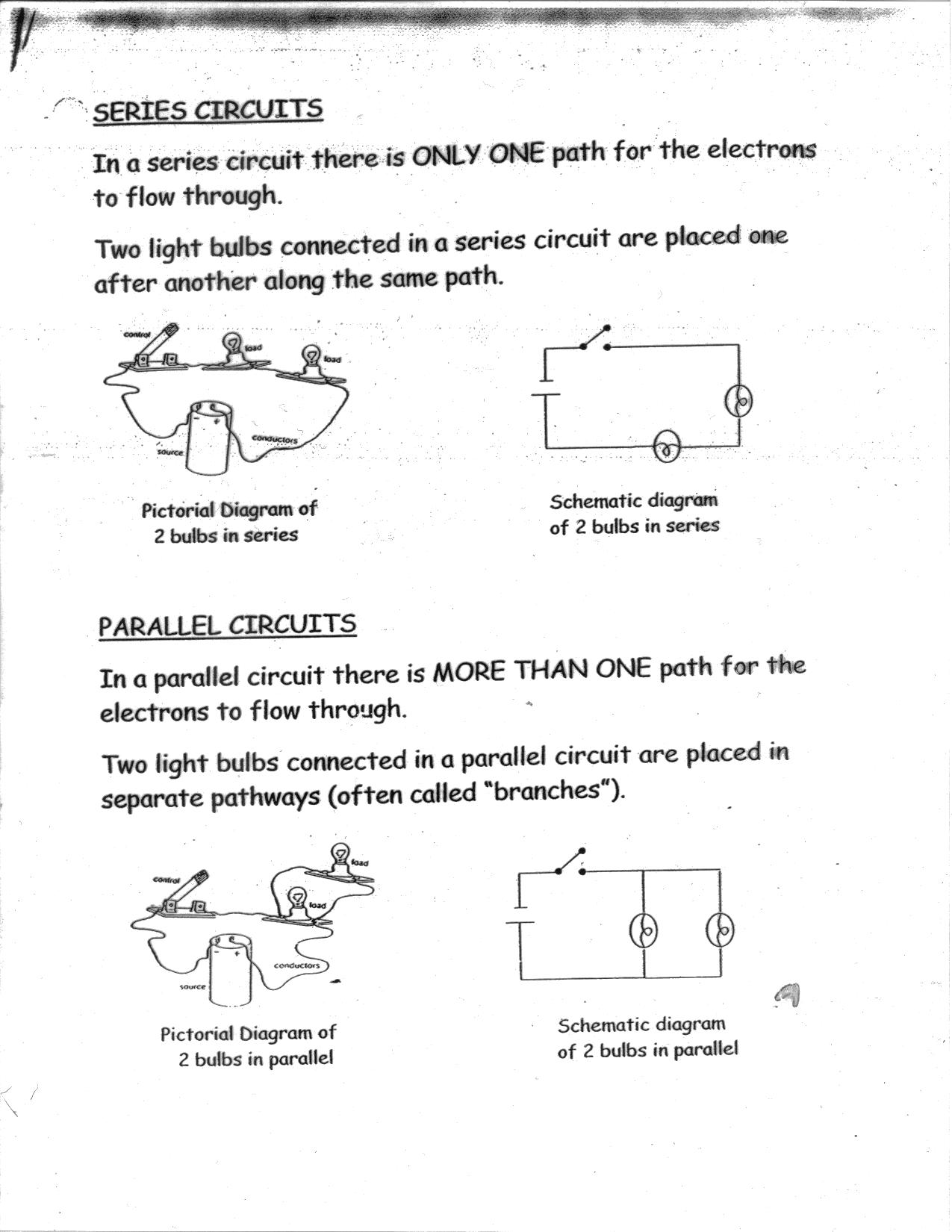
What is a series-parallel circuit?
A series-parallel circuit is a combination of series and parallel connections in an electrical circuit. In this type of circuit, components are arranged in both series and parallel configurations to achieve a specific electrical behavior or desired outcome. Series connections involve components connected in a straight line, where the current flows through each component in sequence, while parallel connections have components connected in branches, allowing the current to divide and flow through different paths. This type of circuit design is commonly used in complex electrical systems to control and distribute electrical currents effectively.
What is the main advantage of using a series-parallel circuit?
The main advantage of using a series-parallel circuit is that it allows for both high voltage and high current to be efficiently utilized in electrical systems. By combining the benefits of both series and parallel circuits, series-parallel circuits can provide a balance between voltage and current requirements, making them versatile and suitable for various applications in electronics and electrical engineering.
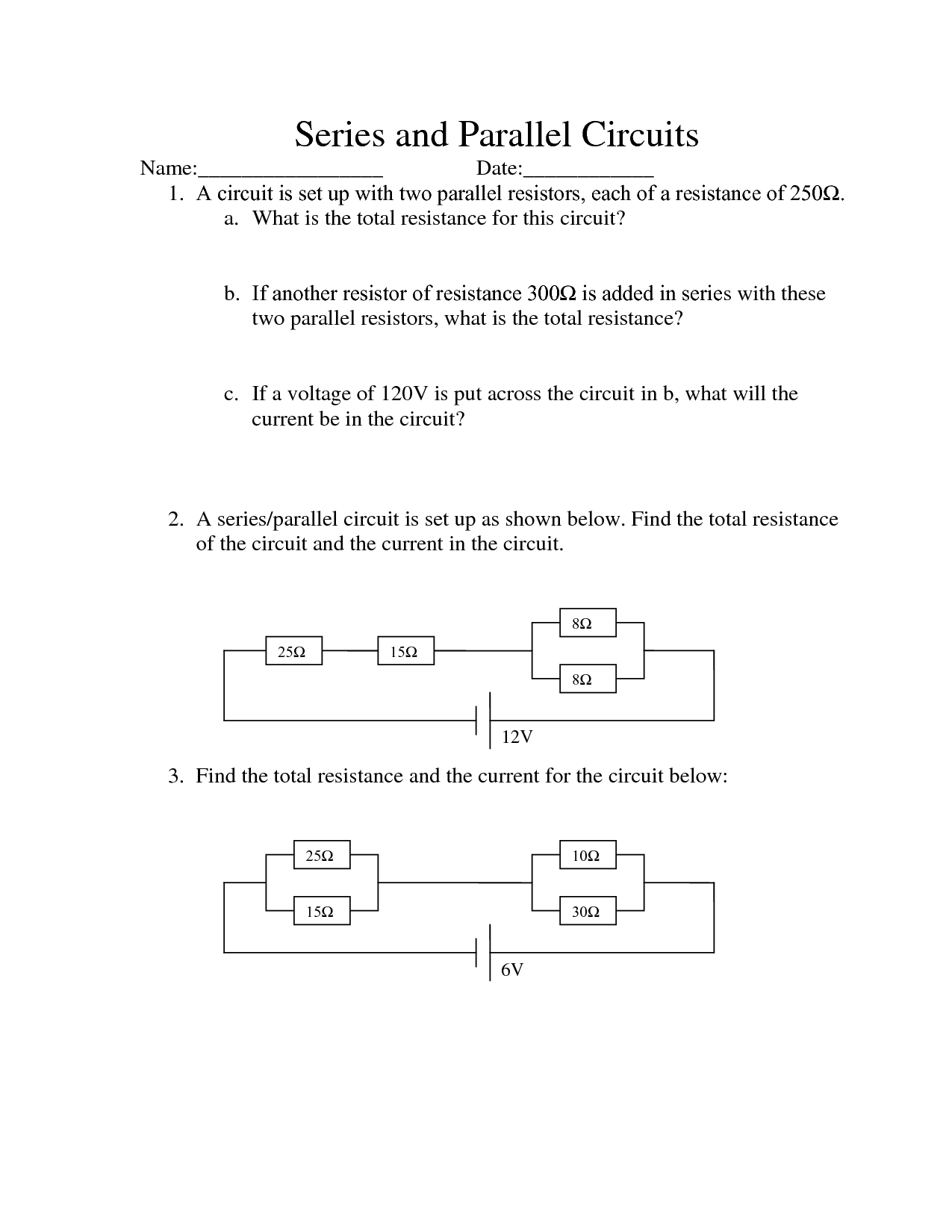
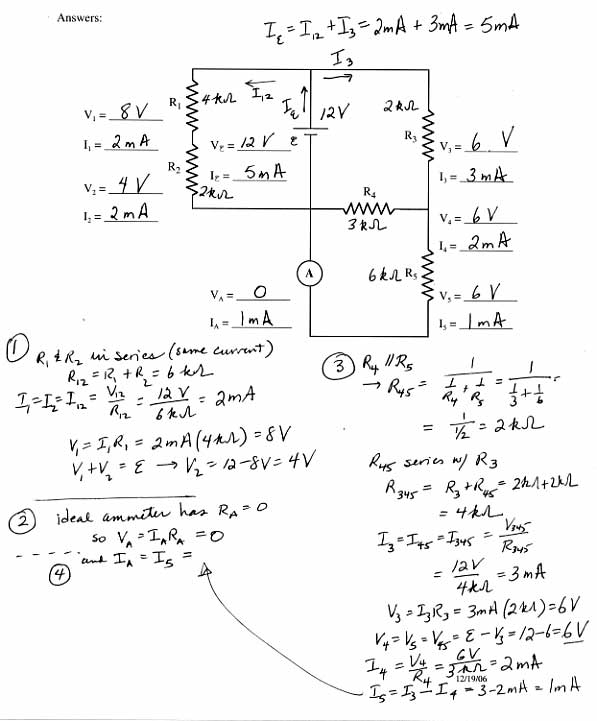
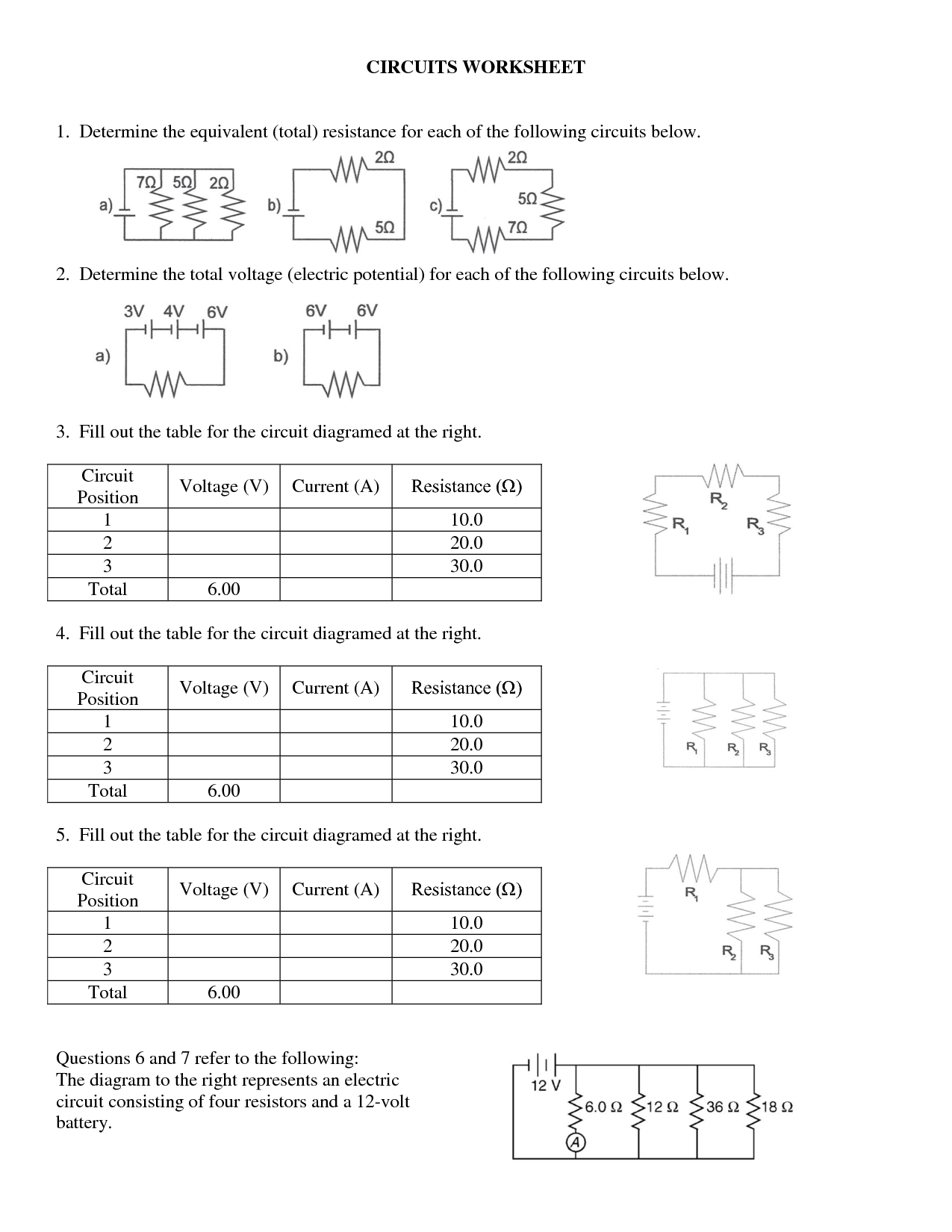
How do you calculate total resistance in a series-parallel circuit?
To calculate the total resistance in a series-parallel circuit, first identify which resistors are in series and calculate their total resistance using the formula: RT = R1 + R2 + R3 + ... for resistors in series. Then, identify which resistors are in parallel and calculate their total resistance using the formula: 1/RT = 1/R1 + 1/R2 + 1/R3 + ... for resistors in parallel. Finally, combine these total resistances from the series and parallel parts of the circuit to find the overall total resistance.
How do you calculate total current in a series-parallel circuit?
To calculate the total current in a series-parallel circuit, you first calculate the total resistance by combining resistors in series and parallel using the appropriate formulas. Once you have the total resistance, you can use Ohm's Law (I = V/R) to calculate the total current by dividing the total voltage in the circuit by the total resistance.
How do you calculate voltage across different resistors in a series-parallel circuit?
To calculate the voltage across different resistors in a series-parallel circuit, you first need to determine the total resistance of the circuit by considering the arrangement of resistors in series and parallel. Once you have the total resistance, you can use Ohm's Law (V = I x R) along with the current flowing through the circuit to calculate the voltage drop across each resistor. Alternatively, you can use voltage divider rules for resistors in series or parallel to find the voltage across individual resistors in the circuit.
What is the difference between voltage in a series circuit and voltage in a parallel circuit?
In a series circuit, the voltage is the same across all components, as the total voltage provided by the source is divided among the components. In a parallel circuit, each component has the full voltage of the source applied to it, as they are connected across the same voltage source independently. This means that the voltage in a series circuit is constant throughout all components, while in a parallel circuit, each component receives the full voltage separately.
How do you determine the current flowing through each resistor in a series-parallel circuit?
To determine the current flowing through each resistor in a series-parallel circuit, you first need to analyze the circuit to identify the series and parallel sections. In series sections, the current is the same across all resistors, while in parallel sections, the total current splits based on the resistance values. Use Ohm's Law (I = V/R) and Kirchhoff's laws to calculate the current flowing through each resistor by considering the voltage across the resistors, individual resistance values, and the total circuit resistance.
How do you determine the total power consumed in a series-parallel circuit?
To determine the total power consumed in a series-parallel circuit, you need to first calculate the power consumed by each individual resistor using the formula P = I^2 * R or P = V^2 / R, where P is power, I is current, R is resistance, and V is voltage. Next, you can find the total power by summing up the powers consumed by all the resistors in the circuit. Remember to take into account the rules for series and parallel connections when calculating the total power in the circuit.
What happens to the overall resistance of a series-parallel circuit when resistors are added in parallel?
When resistors are added in parallel in a series-parallel circuit, the overall resistance of the circuit decreases. This is because adding more resistors in parallel provides additional pathways for the current to flow through, reducing the total resistance that the current encounters. This results in a lower overall resistance for the circuit.
How do you solve complex series-parallel circuit problems using circuit analysis techniques?
To solve complex series-parallel circuit problems using circuit analysis techniques, you can start by analyzing each branch of the circuit individually by applying Ohm's Law, Kirchhoff's Laws (Kirchhoff's Current Law and Kirchhoff's Voltage Law), and the rules for series and parallel circuits. Then, you can simplify the circuit by combining resistors in series and parallel to reduce the circuit to an equivalent resistance value. Finally, you can use this equivalent resistance value to analyze the circuit as a simple series or parallel circuit, applying the same techniques to solve for voltages, currents, or power in the circuit.
Have something to share?
Who is Worksheeto?
At Worksheeto, we are committed to delivering an extensive and varied portfolio of superior quality worksheets, designed to address the educational demands of students, educators, and parents.






















Comments