Seed and Plant Worksheets
Are you a teacher or a parent looking for engaging and educational activities to help your students or children learn about seeds and plants? If so, you've come to the right place. In this blog post, we will explore a variety of worksheets that are designed to teach young learners all about the fascinating world of plants and how they grow. From labeling the parts of a flower to categorizing different types of seeds, these worksheets are the perfect tool to help the young minds grasp the concepts of botany in an interactive and enjoyable way.
Table of Images 👆
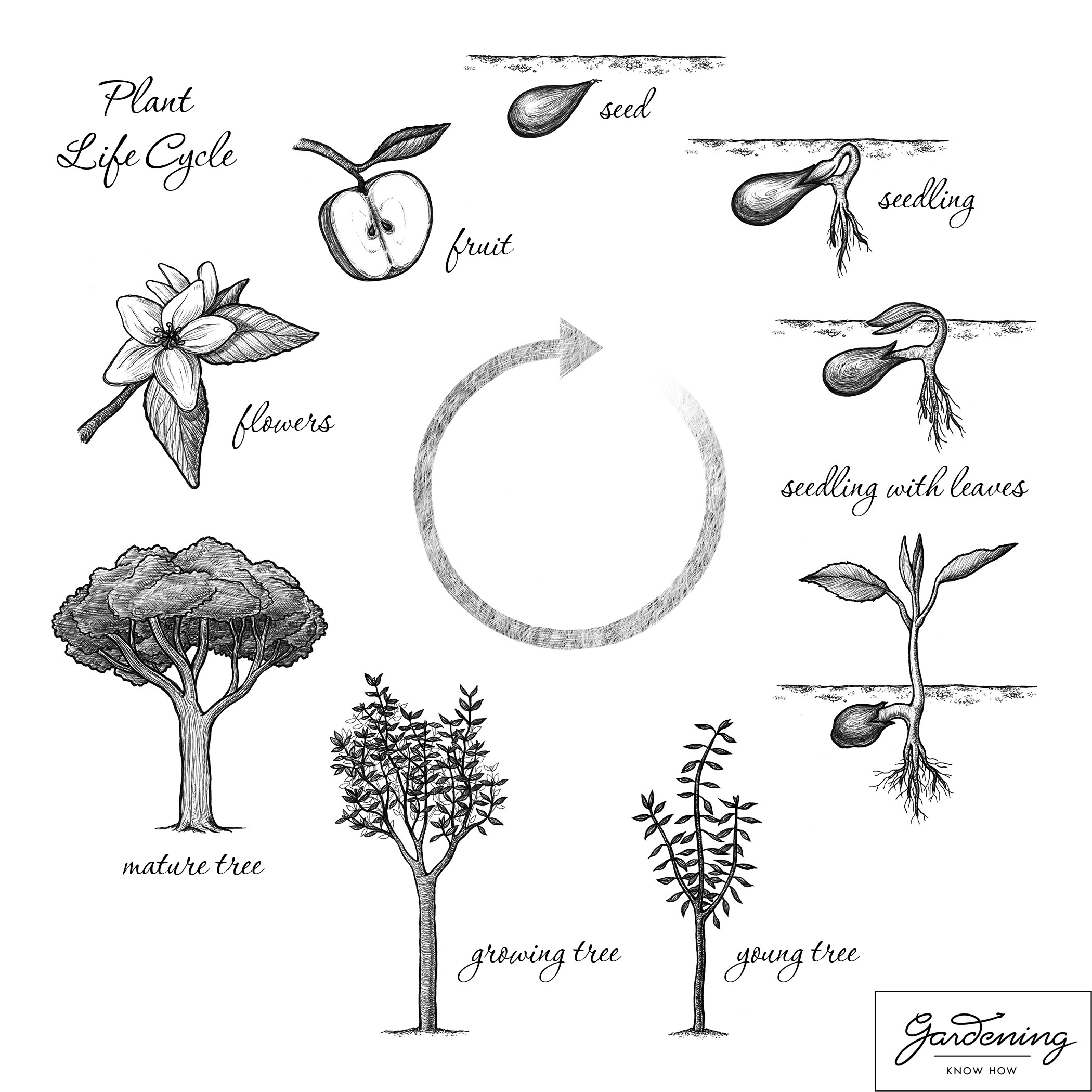
- Plant Life Cycle Seed Worksheet
- Parts of a Bean Seed Worksheet
- Growing Plants Worksheet
- Printable Plant Parts Worksheet
- Parts of a Lima Bean Seed Worksheet for Kindergarten
- Plant Parts Worksheet 3rd Grade
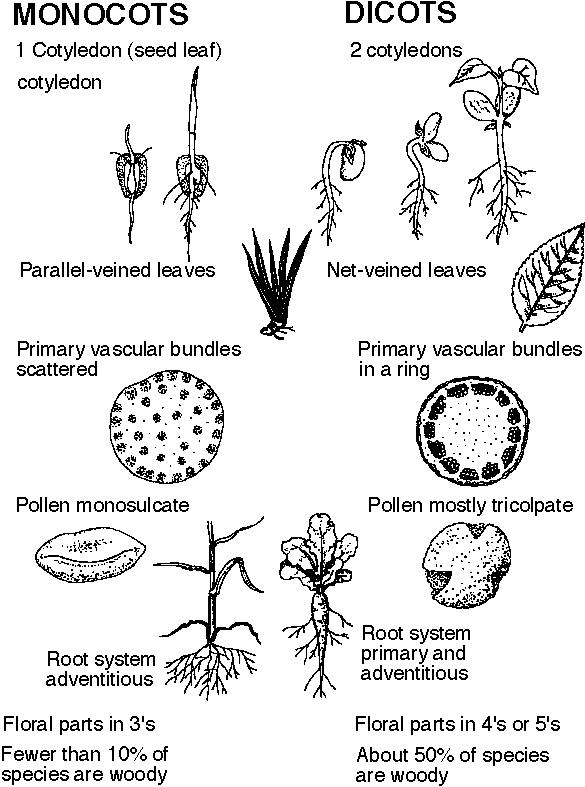
- Monocot vs Dicot
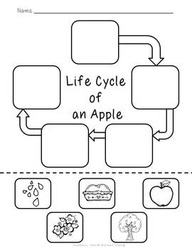
- Apple Life Cycle Worksheet
- Free Printable Worksheets Plant Life Cycle
- Flowering Plant Life Cycle for Kids
- Free Pumpkin Life Cycle Printable Worksheets
- Spring Flowers Word Search Printable
- Corn Coloring Page Template
- Reduce Reuse Recycle Worksheets
- Reduce Reuse Recycle Worksheets
More Other Worksheets
Kindergarten Worksheet My RoomSpanish Verb Worksheets
Cooking Vocabulary Worksheet
My Shadow Worksheet
Large Printable Blank Pyramid Worksheet
Relationship Circles Worksheet
DNA Code Worksheet
Meiosis Worksheet Answer Key
Art Handouts and Worksheets
7 Elements of Art Worksheets
What is a seed?
A seed is a small, embryonic plant enclosed in a protective outer covering. It contains the genetic material needed for the plant to grow and develop into a new plant. Seeds are essential for the reproduction and propagation of plants, as they germinate under the right conditions to produce roots, stems, leaves, and eventually flowers and fruits.
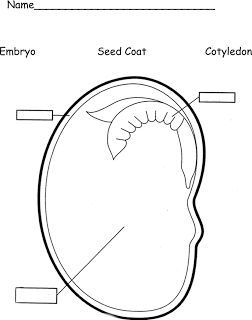
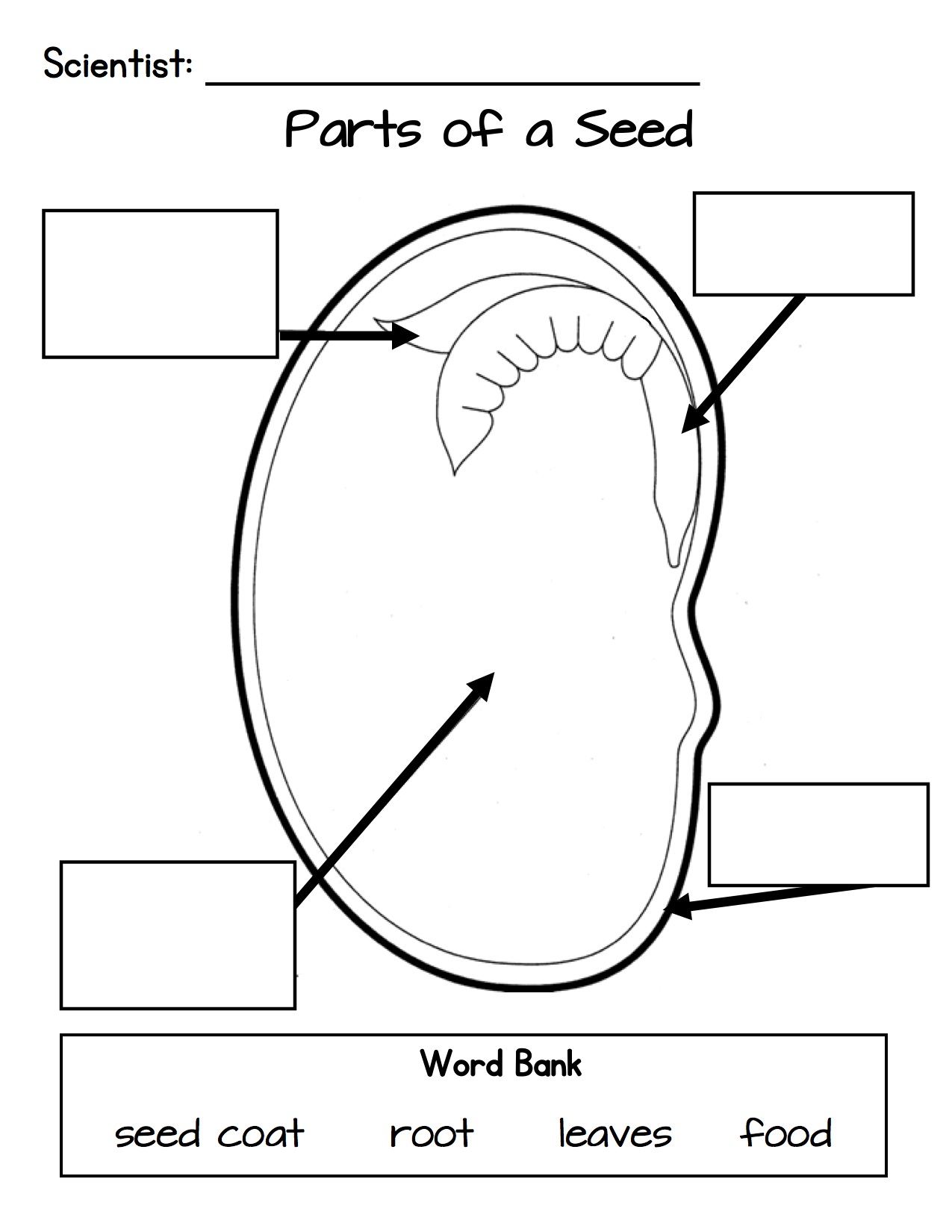
What are the different parts of a seed?
A seed is composed of three primary parts: the outer seed coat, which protects the seed and regulates water intake; the endosperm, a nutrient-rich tissue that provides nourishment for the developing seedling; and the embryo, which contains the genetic material and the beginnings of the plant's root, shoot, and seed leaves.
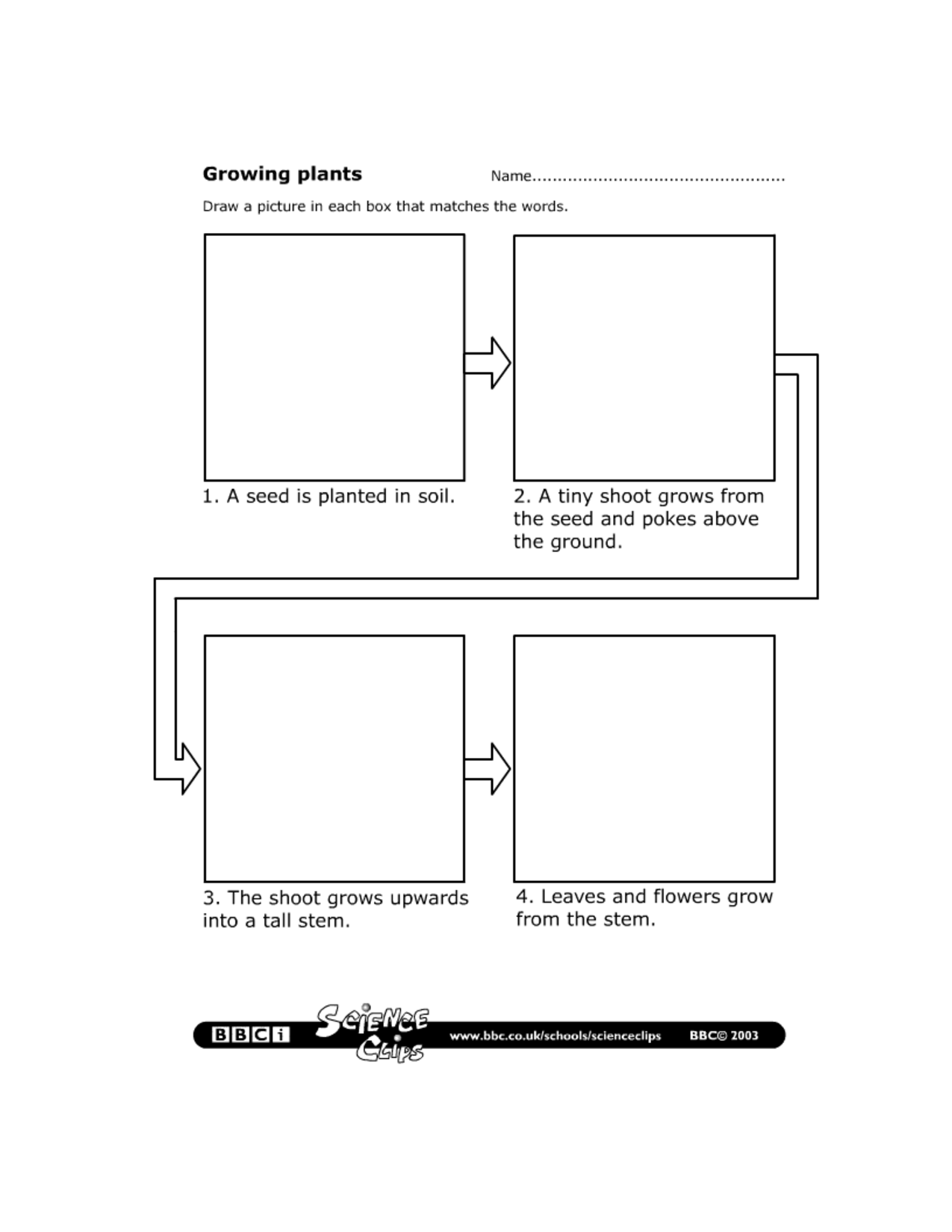
How do seeds germinate?
Seeds germinate when they are exposed to the right combination of water, oxygen, and temperature. The process typically begins with the absorption of water, which triggers the seed to swell and break open. Enzymes are then activated to break down stored food in the seed, providing energy for the growth of the root and shoot. As the root emerges from the seed, it anchors the plant into the soil, while the shoot grows upwards towards the light. Eventually, the seed coat falls away, and the plant continues to grow and develop through photosynthesis and nutrient uptake from the soil.
What factors are necessary for successful seed germination?
For successful seed germination, several factors are essential, including water, oxygen, proper temperature, and light (for some species). Water is needed to soften the seed coat and initiate metabolic processes, while oxygen is necessary for respiration. The temperature should be within a specific range suitable for the specific plant species, as it affects enzyme activity and biological processes. Light can trigger the germination of certain seeds through the stimulation of hormones. Overall, the right combination of these factors is crucial for the successful germination of seeds.
How do plants reproduce using seeds?
Plants reproduce using seeds through a process called sexual reproduction. This involves the formation of seeds that contain genetic information from both parent plants. The process starts with the formation of male and female reproductive cells (pollen and ovules) in the flowers of the plant. Pollen is transferred to the stigma of the flower, leading to fertilization and the formation of a zygote. This zygote then develops into an embryo within the seed, which is surrounded by a protective seed coat. When conditions are favorable, the seed germinates, leading to the growth of a new plant.
What are the benefits of seed dispersal?
Seed dispersal plays a crucial role in the reproduction and survival of plants by increasing their chances of germination and successful growth. It helps plants colonize new habitats, escape competition with parent plants, and reduce the risk of disease and pest outbreaks. Additionally, seed dispersal promotes genetic diversity within plant populations and supports ecosystem resilience by maintaining plant diversity. Overall, seed dispersal is essential for sustaining healthy plant populations and maintaining the balance of ecosystems.
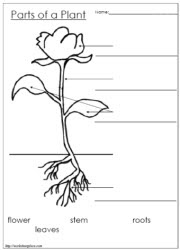
What is the purpose of a plant's roots?
The purpose of a plant's roots is to anchor the plant in the soil, absorb water and nutrients from the soil, and provide support for the above-ground parts of the plant. Additionally, roots store food and energy reserves for the plant's growth and reproduction.
How do plants obtain water and nutrients through their roots?
Plants obtain water and nutrients through their roots via a process called root absorption. The root system of a plant contains specialized structures called root hairs which increase the surface area for absorption. Water and nutrients are absorbed by the roots through osmosis and active transport, allowing the plant to transport these essential elements to the rest of its body for growth and development.
What is photosynthesis and how does it relate to plant growth?
Photosynthesis is the process by which green plants, algae, and some bacteria convert sunlight, water, and carbon dioxide into glucose (energy) and oxygen. This process is crucial for plant growth because glucose provides plants with the energy they need to grow, reproduce, and carry out other vital functions. Essentially, photosynthesis is the source of organic compounds that fuel plant development and enable them to thrive.
What are some adaptations that plants have developed to survive in different environments?
Plants have developed various adaptations to survive in different environments, such as thick waxy cuticles to reduce water loss in arid environments, specialized root systems like taproots for deep water access or shallow roots for surface water absorption, mechanisms like succulence in desert plants to store water, structures like spines or thorns for defense against herbivores, and even strategies like rapid growth in seasonal environments to complete their life cycle before unfavorable conditions occur. These adaptations help plants thrive and survive in diverse habitats across the world.
Have something to share?
Who is Worksheeto?
At Worksheeto, we are committed to delivering an extensive and varied portfolio of superior quality worksheets, designed to address the educational demands of students, educators, and parents.























Comments