Science Worksheets Plants
Science worksheets on plants provide an engaging and interactive way for students to learn about the entity of plants and their various subjects, such as anatomy, life cycles, and ecological roles. These worksheets offer a valuable resource for teachers seeking to enhance their lessons and ensure their students grasp important concepts related to the fascinating world of plants.
Table of Images 👆
- Grade Science Worksheets Plants
- 1st Grade Science Worksheets Plants
- Patricks Day
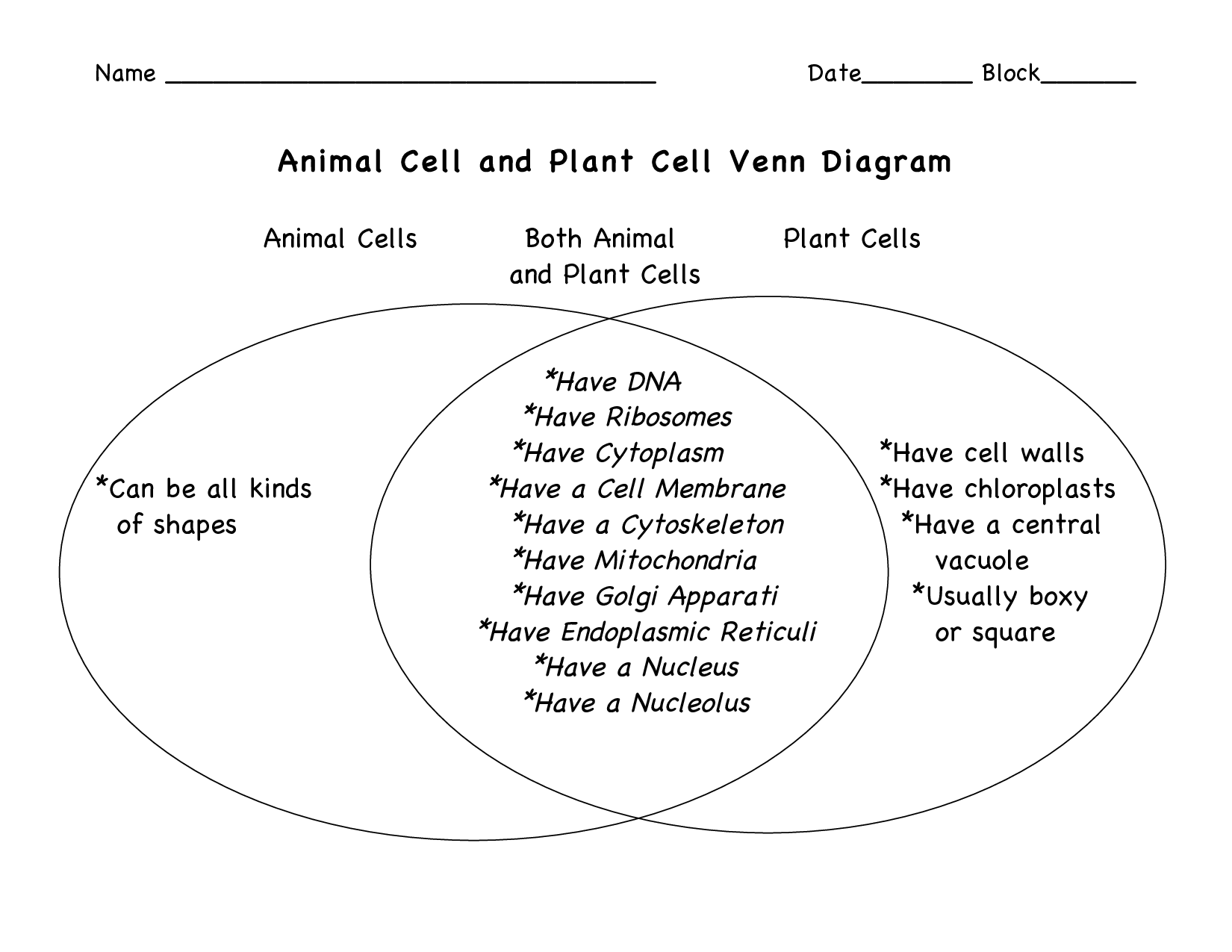
- Plant and Animal Cell Venn Diagram
- Forest Animal Worksheets
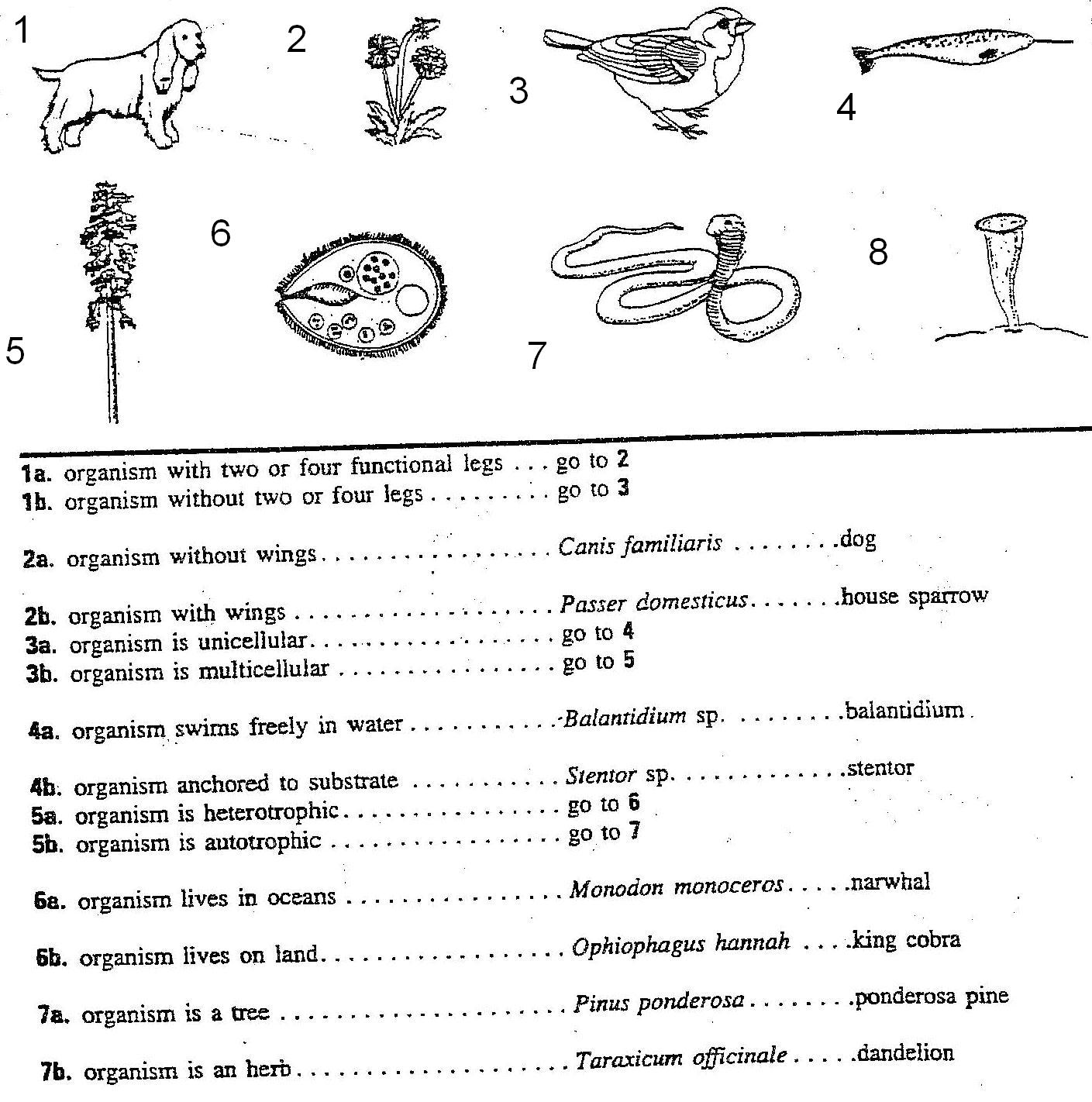
- Dichotomous Key Worksheets
- Plants and Animals Worksheet Kindergarten
- Energy Worksheets 3rd Grade Forms
- Compare and Contrast Graphic Organizer Printable
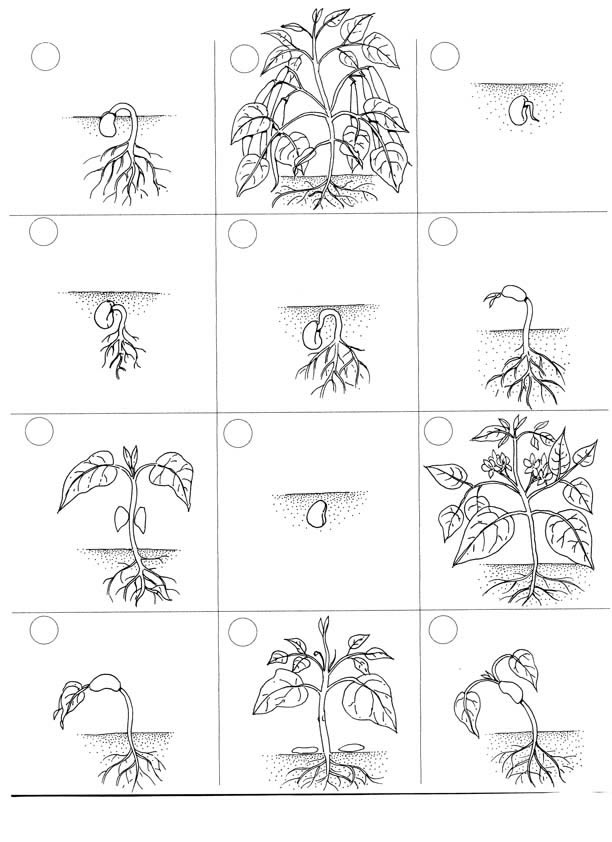
- Plant Life Cycle Book
- 3rd Grade Plant and Animal Adaptation Worksheet
- Free Printable Connect the Dots Pages
- Free Printable Connect the Dots Pages
More Science Worksheets
6 Grade Science WorksheetsScience Heat Energy Worksheets with Answer
Science Worksheets Light and Sound
1st Grade Life Science Worksheets
7th Grade Science Cells Worksheets
Worksheets Life Science Vocabulary
8th Grade Science Scientific Method Worksheet
Science Worksheets All Cells
5th Grade Science Mixtures and Solutions Worksheets
What is photosynthesis and how does it contribute to a plant's growth?
Photosynthesis is the process by which green plants, algae, and some bacteria convert light energy, usually from the sun, into chemical energy in the form of glucose. This process is essential for a plant's growth and survival as it provides the plant with the energy it needs to carry out metabolic activities and build new plant tissue. In photosynthesis, plants absorb carbon dioxide from the air and water from the soil, using sunlight to convert these ingredients into glucose and oxygen. The glucose produced is used by the plant as a source of energy for growth, repair, and reproduction, ultimately fueling the plant's overall development and vitality.
Explain the different types of plant cells and their functions.
There are two main types of plant cells: meristematic cells and permanent cells. Meristematic cells are undifferentiated and responsible for cell division and growth, found in areas of active growth like the root and shoot tips. Permanent cells make up the bulk of plant tissues and can be further classified into various cell types based on their functions, such as parenchyma cells for storage, collenchyma cells for support, and sclerenchyma cells for structural strength. Additionally, there are specialized cells like xylem and phloem cells for water and nutrient transport, epidermal cells for protection, and guard cells for regulating gas exchange through the stomata. Each type of plant cell plays a crucial role in the growth, development, and functioning of the plant.
How do plants reproduce and what are the various methods of plant reproduction?
Plants reproduce through both sexual and asexual methods. Sexual reproduction involves the fusion of male and female gametes, typically through pollination and fertilization, resulting in seeds. Asexual reproduction, on the other hand, does not involve the formation of seeds and occurs through mechanisms such as fragmentation, budding, rhizomes, tubers, and spores. These methods allow plants to reproduce and propagate without the need for pollination or fertilization, enabling them to colonize new areas and ensure genetic diversity within populations.
Describe the process of germination and the factors that can affect it.
Germination is the process by which a plant embryo begins to grow and develop into a seedling. It typically involves the seed absorbing water, swelling, and breaking through the seed coat. Factors that can affect germination include water availability, temperature, light, oxygen levels, and presence of certain chemicals or hormones. Optimal conditions for germination vary among plant species, but generally involve a balance of these factors to trigger the necessary biochemical and physiological changes for successful seedling growth.
What are the different parts of a flower and their roles in plant reproduction?
A flower consists of various parts: the male reproductive organ, the stamen, which produces pollen; the female reproductive organ, the pistil, which contains the stigma, style, and ovary where the ovules are located; sepals, which protect the flower bud; and petals, which attract pollinators. During reproduction, pollen is transferred from the stamen to the stigma through pollination. The ovules are then fertilized by the pollen, leading to seed formation and eventually fruit development, ensuring the continuation of plant species.
Explain the life cycle of a flowering plant, from seed to mature plant.
A flowering plant's life cycle begins with a seed germinating in suitable conditions, where it develops into a seedling. The seedling grows into a mature plant, producing flowers that are pollinated by insects, wind, or other means. After pollination, the flowers develop into fruits containing seeds. The seeds are then dispersed through various methods, such as wind, animals, or water. Once dispersed, the seeds germinate to start the cycle anew, completing the life cycle of a flowering plant from seed to mature plant.
What are the adaptations that allow plants to survive in different environments?
Plants have various adaptations that help them survive in different environments, including specialized root systems for efficient water and nutrient uptake, waxy coatings on leaves to reduce water loss, thorns or spines for defense against herbivores, and mechanisms for storing water in arid conditions. Additionally, plants may have specific leaf shapes or structures that optimize sunlight capture for photosynthesis, as well as the ability to adjust their growth rate and flowering times in response to changing environmental conditions.
Describe the process of pollination and the role of pollinators.
Pollination is the transfer of pollen from the male reproductive organ (anther) of a flower to the female reproductive organ (stigma), which results in fertilization and the production of seeds. Pollinators such as bees, butterflies, birds, and other insects play a crucial role in this process by carrying pollen between flowers as they forage for nectar or pollen. This transfer of pollen enables plants to reproduce, produce fruit, and create new seeds, contributing to biodiversity and the sustainability of plant species.
How does water move through a plant and what are the functions of vascular tissues?
Water moves through a plant by a process called transpiration, which is the loss of water vapor through the stomata in the leaves. Water is absorbed by the roots from the soil and travels up through the xylem tissue, which is part of the plant's vascular system. The xylem transports water and minerals from the roots to the rest of the plant, providing structural support and helping to maintain turgor pressure. The phloem tissue, another part of the vascular system, transports sugars and other organic molecules produced in the leaves to other parts of the plant for growth and energy. Overall, the vascular tissues play a crucial role in the distribution of water, nutrients, and organic compounds throughout the plant.
Explain the importance of plants in the ecosystem and the benefits they provide to humans.
Plants are crucial in the ecosystem as they play a vital role in producing oxygen through photosynthesis, which is essential for all living organisms. They also serve as food sources for animals, help maintain soil health, regulate the water cycle, and provide habitats for various species. Additionally, plants offer numerous benefits to humans, including food production, medicine, air purification, climate regulation, and aesthetic value. Overall, plants are fundamental to the balance and health of ecosystems, as well as our well-being and survival.
Have something to share?
Who is Worksheeto?
At Worksheeto, we are committed to delivering an extensive and varied portfolio of superior quality worksheets, designed to address the educational demands of students, educators, and parents.























Comments