Science Sound Worksheets for Kindergarten
Are you in search of engaging and educational worksheets to help your kindergarten students explore the fascinating world of sound? Look no further! Our Science Sound Worksheets are designed to captivate young minds and provide a solid foundation in the subject. With a variety of activities and exercises, these worksheets are perfect for introducing the concept of sound to your little learners.
Table of Images 👆
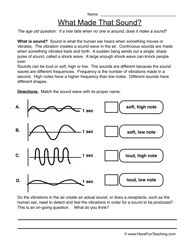
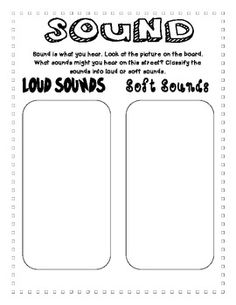
- Loud and Soft Sounds Worksheets
- First Grade Worksheets Science Sound Energy
- First Grade Science Sound Worksheets
- Kindergarten Grade Reading Worksheets
- 2nd Grade Reading Worksheets
- Properties of Matter Worksheet Grade 2
- Uppercase Lowercase Letters Worksheet
- Kindergarten Science Worksheets
- 5 Senses NatureWalk
- Forms of Energy Worksheets 2nd Grade
- Forms of Energy Worksheets 2nd Grade
More Science Worksheets
6 Grade Science WorksheetsScience Heat Energy Worksheets with Answer
Science Worksheets Light and Sound
1st Grade Life Science Worksheets
7th Grade Science Cells Worksheets
Worksheets Life Science Vocabulary
8th Grade Science Scientific Method Worksheet
Science Worksheets All Cells
5th Grade Science Mixtures and Solutions Worksheets
What is sound?
Sound is a form of energy that creates vibrations in the air, water, or another medium, which our ears perceive as sound waves. These waves travel to our ears, where they are converted into nerve signals that our brain interprets as sound.
How is sound produced?
Sound is produced when an object vibrates, causing molecules in the surrounding medium (such as air, water, or a solid) to also vibrate. These vibrations create waves of pressure that travel through the medium until they reach our ears. The ear then detects these vibrations and converts them into electrical signals that our brain interprets as sound.
What are some examples of sounds in our environment?
Some examples of sounds in our environment include birds chirping, cars honking, water flowing in a river, wind rustling through trees, people talking, footsteps on the ground, music playing, rain falling, and waves crashing against the shore.
How does sound travel?
Sound travels in the form of waves through a medium, such as air, water, or other materials. When an object vibrates, it creates sound waves that propagate through the medium by transferring energy from one particle to another. These vibrations cause compressions and rarefactions in the medium, creating areas of high and low pressure, which our ears detect as sound. The speed of sound varies depending on the properties of the medium it travels through, such as temperature and density.
What is the difference between loud and soft sounds?
The difference between loud and soft sounds lies in their amplitude. Loud sounds have a higher amplitude, meaning they have more energy and create stronger vibrations that travel farther and are perceived as louder to the human ear. In contrast, soft sounds have a lower amplitude with less energy and weaker vibrations, resulting in a quieter perception.
How can we change the pitch of a sound?
To change the pitch of a sound, you can use audio editing software to adjust the frequency of the sound wave. Increasing the frequency will raise the pitch, while decreasing the frequency will lower the pitch. Another way to change pitch is by using instruments such as a pitch shifter or a guitar capo, which physically alter the tension on strings to raise or lower the pitch of a sound.
Why do some sounds make us feel happy or sad?
Sounds can trigger emotional responses due to their association with past experiences, memories, or cultural norms. Happy sounds, such as laughter or uplifting music, may evoke positive emotions because they are linked to joyous occasions or pleasant experiences. Conversely, sad sounds, like mournful music or crying, may elicit feelings of melancholy or sorrow due to their connection to loss or difficult situations. Additionally, the tones, rhythms, and frequencies of sounds can impact our brain chemistry and trigger the release of neurotransmitters that influence our emotions, further shaping our feelings towards certain sounds.
How do our ears help us hear sound?
Our ears help us hear sound through a complex process that involves three main parts: the outer ear, the middle ear, and the inner ear. When sound waves enter the outer ear, they travel down the ear canal and cause the eardrum to vibrate. These vibrations are then transmitted through three small bones in the middle ear called the ossicles, which amplify the sound and send it to the cochlea in the inner ear. The cochlea converts the vibrations into electrical signals that are then sent to the brain through the auditory nerve, where they are processed and interpreted as sound.
What is an echo?
An echo is the reflection of sound waves off a surface back to the listener, resulting in a repeated, fainter version of the original sound. This phenomenon occurs when sound waves bounce off a solid object and travel back to the listener's ears, creating a delayed repetition of the sound heard.
Why is it important to protect our ears from loud sounds?
It is important to protect our ears from loud sounds to prevent hearing loss and potential damage to our auditory system. Exposure to loud noises can lead to permanent hearing impairment, tinnitus, and other hearing-related issues. By using ear protection and being mindful of our surroundings, we can preserve our hearing health and maintain our quality of life.
Have something to share?
Who is Worksheeto?
At Worksheeto, we are committed to delivering an extensive and varied portfolio of superior quality worksheets, designed to address the educational demands of students, educators, and parents.
























Comments