RNA and Transcription Worksheet Answers
Are you a biology student seeking a comprehensive resource to reinforce your understanding of RNA and transcription? Look no further! In this blog post, we provide the answers to a challenging worksheet on RNA and transcription, allowing you to review and assess your knowledge in this complex subject.
Table of Images 👆
- DNA Transcription and Translation Worksheet
- Protein Synthesis Worksheet DNA and RNA
- Transcription and Translation Worksheet Answer Key
- Transcription and RNA Worksheet Answer Key
- DNA Coloring Transcription and Translation Answer Key
- DNA Transcription Translation Worksheet Answers
- Transcription and Translation Worksheet Answer Key
- Protein Synthesis Worksheet Answers
- Protein Synthesis Worksheet Answer Key
- DNA RNA Transcription Translation Worksheets
- Transcription Translation Worksheet Answer Key
- Transcription and Translation Worksheet Answers
- DNA Replication Transcription Translation Worksheet
- DNA Transcription and Translation Worksheet Answers
- Transcription and Translation Worksheet Answer Key
- Protein Synthesis Worksheet Answer Key
- Protein Synthesis Worksheet Answer Key
- Transcription and Translation Practice Worksheet
More Other Worksheets
Kindergarten Worksheet My RoomSpanish Verb Worksheets
Cooking Vocabulary Worksheet
My Shadow Worksheet
Large Printable Blank Pyramid Worksheet
Relationship Circles Worksheet
DNA Code Worksheet
Meiosis Worksheet Answer Key
Art Handouts and Worksheets
7 Elements of Art Worksheets
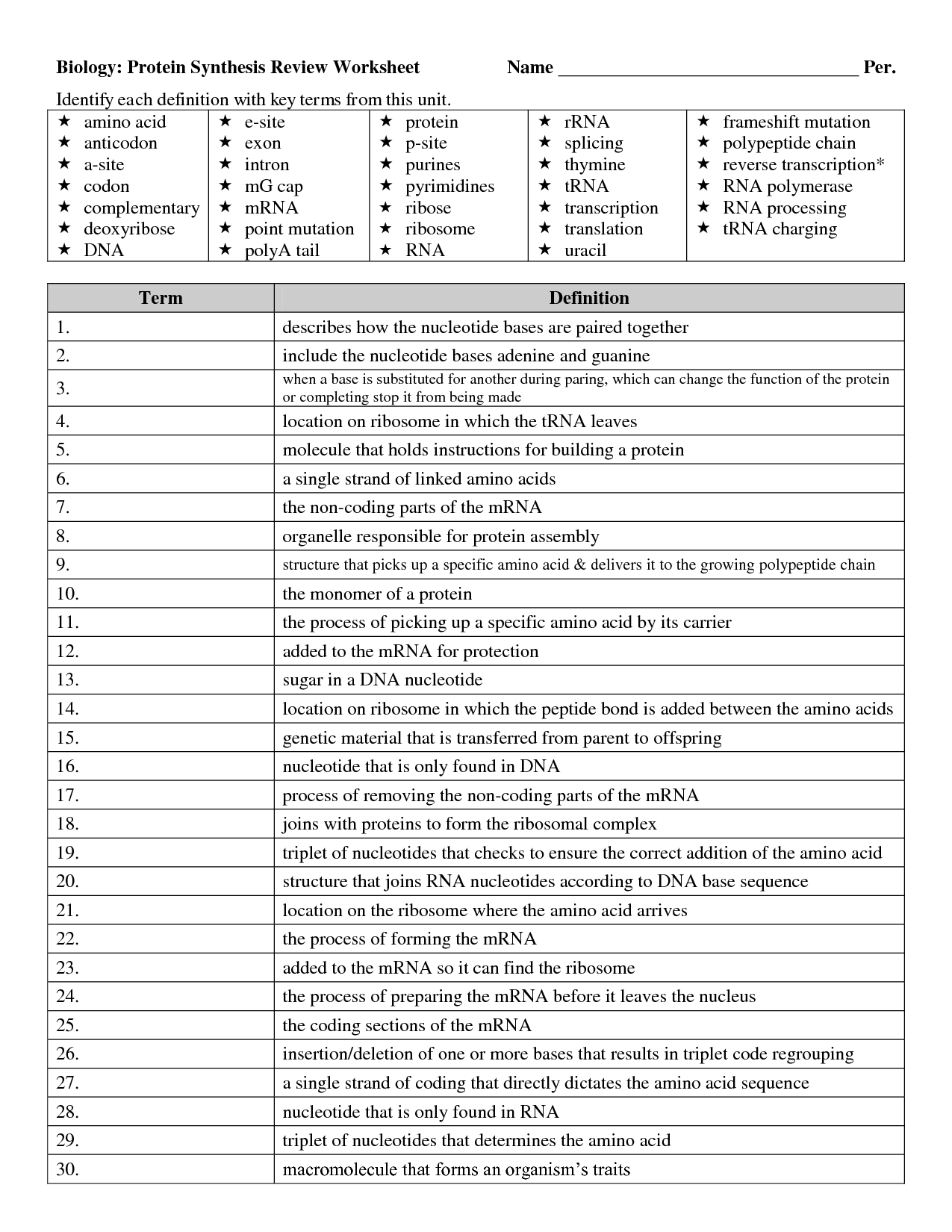
What is the primary function of RNA in the cell?
The primary function of RNA in the cell is to transfer genetic information from DNA to protein synthesis by serving as a messenger molecule for the translation of genes into proteins. RNA plays a crucial role in the process of protein synthesis as it carries the genetic code from the DNA in the cell's nucleus to the ribosomes in the cytoplasm where proteins are assembled.
RNA serves as a messenger molecule that carries genetic information from DNA to the protein synthesis machinery.
RNA serves as a messenger molecule that carries genetic information from DNA to the protein synthesis machinery.
How is RNA different from DNA?
RNA differs from DNA in several ways. RNA is single-stranded, while DNA is double-stranded. RNA contains the sugar ribose, whereas DNA contains deoxyribose. RNA uses uracil as a base instead of thymine found in DNA. RNA is typically shorter in length than DNA and has various types such as messenger RNA (mRNA), transfer RNA (tRNA), and ribosomal RNA (rRNA), each with specific functions in protein synthesis.
RNA is single-stranded, contains the sugar ribose, and has uracil (U) instead of thymine (T) as a base.
Yes, that is correct. RNA is single-stranded and contains the sugar ribose. Unlike DNA, RNA has uracil (U) as one of the four bases instead of thymine (T).
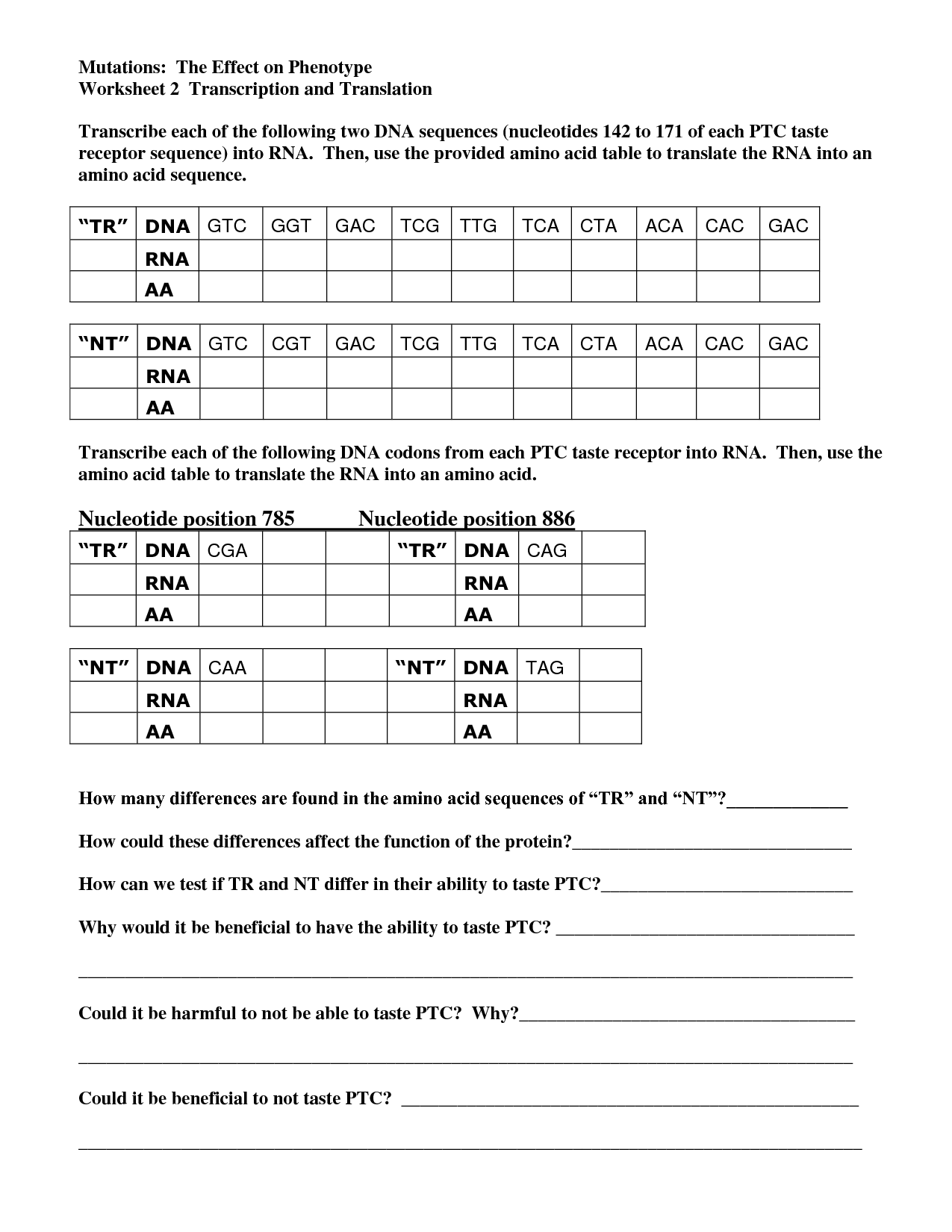
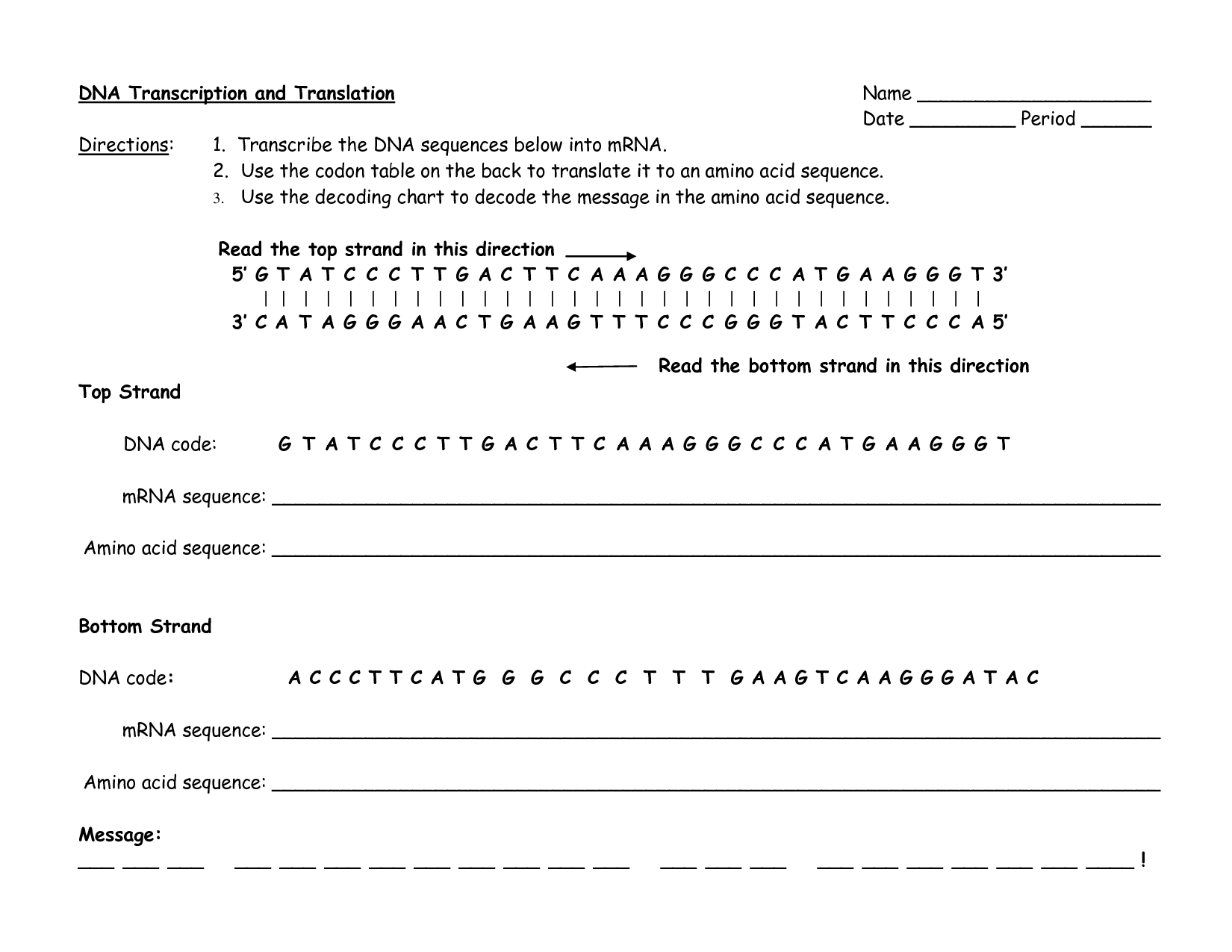
What is transcription?
Transcription is the process of converting DNA into messenger RNA (mRNA) by the enzyme RNA polymerase. This process involves the synthesis of a complementary RNA strand from a template DNA strand, which serves as a blueprint for protein synthesis through translation. Transcription is a crucial step in the gene expression pathway, where the genetic information stored in DNA is transcribed into a format that can be used by the cell to make proteins.
Transcription is the process by which an RNA molecule is synthesized using a DNA template.
Transcription is the biological process where an RNA molecule is synthesized using a DNA template.
Where does transcription occur in the cell?
Transcription occurs in the cell nucleus.
Transcription occurs in the nucleus of eukaryotic cells and in the nucleoid region of prokaryotic cells.
Transcription, the process of synthesizing RNA from a DNA template, takes place in the nucleus of eukaryotic cells and in the nucleoid region of prokaryotic cells. In eukaryotes, the DNA is housed within the nucleus, where transcription occurs before the RNA molecules are processed and transported to the cytoplasm for translation. In prokaryotes, which lack a nucleus, transcription occurs in the nucleoid region where the DNA is compacted and located within the cytoplasm.
What is the role of RNA polymerase in transcription?
RNA polymerase is an enzyme responsible for catalyzing the process of transcription in the cell. It binds to a specific region of DNA called the promoter and unwinds the DNA helix to expose the coding strand. It then synthesizes an RNA molecule by adding complementary nucleotides to the template strand of DNA. This results in the creation of a single-stranded RNA molecule that is complementary to the coding strand of the DNA. Ultimately, RNA polymerase plays a vital role in gene expression by transcribing genetic information from DNA into RNA.
RNA polymerase is an enzyme that catalyzes the synthesis of RNA by reading the DNA template and assembling the corresponding RNA strand.
RNA polymerase is an enzyme that catalyzes the synthesis of RNA by reading the DNA template and assembling the corresponding RNA strand.
Have something to share?
Who is Worksheeto?
At Worksheeto, we are committed to delivering an extensive and varied portfolio of superior quality worksheets, designed to address the educational demands of students, educators, and parents.































Comments