Rib Cage Worksheet
The rib cage is a vital part of the human body, providing protection for important organs such as the heart and lungs. If you are seeking a better understanding of the rib cage and its structure, you are in the right place. In this blog post, we will explore worksheets that focus on the entity and subject of the rib cage, allowing you to delve deeper into its anatomy and function. Whether you are a student studying anatomy or a healthcare professional looking to refresh your knowledge, these worksheets will provide an informative and engaging learning experience.
Table of Images 👆
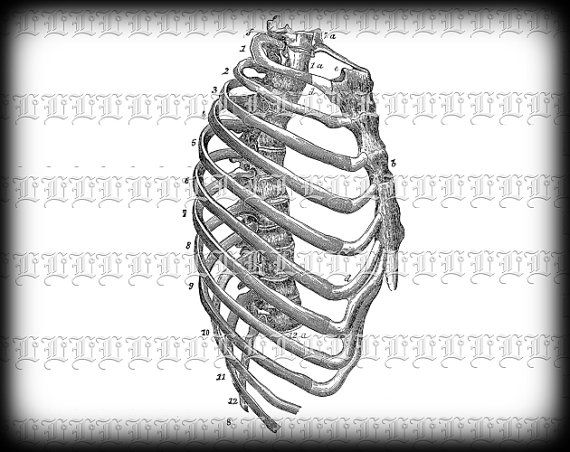
- Rib Cage Diagram Unlabeled
- Thoracic Rib Cage
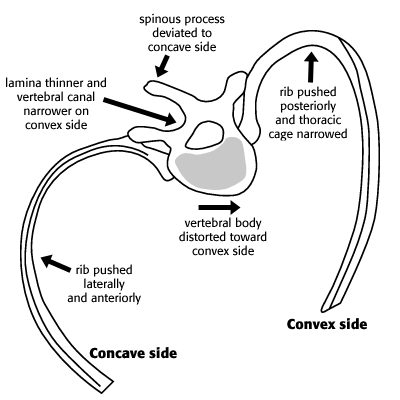
- Right Thoracic Scoliosis Rib Hump
- Cage Rib Bone Labeling Worksheet
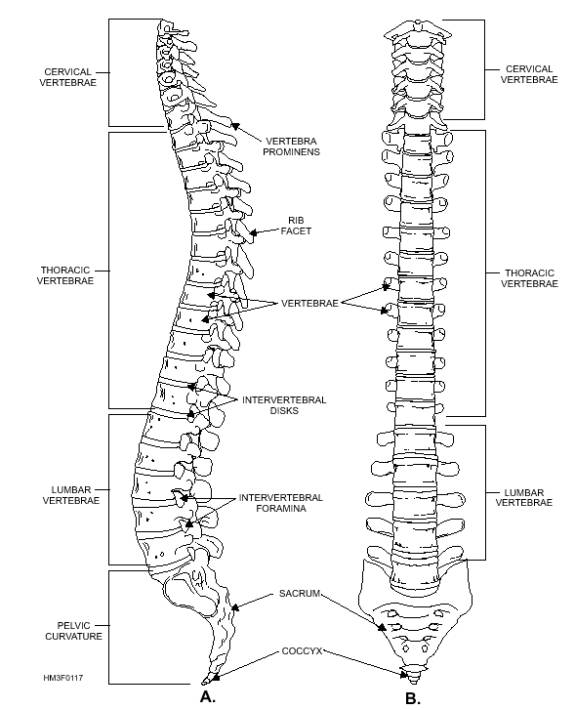
- Unlabeled Vertebral Column Worksheet
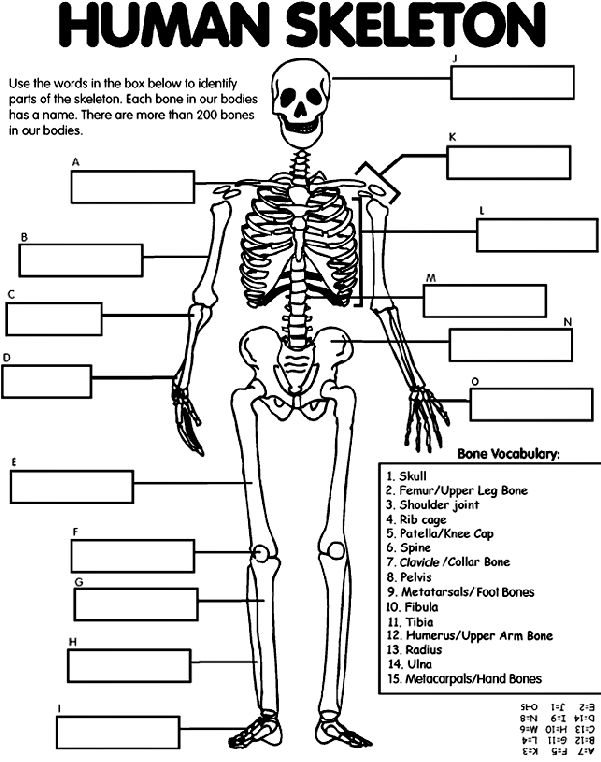
- Human Skeleton Bones Worksheet
- Printed circuit board
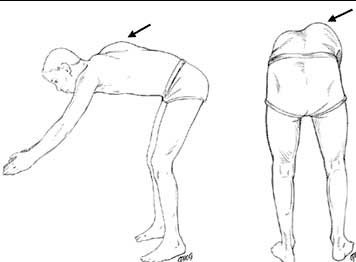
- Adams Forward Bend Test Scoliosis
- Human Rib Cage Side View
- Vertebral Column Posterior View Diagram
- Rib Cage Drawing
- Unlabeled Long Bone Anatomy
More Other Worksheets
Kindergarten Worksheet My RoomSpanish Verb Worksheets
Cooking Vocabulary Worksheet
My Shadow Worksheet
Large Printable Blank Pyramid Worksheet
Relationship Circles Worksheet
DNA Code Worksheet
Meiosis Worksheet Answer Key
Art Handouts and Worksheets
7 Elements of Art Worksheets
What is the rib cage?
The rib cage is a bony structure in the chest that protects vital organs such as the heart and lungs. It consists of 12 pairs of ribs, which are connected to the spine in the back and the sternum in the front, forming a protective cage around the thoracic cavity.
How many ribs are in the human rib cage?
There are typically 12 pairs of ribs in the human rib cage, making a total of 24 ribs.
What is the main function of the rib cage?
The main function of the rib cage is to protect the vital organs within the thoracic cavity, including the heart and lungs, from external trauma or injury. Additionally, the rib cage supports the upper body, assists in breathing by expanding and contracting with the diaphragm, and provides attachment points for muscles involved in respiration and upper body movement.
Which bones form the rib cage?
The rib cage is formed by the ribs, which connect to the thoracic vertebrae in the spine at the back and wrap around to the sternum at the front of the body. The rib cage also includes the costal cartilage that connects the ribs to the sternum.
How are the ribs connected to the spine?
The ribs are connected to the spine through the thoracic vertebrae, specifically through the facet joints where the ribs articulate with the vertebrae. There are 12 thoracic vertebrae, and each rib corresponds to a specific vertebra with the head of the rib articulating with the body of the vertebra and the tubercle of the rib articulating with the transverse process of the vertebra, forming a joint that allows for movement during respiration.
What is the sternum and what is its role in the rib cage?
The sternum, also known as the breastbone, is a flat bone located in the center of the chest. It plays a crucial role in the rib cage by providing a protective structure for the heart, lungs, and major blood vessels. The sternum also acts as an attachment point for several muscles that assist in breathing and movement of the arms and shoulders. Additionally, the sternum helps to stabilize and support the ribs, contributing to the overall structure and function of the rib cage.
What are the two main types of ribs?
The two main types of ribs are true ribs, which are attached directly to the sternum via cartilage, and false ribs, which are connected to the sternum indirectly or not at all. True ribs are ribs 1-7, while false ribs include ribs 8-12.
How are the true ribs different from the false ribs?
True ribs are directly attached to the sternum through their own costal cartilage, while false ribs do not attach directly to the sternum and their costal cartilage either attaches indirectly to the sternum or does not attach at all. Additionally, true ribs (ribs 1-7) are also called vertebrosternal ribs as they are connected to the thoracic vertebrae as well as the sternum, whereas false ribs (ribs 8-12) are also known as vertebrochondral (ribs 8-10) or floating (ribs 11-12) ribs due to their indirect or lack of connection to the sternum.
What is the purpose of the floating ribs?
The purpose of the floating ribs, also known as false ribs, is to help protect the internal organs in the lower chest and upper abdominal regions. They provide some degree of support and structure to these areas while still allowing for flexibility and movement during breathing and other bodily functions.
How does the rib cage protect vital organs?
The rib cage protects vital organs by forming a strong, bony structure that surrounds and encloses organs such as the heart, lungs, and liver. Its curved shape provides a rigid and protective barrier that helps absorb and distribute forces from impacts or compression, reducing the risk of injury to these crucial organs. Additionally, the rib cage also plays a role in supporting the overall structure of the chest and assisting in the process of respiration.
Have something to share?
Who is Worksheeto?
At Worksheeto, we are committed to delivering an extensive and varied portfolio of superior quality worksheets, designed to address the educational demands of students, educators, and parents.






















Comments