Respiratory System Worksheet Answer Key
The respiratory system is a complex network of organs and structures that play a crucial role in our everyday lives. From breathing in fresh air to exhaling carbon dioxide, understanding how this system works is essential for anyone studying biology or interested in learning more about the human body. If you're looking for a comprehensive and accurate answer key to a respiratory system worksheet, you've come to the right place. Our answer key will provide you with the entity and subject you need to successfully complete your worksheet.
Table of Images 👆
- Respiratory System Worksheet Answers
- The Respiratory System Fill in Blanks Worksheet Answers
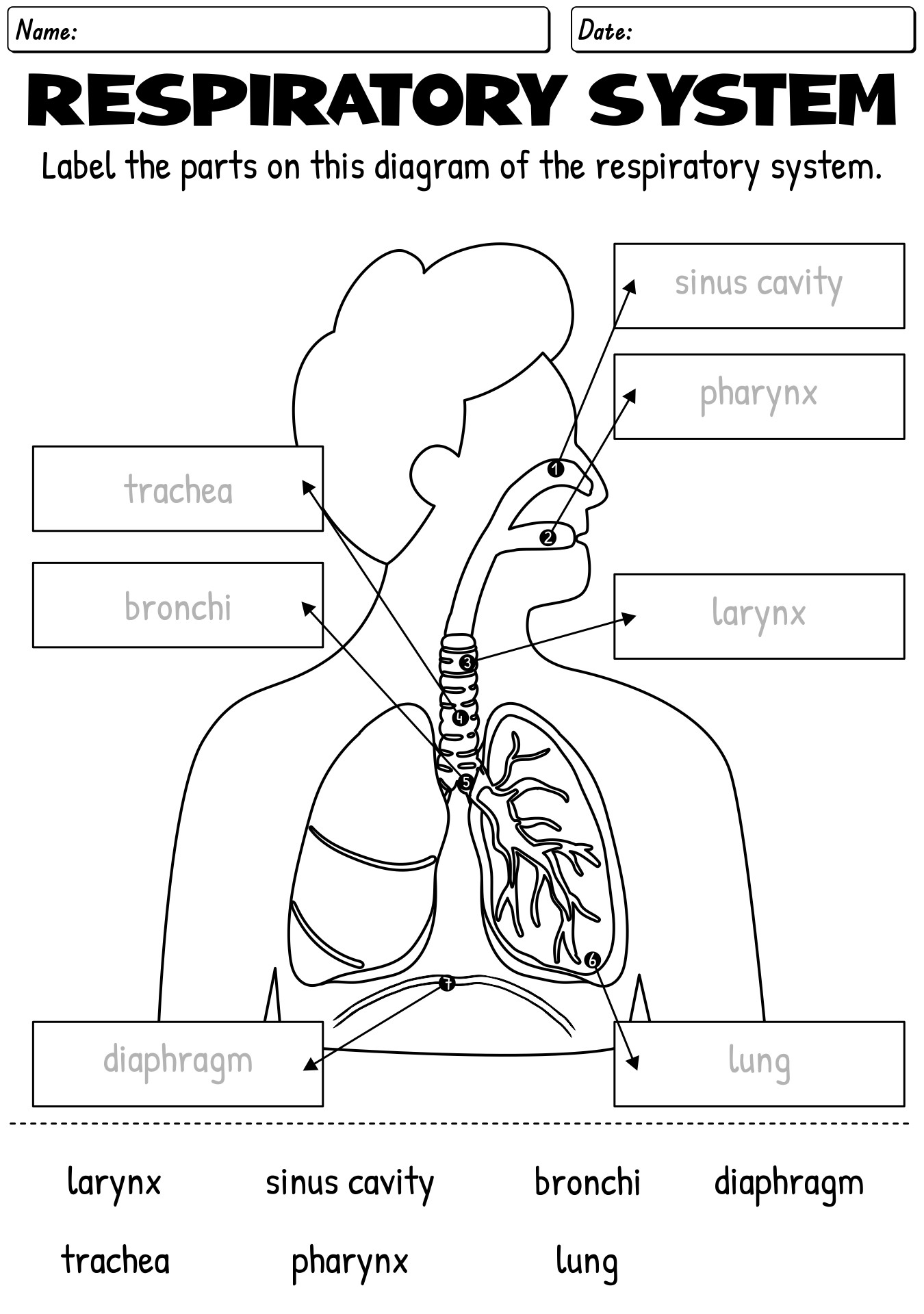
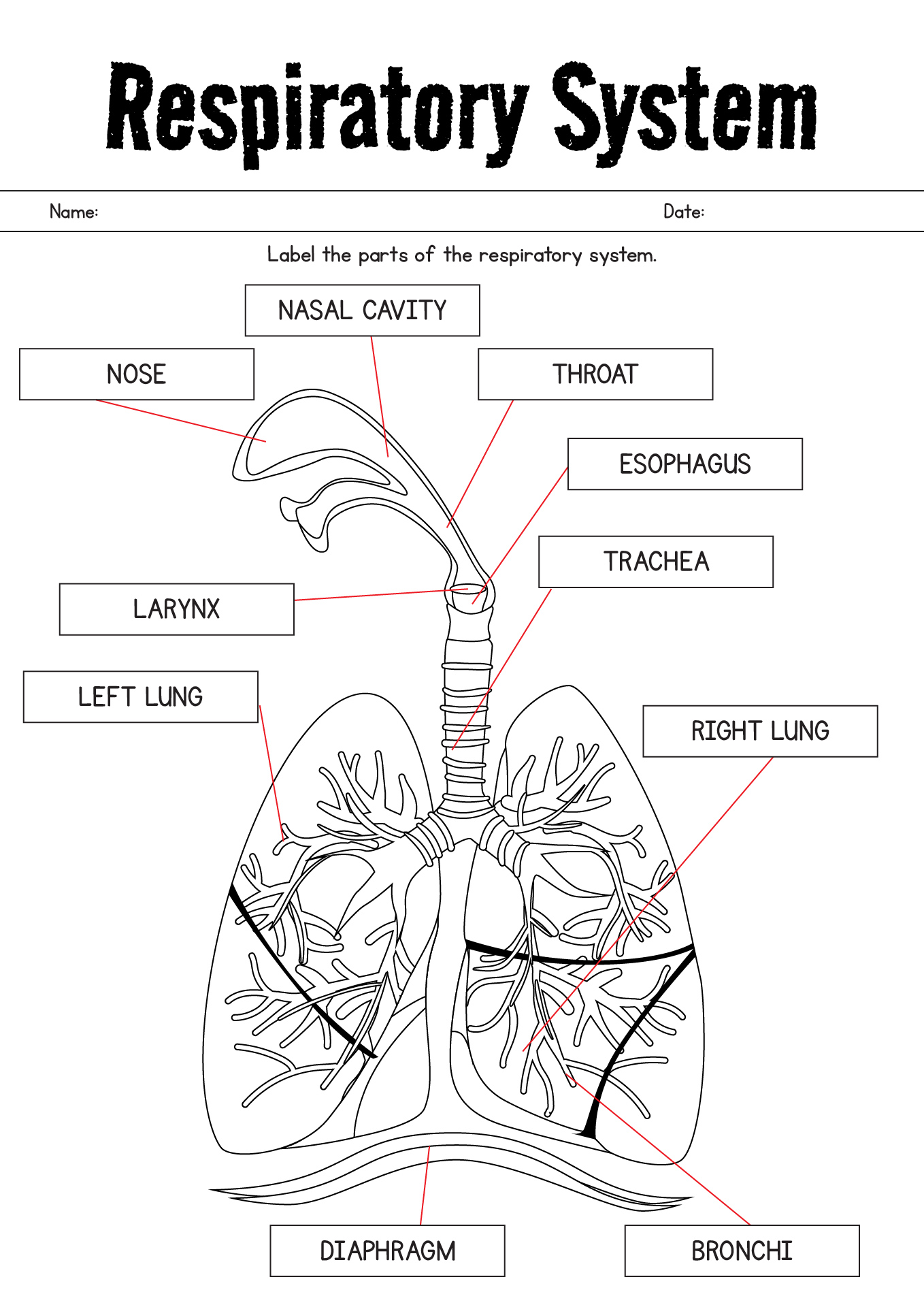
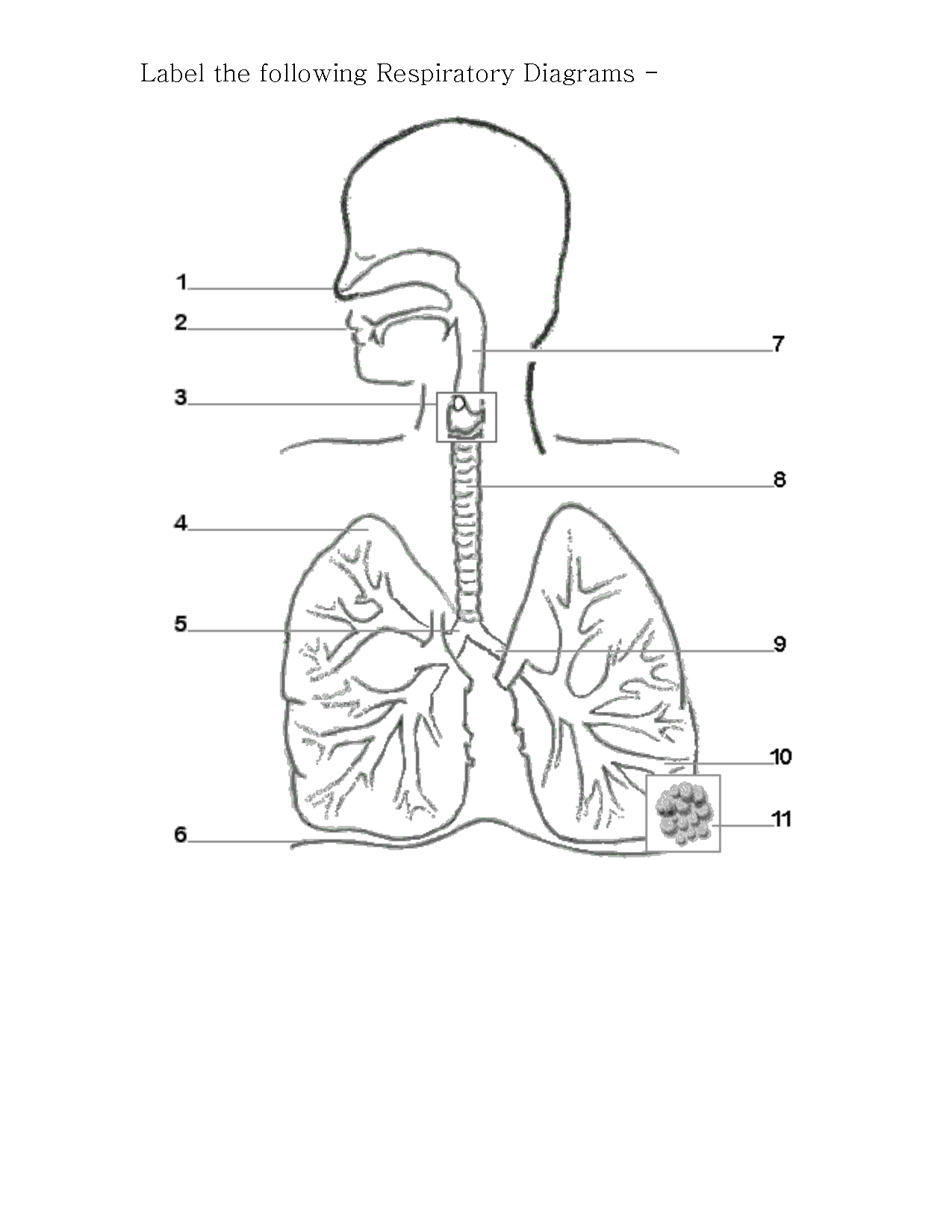
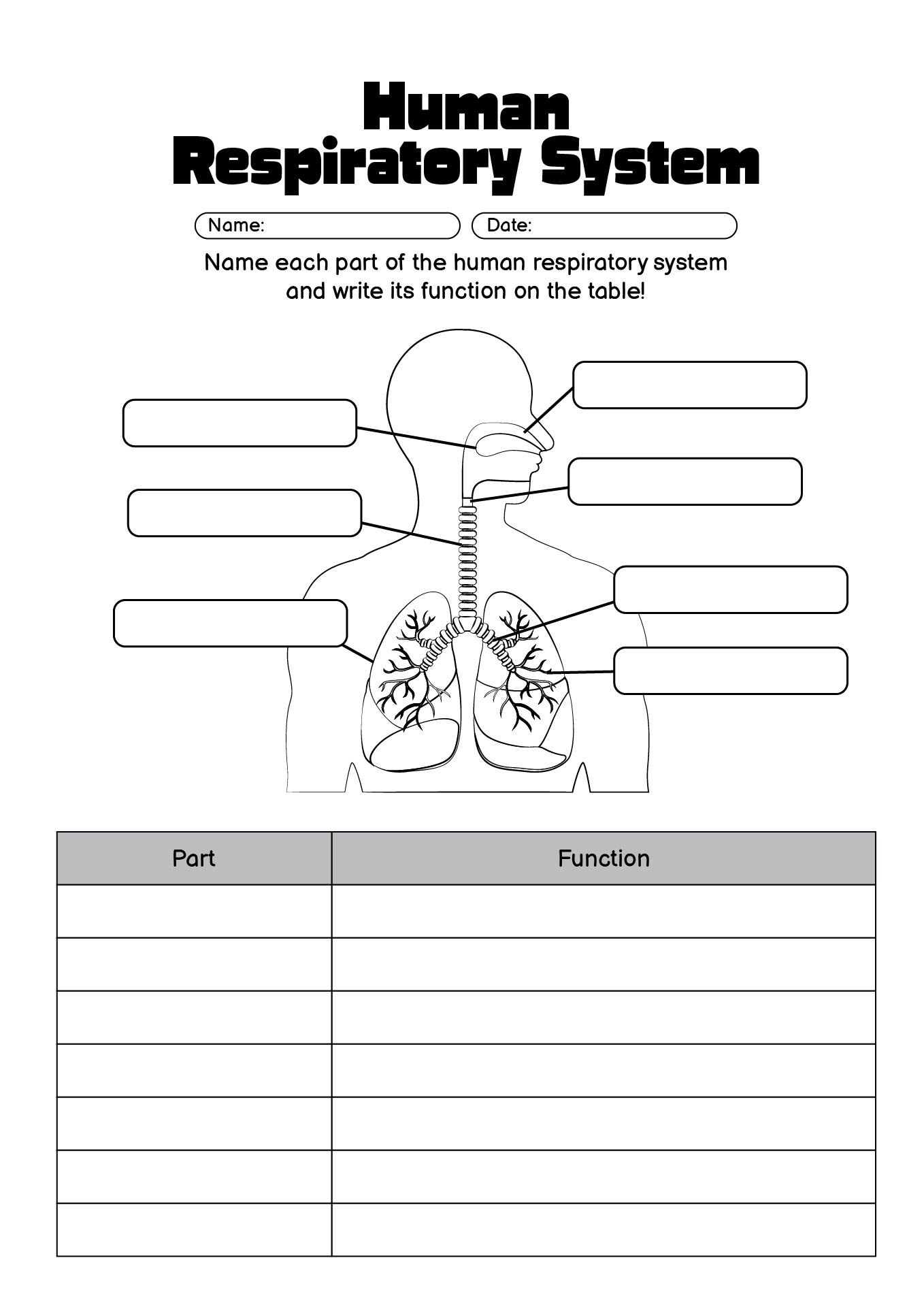
- Human Respiratory System Diagram Labeled
- Respiratory System Diagram Worksheet Answers
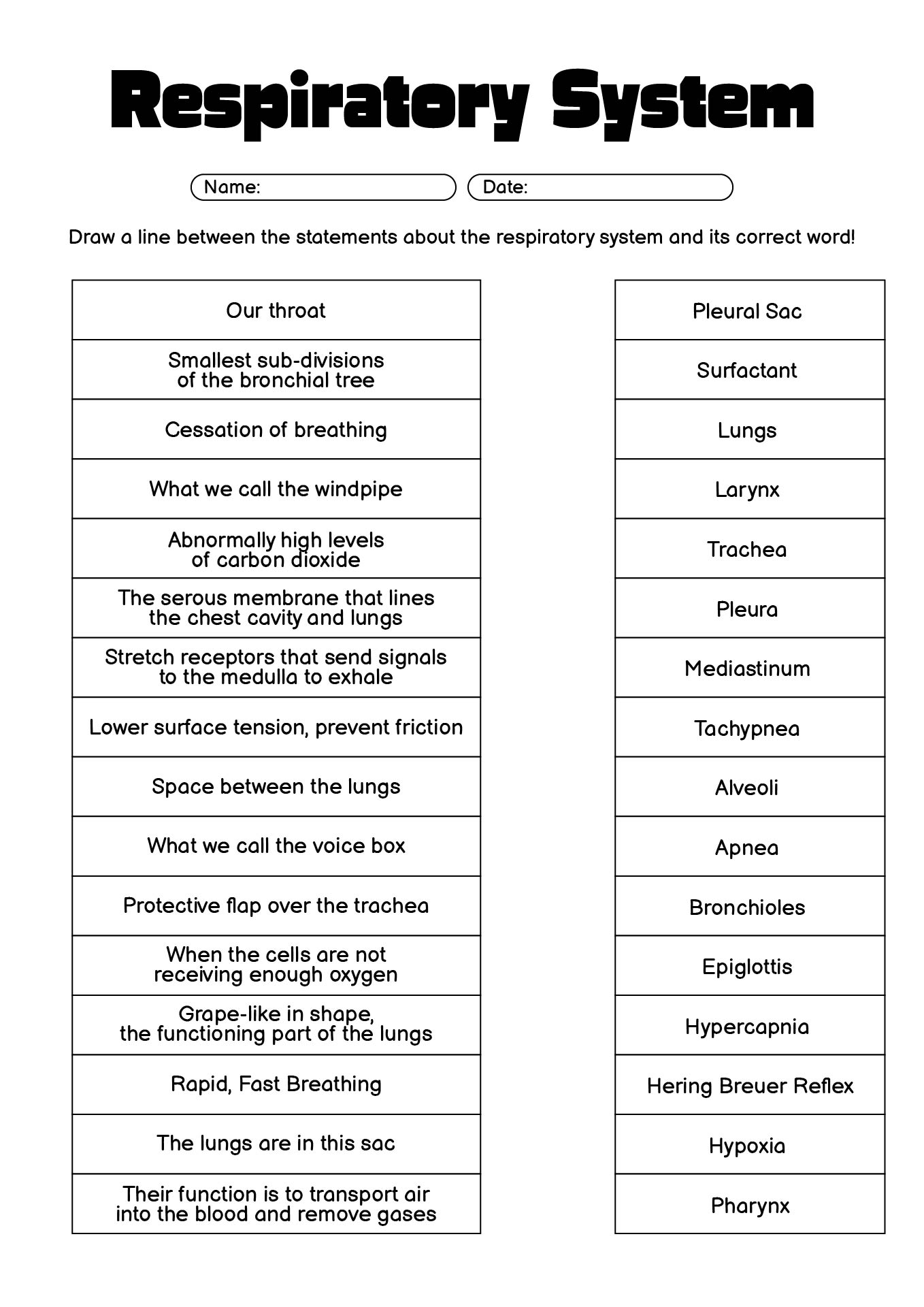
- Respiratory System Worksheet Answers
- Cellular Respiration Worksheet Answer Key
- Respiratory System Worksheets
- Respiratory System Worksheets
- Respiratory System Worksheet with Word Bank
- Respiratory System Worksheets
- Human Respiratory System Worksheet Key
- Respiratory Function Worksheet Answer Sheet
- Respiratory System Worksheet Solutions

More Other Worksheets
Kindergarten Worksheet My RoomSpanish Verb Worksheets
Cooking Vocabulary Worksheet
My Shadow Worksheet
Large Printable Blank Pyramid Worksheet
Relationship Circles Worksheet
DNA Code Worksheet
Meiosis Worksheet Answer Key
Art Handouts and Worksheets
7 Elements of Art Worksheets
What is the main function of the respiratory system?
The main function of the respiratory system is to facilitate the exchange of oxygen and carbon dioxide between the body and the environment through breathing. Oxygen is taken in during inhalation and is transported to the cells where it is used for cellular respiration, while carbon dioxide, a waste product of this process, is removed from the body through exhalation.
Which organs make up the respiratory system?
The organs that make up the respiratory system are the nose, pharynx, larynx, trachea, bronchi, and lungs.
What happens during the process of inhalation?
During inhalation, the diaphragm contracts and moves downward while the intercostal muscles between the ribs contract, causing the rib cage to expand. This increase in the volume of the chest cavity results in a decrease in air pressure within the lungs. As a result, air moves from outside the body into the lungs, filling them with oxygen to be used for cellular respiration.
What is the role of the diaphragm in breathing?
The diaphragm plays a crucial role in breathing by contracting and flattening when you inhale, creating a vacuum that pulls air into the lungs. This muscle separates the chest cavity (containing the lungs) from the abdominal cavity (containing organs like the stomach and liver), and its movement helps to increase the volume of the chest cavity, allowing the lungs to expand and fill with air. When you exhale, the diaphragm relaxes and returns to its dome shape, pushing air out of the lungs.
How does the oxygen in the air reach the lungs?
When you inhale, air enters through the nose or mouth and travels down the trachea (windpipe) into the lungs. Inside the lungs, the air passes through smaller tubes called bronchi and bronchioles until it reaches the tiny air sacs called alveoli. It is in the alveoli that the exchange of gases takes place, with oxygen passing from the air into the blood stream and carbon dioxide moving from the blood into the air to be exhaled.
What happens to the oxygen in the lungs?
In the lungs, oxygen is taken in during inhalation and diffuses across the walls of the alveoli into the surrounding capillaries. It then binds to red blood cells and is transported throughout the body to tissues and organs where it is used for energy production through cellular respiration.
What is the function of the alveoli in the respiratory system?
The alveoli are small air sacs in the lungs where gas exchange occurs. Oxygen from inhaled air enters the blood in the alveoli, while carbon dioxide is removed from the blood and exhaled out of the body. This process is essential for the body to obtain oxygen for cellular functions and to eliminate carbon dioxide, a waste product of metabolism.
How does the exchange of gases occur in the alveoli?
The exchange of gases in the alveoli occurs through diffusion. Oxygen from the air in the alveoli passes through the alveolar walls and enters the bloodstream, binding to hemoglobin in red blood cells. At the same time, carbon dioxide from the bloodstream diffuses out of the capillaries and into the alveoli to be exhaled. This process is facilitated by the thin walls of the alveoli and the dense network of capillaries surrounding them, allowing for efficient exchange of oxygen and carbon dioxide between the lungs and the bloodstream.
What is the importance of the respiratory system in maintaining pH balance in the body?
The respiratory system helps in maintaining pH balance in the body by regulating the levels of carbon dioxide (CO2) in the blood. When we breathe, we exhale CO2, which is a waste product of cellular respiration. If CO2 levels increase in the blood, it forms carbonic acid, leading to a decrease in pH and causing acidosis. The lungs help to rid the body of excess CO2, thus preventing acidosis and helping to maintain a proper pH balance in the blood.
How does the respiratory system help in removing waste products from the body?
The respiratory system helps in removing waste products from the body by expelling carbon dioxide, a byproduct of metabolism, during the process of exhalation. This waste gas is carried from the blood into the lungs, where it is released into the air when we breathe out. By removing carbon dioxide from the body, the respiratory system helps to maintain the body's acid-base balance and overall health.
Have something to share?
Who is Worksheeto?
At Worksheeto, we are committed to delivering an extensive and varied portfolio of superior quality worksheets, designed to address the educational demands of students, educators, and parents.


























Comments