Protein Synthesis Practice Worksheet
Protein synthesis is a fundamental process in biology that involves the creation of new proteins within our cells. For students and individuals seeking to reinforce their understanding of this intricate process, a protein synthesis practice worksheet can be an invaluable tool. This particular worksheet focuses on the entity of protein synthesis and provides subject-specific questions and exercises to enhance comprehension.
Table of Images 👆
- Protein Synthesis Worksheet Answer Key
- DNA Protein Synthesis Worksheet Answers
- Protein Synthesis Worksheet Answers
- Protein Synthesis Worksheet Answers
- DNA and RNA Protein Synthesis Worksheet Answers
- Protein Synthesis Worksheet Answer Key
- RNA and Protein Synthesis Answers
- Transcription and Translation Practice Worksheet
- Protein Synthesis Practice 1 Worksheet Answers
- Protein Synthesis Worksheet DNA and RNA
- DNA Structure and Replication Worksheet Answer Key
- Protein Synthesis Worksheet
- DNA and Protein Synthesis Worksheet Answers
- Protein Synthesis Worksheet Answers
- Protein Synthesis Transcription and Translation Worksheet
- Transcription Translation Worksheet Answer Key
- Transcription and Translation Worksheet Answers
More Other Worksheets
Kindergarten Worksheet My RoomSpanish Verb Worksheets
Cooking Vocabulary Worksheet
My Shadow Worksheet
Large Printable Blank Pyramid Worksheet
Relationship Circles Worksheet
DNA Code Worksheet
Meiosis Worksheet Answer Key
Art Handouts and Worksheets
7 Elements of Art Worksheets
What is protein synthesis?
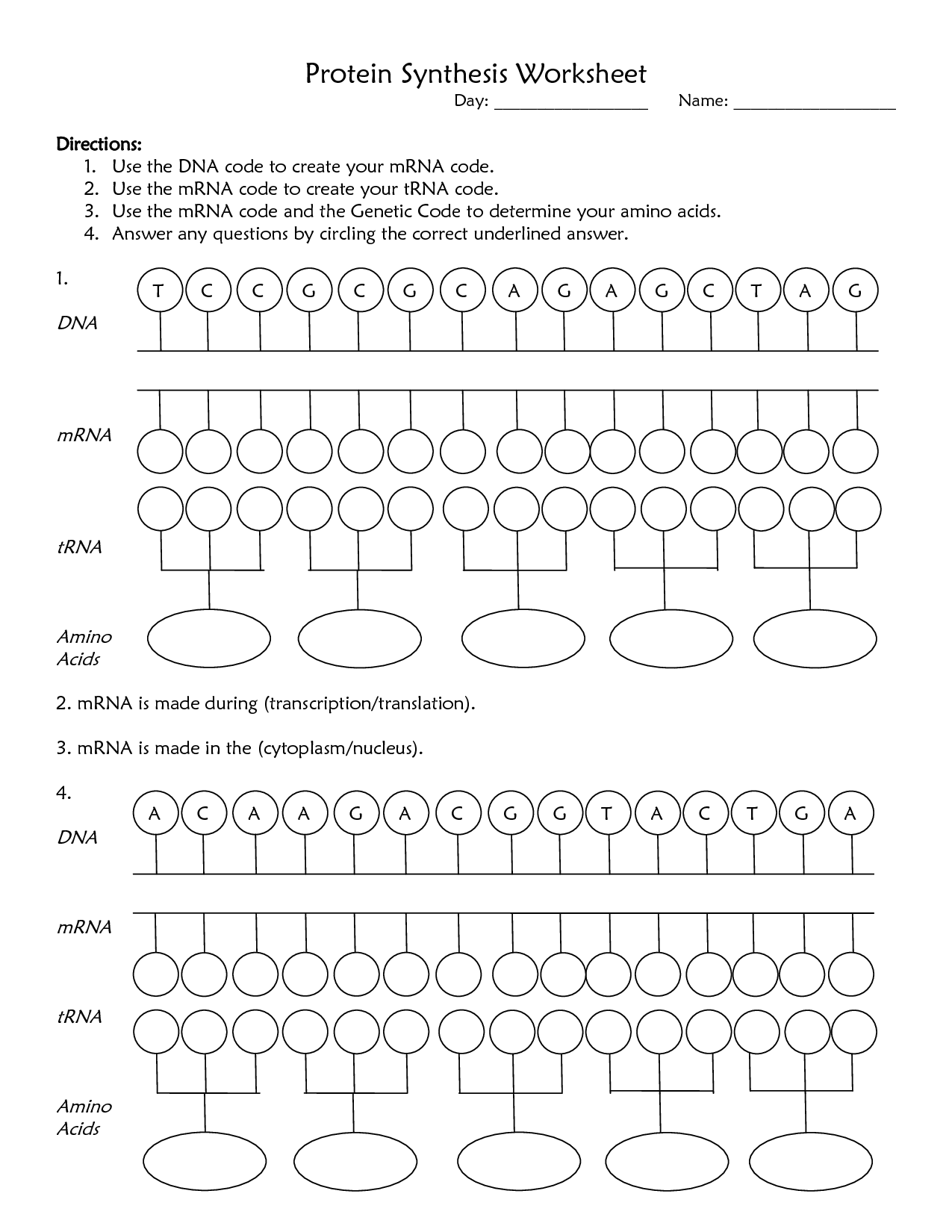
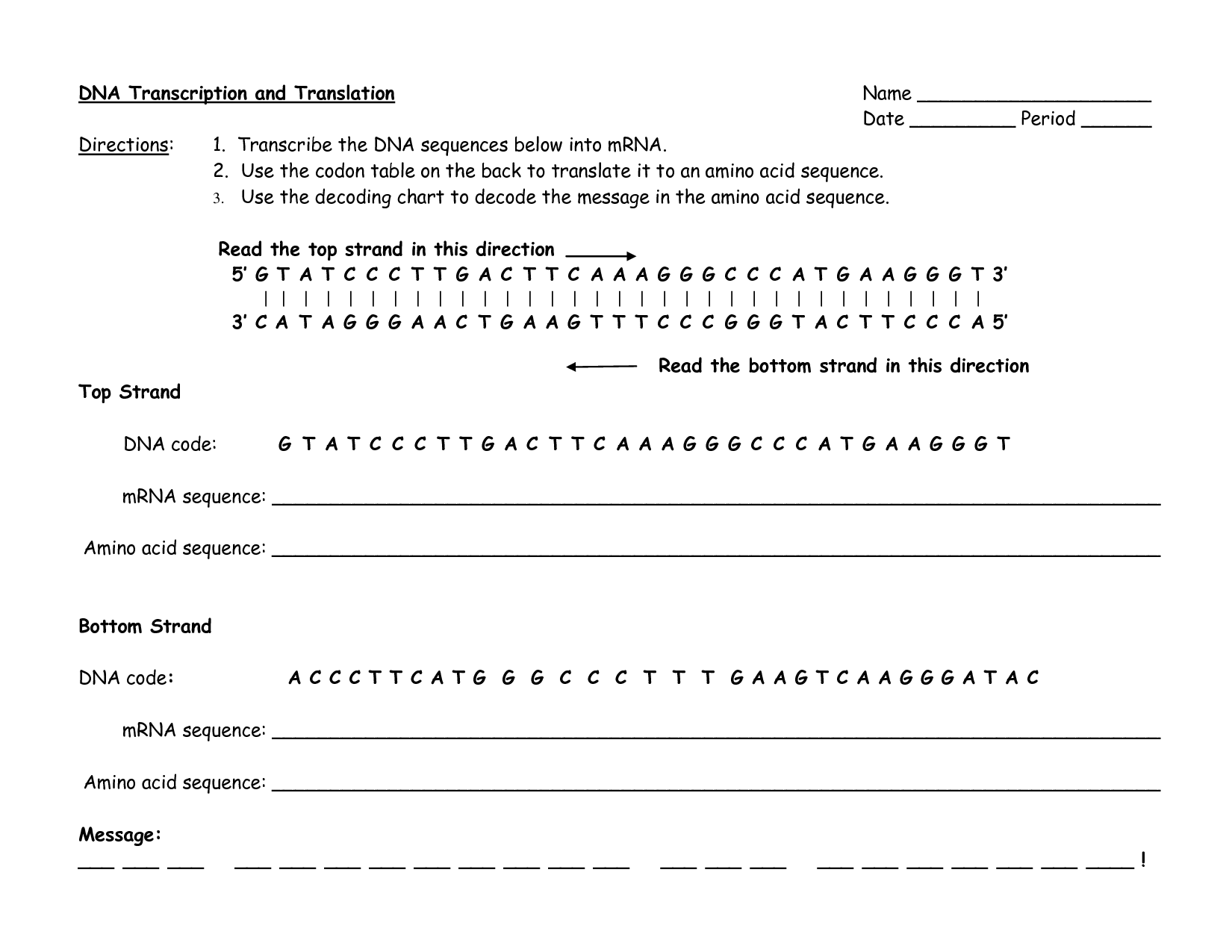
Protein synthesis is the process by which cells build proteins using instructions encoded in the DNA. It involves two main phases: transcription, where a gene's DNA sequence is copied into a messenger RNA (mRNA) molecule, and translation, where the mRNA is used as a template to assemble amino acids into a protein. This complex process is essential for the growth, repair, and functioning of the body.
What are the two main stages of protein synthesis?
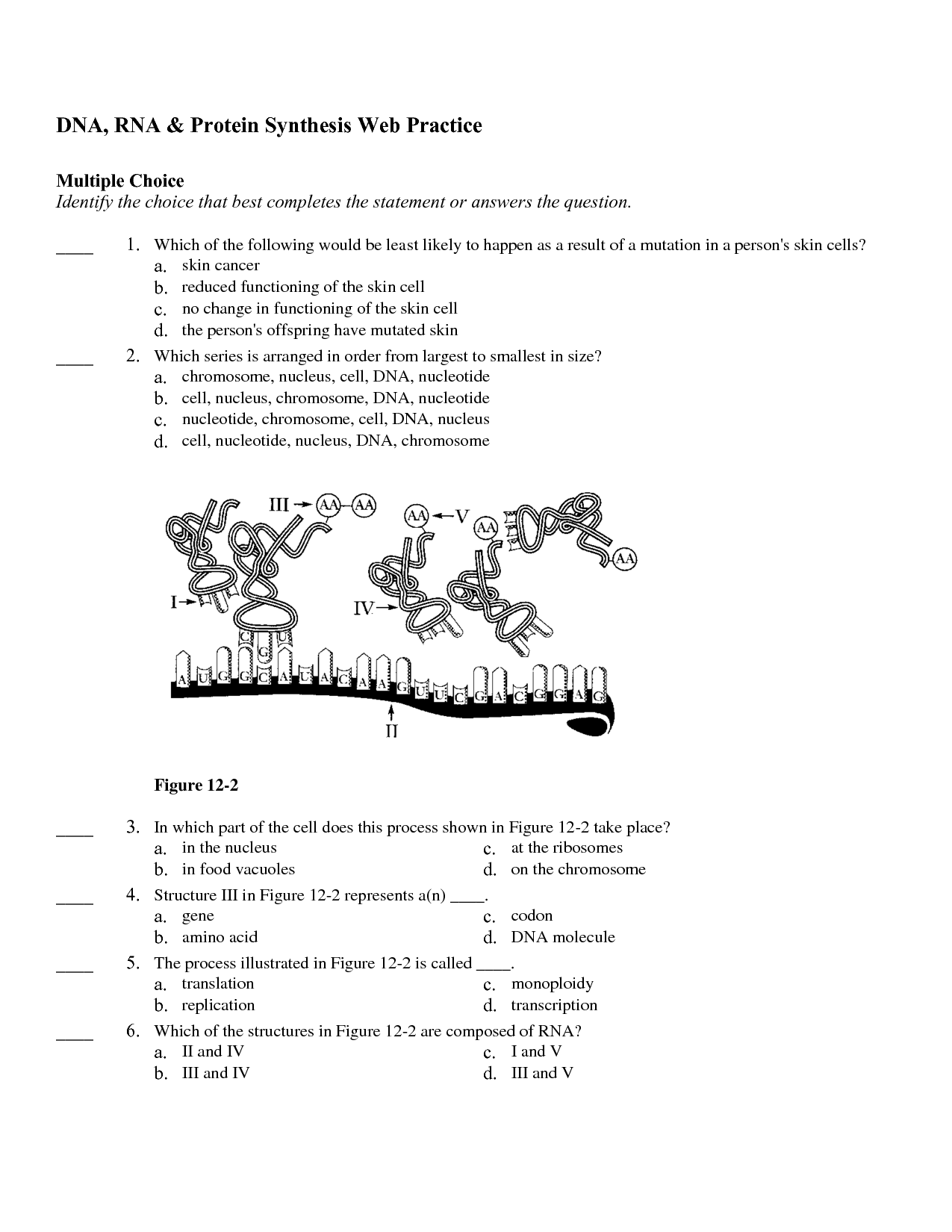
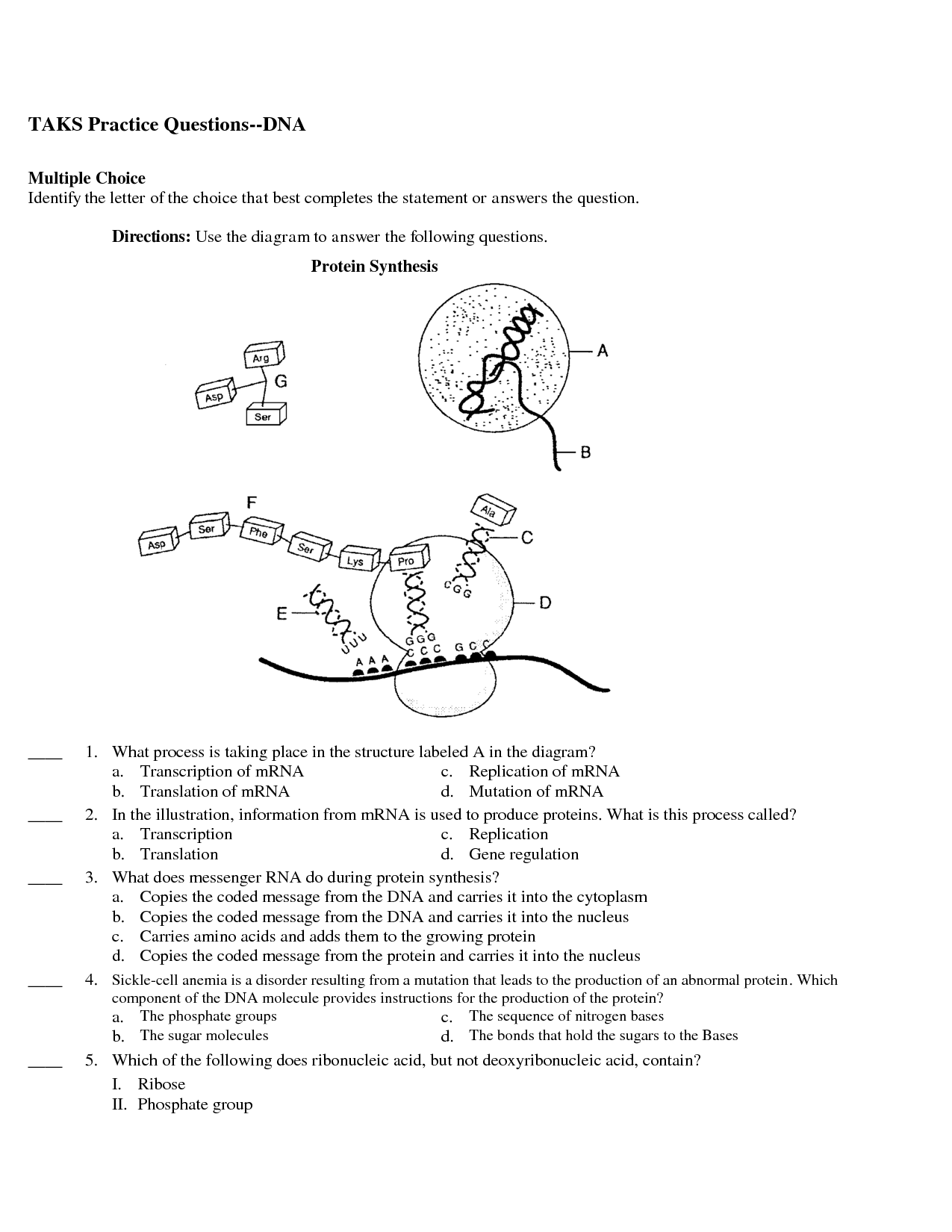
The two main stages of protein synthesis are transcription and translation. Transcription occurs in the nucleus where a complementary mRNA strand is synthesized from a template DNA strand. This mRNA strand then moves to the ribosome where translation takes place, during which the mRNA is read in codons and tRNA molecules bring in amino acids to build the protein as per the mRNA instructions.
Where does transcription occur in a eukaryotic cell?
Transcription occurs in the cell nucleus of a eukaryotic cell. It is the process where the genetic information stored in DNA is transcribed into messenger RNA (mRNA) by RNA polymerase enzymes. The mRNA molecule then leaves the nucleus and serves as a template for protein synthesis in the cytoplasm.
What is the purpose of transcription in protein synthesis?
The purpose of transcription in protein synthesis is to transcribe the genetic information encoded in the DNA into messenger RNA (mRNA). This process is essential because mRNA serves as a template for protein synthesis in the ribosomes. Therefore, transcription is a crucial step in the central dogma of molecular biology, where the information contained in the DNA is ultimately translated into functional proteins.
What is the role of messenger RNA (mRNA) in protein synthesis?
Messenger RNA (mRNA) plays a crucial role in protein synthesis by carrying genetic information from the DNA in the cell's nucleus to the ribosomes in the cytoplasm. The mRNA molecule is transcribed from a specific gene and then serves as a template for the ribosomes to translate the genetic code into a specific sequence of amino acids, which ultimately results in the synthesis of a protein according to the instructions encoded in the DNA. This process of mRNA translation is a key step in the central dogma of molecular biology, where genetic information is transferred from DNA to RNA to protein.
What happens during translation in protein synthesis?
During translation in protein synthesis, mRNA is decoded by ribosomes to produce a specific amino acid sequence that forms a protein. Transfer RNA (tRNA) molecules bring the corresponding amino acids to the ribosome, where they are joined together to form a polypeptide chain. This process occurs in the ribosomes and continues until a stop codon is reached, signaling the end of protein synthesis.
Where does translation occur in a eukaryotic cell?
Translation occurs in the cytoplasm of a eukaryotic cell. It is the process where messenger RNA (mRNA) is decoded by ribosomes to produce a specific protein. The ribosomes read the mRNA sequence and assemble the corresponding amino acids to form a protein in the cytoplasm of the cell.
What is the function of transfer RNA (tRNA) in protein synthesis?
Transfer RNA (tRNA) plays a crucial role in protein synthesis by bringing specific amino acids to the ribosome during translation. Each tRNA molecule carries a specific amino acid at one end and has a complementary anticodon sequence at the other end, which base pairs with the mRNA codon. This enables tRNA to accurately deliver the correct amino acid to the growing polypeptide chain according to the codons on the mRNA, facilitating the assembly of proteins with the correct sequence of amino acids.
What is a codon and how does it relate to protein synthesis?
A codon is a sequence of three nucleotides in DNA or RNA that codes for a specific amino acid or a stop signal during protein synthesis. During translation, tRNA molecules bind to complementary codons on the mRNA strand, bringing the corresponding amino acids to the ribosome. This process repeats, linking amino acids together to form a polypeptide chain that ultimately folds into a functional protein. The sequence of codons determines the order in which amino acids are added to the growing protein, playing a crucial role in determining the final structure and function of the protein being synthesized.
How does the process of protein synthesis contribute to cellular functioning and overall organismal health?
Protein synthesis is essential for cellular functioning and overall organismal health because proteins are crucial for almost all biological processes. Proteins perform various functions in cells, such as enzyme catalysis, cell signaling, structural support, transport of molecules, and immune response. Without proper protein synthesis, cells would not be able to carry out these vital functions, leading to cellular dysfunction and ultimately impacting the health of the entire organism. Thus, protein synthesis plays a foundational role in maintaining the integrity and functionality of cells, tissues, and organs, ultimately contributing to overall organismal health.
Have something to share?
Who is Worksheeto?
At Worksheeto, we are committed to delivering an extensive and varied portfolio of superior quality worksheets, designed to address the educational demands of students, educators, and parents.































Comments