Protein Synthesis Diagram Worksheet
A protein synthesis diagram worksheet provides an essential tool for biology students to comprehend and visualize the complex process of protein synthesis. By breaking down the steps and components, this worksheet becomes an effective learning resource for high school and college students who are studying molecular biology or genetics. With this worksheet, students can gain a deeper understanding of the entities involved in protein synthesis and the roles they play, allowing them to grasp this fundamental concept with clarity.
Table of Images 👆
- Protein Synthesis Worksheet Answer Key
- DNA Mutations Practice Worksheet Answer Key
- Protein Synthesis Worksheet Answer Key
- Protein Synthesis Worksheet
- DNA Protein Synthesis Worksheet Answers
- DNA Protein Synthesis Worksheet Answers
- DNA Protein Synthesis Diagram
- DNA and Protein Synthesis Worksheet Answers
- DNA Transcription and Translation Diagram
- DNA and RNA Protein Synthesis Worksheet Answers
- Protein Synthesis Worksheet Answers
More Other Worksheets
Kindergarten Worksheet My RoomSpanish Verb Worksheets
Cooking Vocabulary Worksheet
My Shadow Worksheet
Large Printable Blank Pyramid Worksheet
Relationship Circles Worksheet
DNA Code Worksheet
Meiosis Worksheet Answer Key
Art Handouts and Worksheets
7 Elements of Art Worksheets
What is the purpose of protein synthesis?
Protein synthesis is a crucial process in living organisms that involves the production of proteins, which are essential for various biological functions. Proteins serve as building blocks for cells, tissues, and organs, contribute to the structure and function of enzymes, hormones, antibodies, and other molecules, and are involved in numerous physiological processes such as growth, repair, and regulation of bodily functions. Therefore, the primary purpose of protein synthesis is to create proteins that are necessary for the structure, function, and regulation of the body.
What are the two main steps involved in protein synthesis?
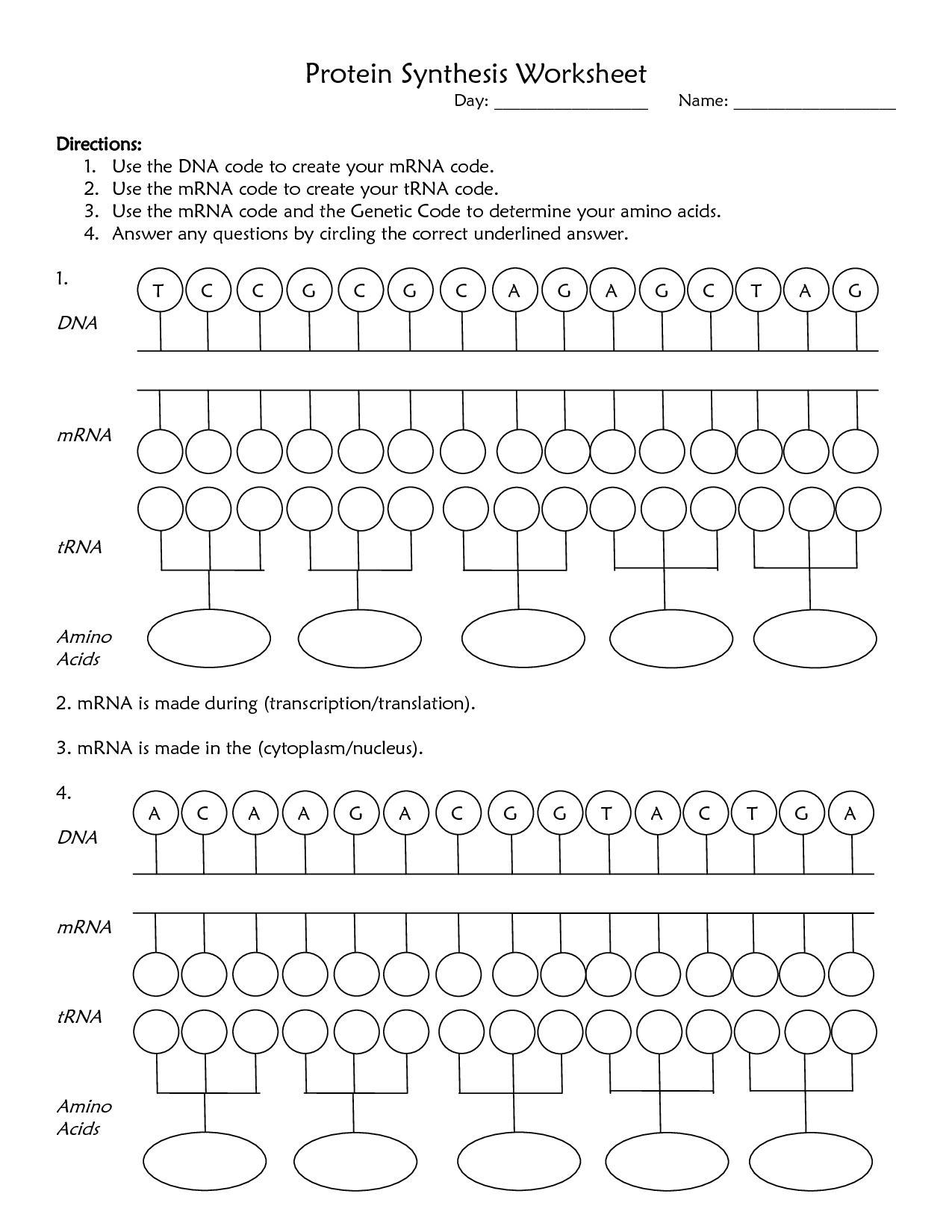
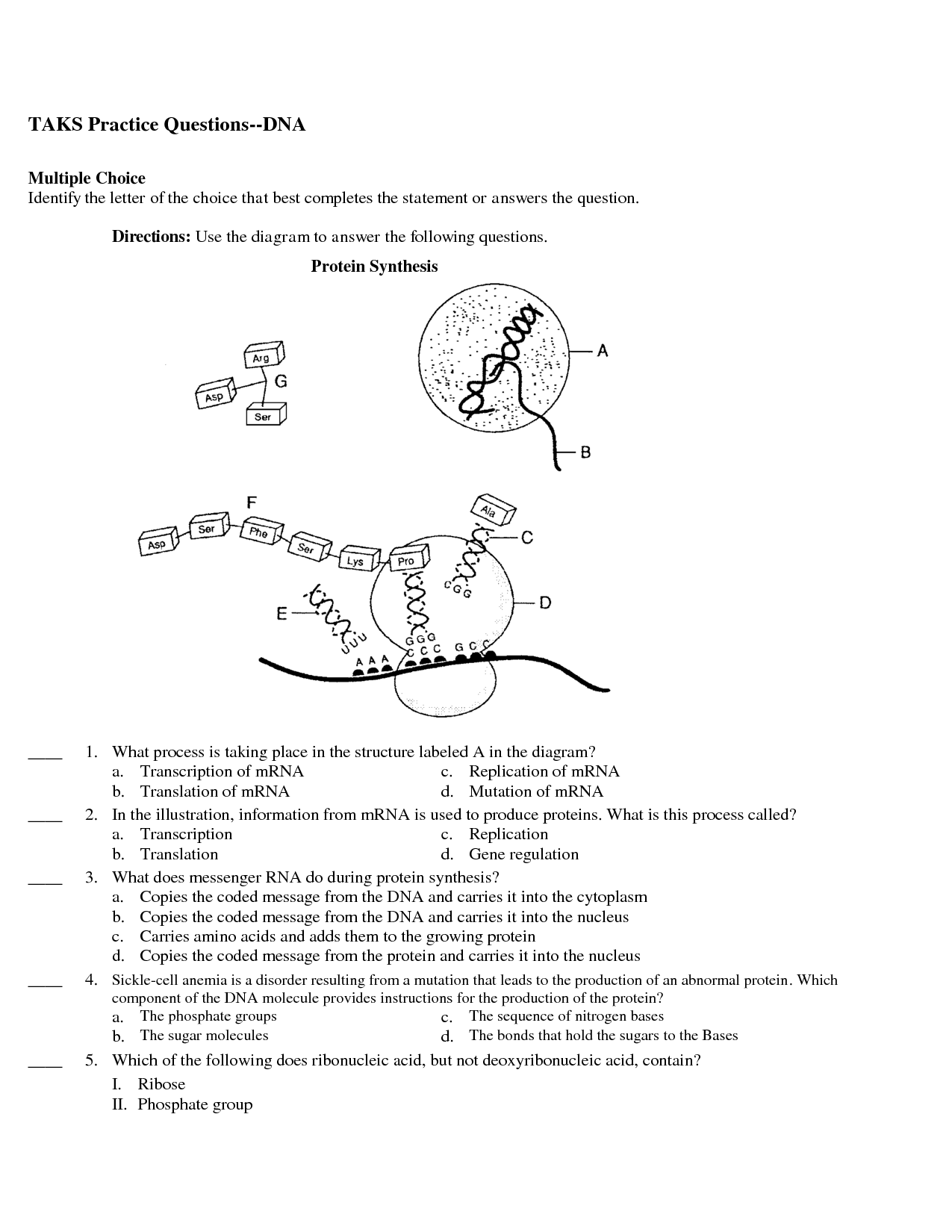
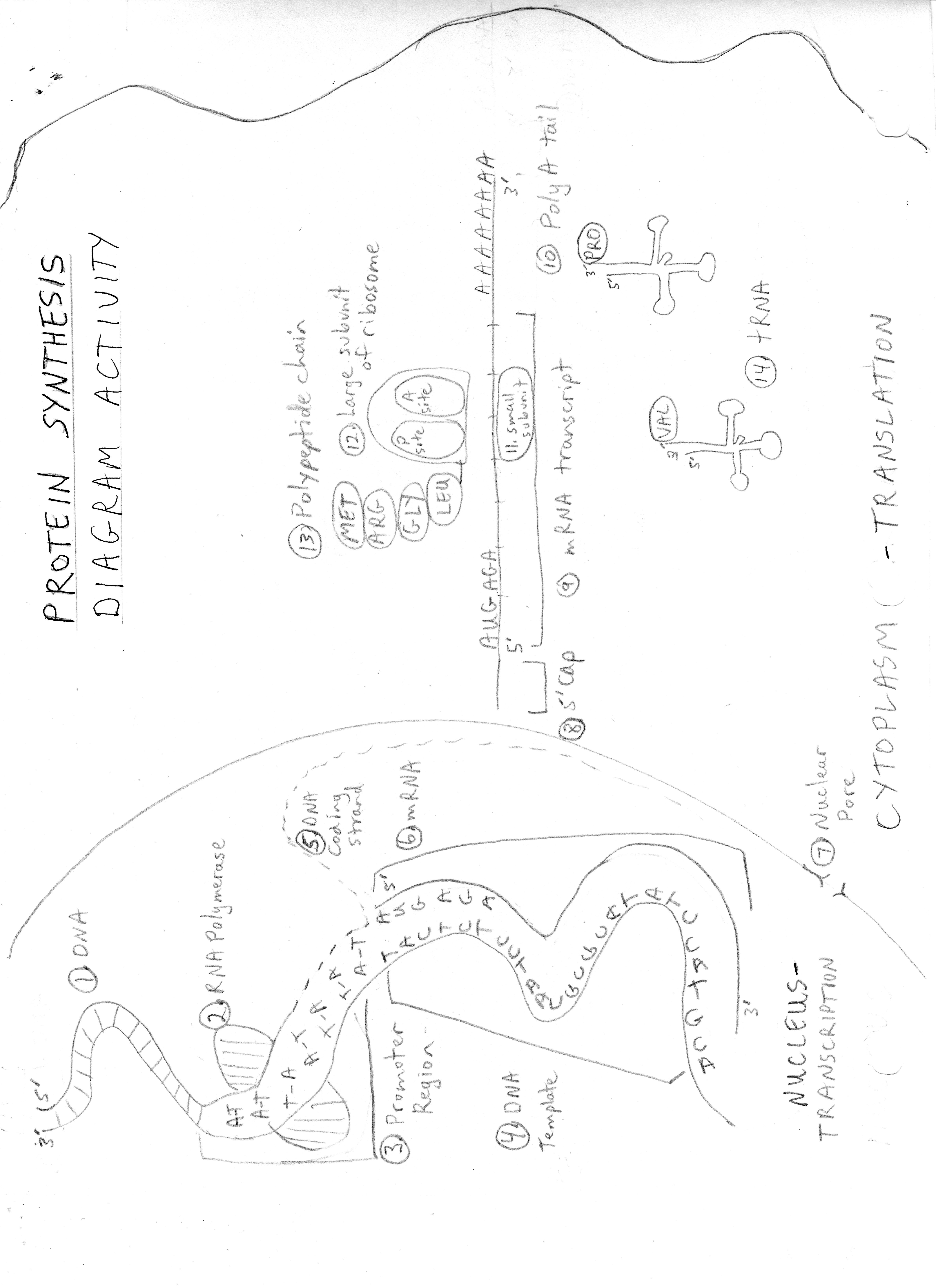
The two main steps involved in protein synthesis are transcription and translation. During transcription, the genetic information in DNA is copied into mRNA in the nucleus of a cell. This mRNA then moves to the cytoplasm where translation occurs, where ribosomes read the mRNA sequence and use it to assemble amino acids into a specific protein according to the genetic code.
Where does protein synthesis occur in a eukaryotic cell?
Protein synthesis in a eukaryotic cell occurs in the cytoplasm. It starts with the transcribing of DNA into messenger RNA (mRNA) in the cell's nucleus, which is then transported to the cytoplasm where it is translated by ribosomes to synthesize proteins.
What is the role of messenger RNA (mRNA) in protein synthesis?
Messenger RNA (mRNA) plays a crucial role in protein synthesis by carrying the genetic information from the DNA in the cell's nucleus to the ribosomes, the protein-building machinery of the cell. The sequence of nucleotides in the mRNA is translated into a specific sequence of amino acids, which ultimately determines the protein's structure and function. By serving as a template for protein synthesis, mRNA bridges the gap between the genetic code stored in the DNA and the actual production of proteins in the cell.
What is the function of transfer RNA (tRNA) in protein synthesis?
Transfer RNA (tRNA) plays a crucial role in protein synthesis by carrying amino acids to the ribosome, where the amino acids are linked together to form a protein chain. Each tRNA molecule has an anticodon that is complementary to a specific codon on the mRNA, allowing the correct amino acid to be brought to the ribosome during translation. This process ensures that the correct sequence of amino acids is incorporated into the growing protein chain, ultimately determining the structure and function of the protein being synthesized.
What are the codons and anticodons in protein synthesis?
In protein synthesis, codons are the three-nucleotide sequences in mRNA that correspond to specific amino acids. Anticodons, on the other hand, are the three-nucleotide sequences in tRNA that complement the codons on the mRNA during translation. The pairing between codons and anticodons ensures that the correct amino acid is added to the growing polypeptide chain.
What is the significance of ribosomes in protein synthesis?
Ribosomes are essential cellular organelles responsible for translating genetic information stored in mRNA into proteins. They play a crucial role in protein synthesis by catalyzing the assembly of amino acids into polypeptide chains according to the sequence specified by the mRNA. Ribosomes act as the site where tRNA molecules bring the correct amino acids to be joined together, ultimately leading to the synthesis of functional proteins that are crucial for various cellular processes and functions in organisms.
How is the process of transcription different from translation in protein synthesis?
Transcription is the process of creating an mRNA molecule from a DNA template, while translation is the process of synthesizing proteins from the mRNA code. In transcription, the enzyme RNA polymerase binds to the DNA and creates a complementary mRNA strand, whereas in translation, ribosomes read the mRNA codons and assemble amino acids into a protein. Transcription occurs in the nucleus, while translation takes place in the ribosomes in the cytoplasm.
What is the role of ribosomal RNA (rRNA) in protein synthesis?
Ribosomal RNA (rRNA) plays a crucial role in protein synthesis by serving as a structural and functional component of ribosomes. Within ribosomes, rRNA helps in the assembly of amino acids into proteins by providing the site where messenger RNA (mRNA) is decoded and peptide bonds between amino acids are formed. This process occurs during the translation phase of protein synthesis, where ribosomes move along the mRNA strand to generate the specific sequence of amino acids that form a protein.
What is the importance of protein synthesis in cellular functioning?
Protein synthesis is crucial for cellular functioning as proteins are essential molecules that perform a wide variety of functions within the cell. Proteins are involved in almost every process within cells, such as cell structure, signaling, transport, and enzymatic reactions. Without protein synthesis, cells would not be able to repair themselves, grow, or carry out the tasks necessary for survival. Therefore, the importance of protein synthesis lies in the fact that it is essential for the proper functioning and maintenance of cells and overall biological processes in living organisms.
Have something to share?
Who is Worksheeto?
At Worksheeto, we are committed to delivering an extensive and varied portfolio of superior quality worksheets, designed to address the educational demands of students, educators, and parents.

























Comments