Profile of a Wave Worksheet
If you're searching for a comprehensive and engaging resource to help students grasp the concept of waves, then the Profile of a Wave Worksheet is your ideal solution. Designed with middle and high school students in mind, this worksheet provides a clear and concise overview of the various components and characteristics of waves.
Table of Images 👆
- Sound Wave Worksheet Answer
- Labeling Waves Worksheet Answer Key
- Sound Wave Worksheet Answer
- Waves Worksheet Answer Key
- Mechanical Waves Worksheet
- Labeling Waves Worksheet Answer Key
- Sound Waves Worksheet
- Waves Worksheet Answer Key
- Waves Worksheet Answer Key
- Sound Waves Worksheet
- Waves and Electromagnetic Spectrum Worksheet Answers
- Waves and Electromagnetic Spectrum Worksheet Answers
- Standing Waves Worksheet Answers
More Other Worksheets
Kindergarten Worksheet My RoomSpanish Verb Worksheets
Healthy Eating Plate Printable Worksheet
Cooking Vocabulary Worksheet
My Shadow Worksheet
Large Printable Blank Pyramid Worksheet
Relationship Circles Worksheet
DNA Code Worksheet
Meiosis Worksheet Answer Key
Rosa Parks Worksheet Grade 1
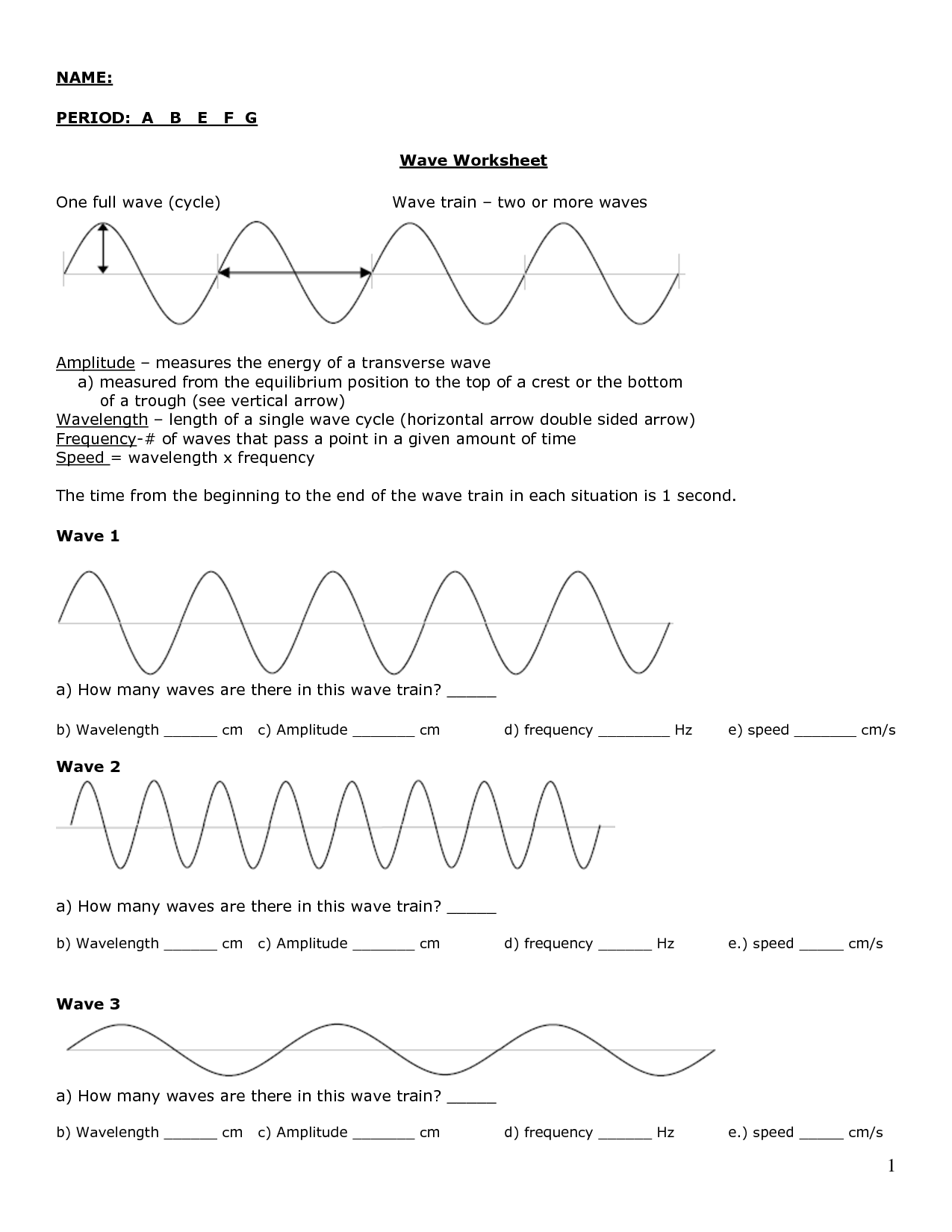
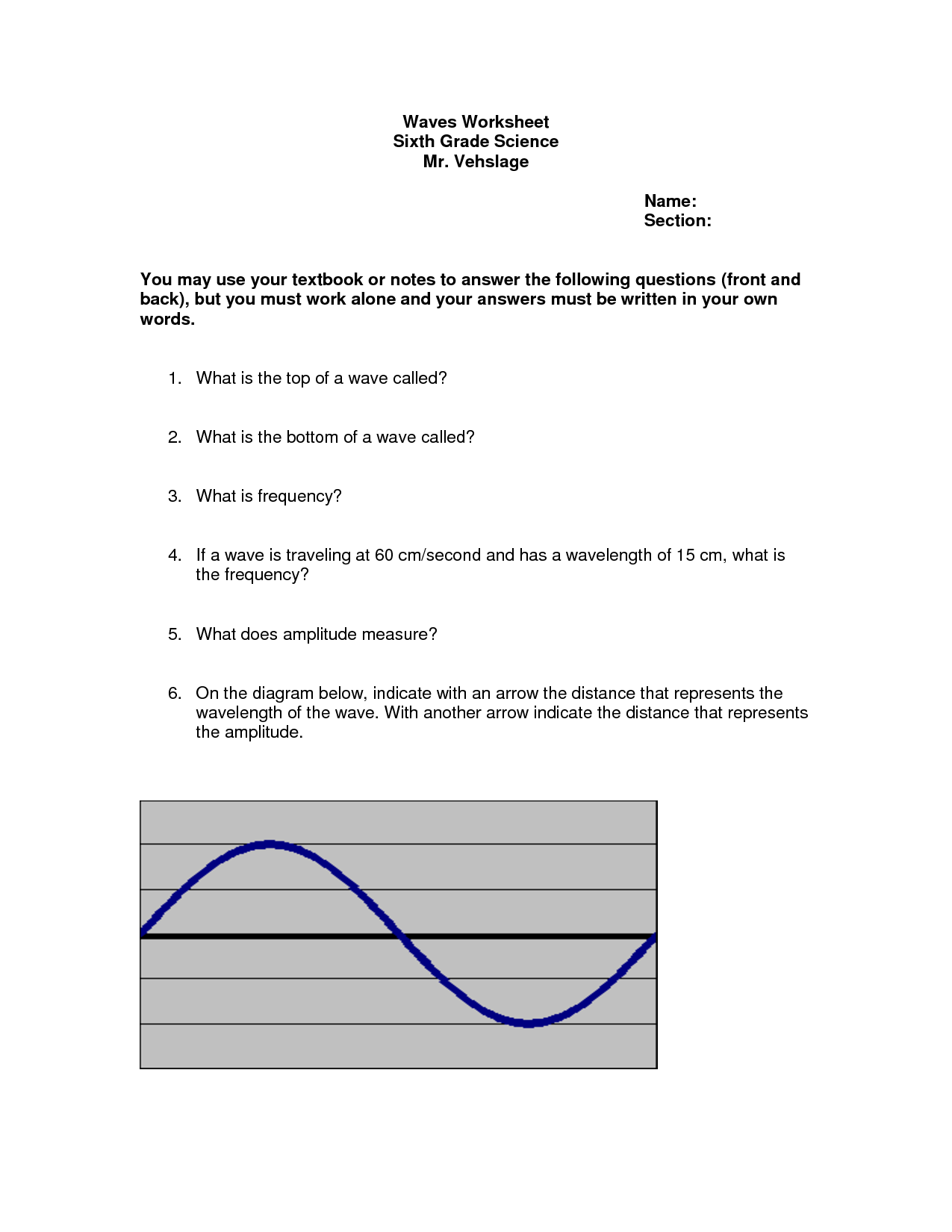
What is the profile of a wave?
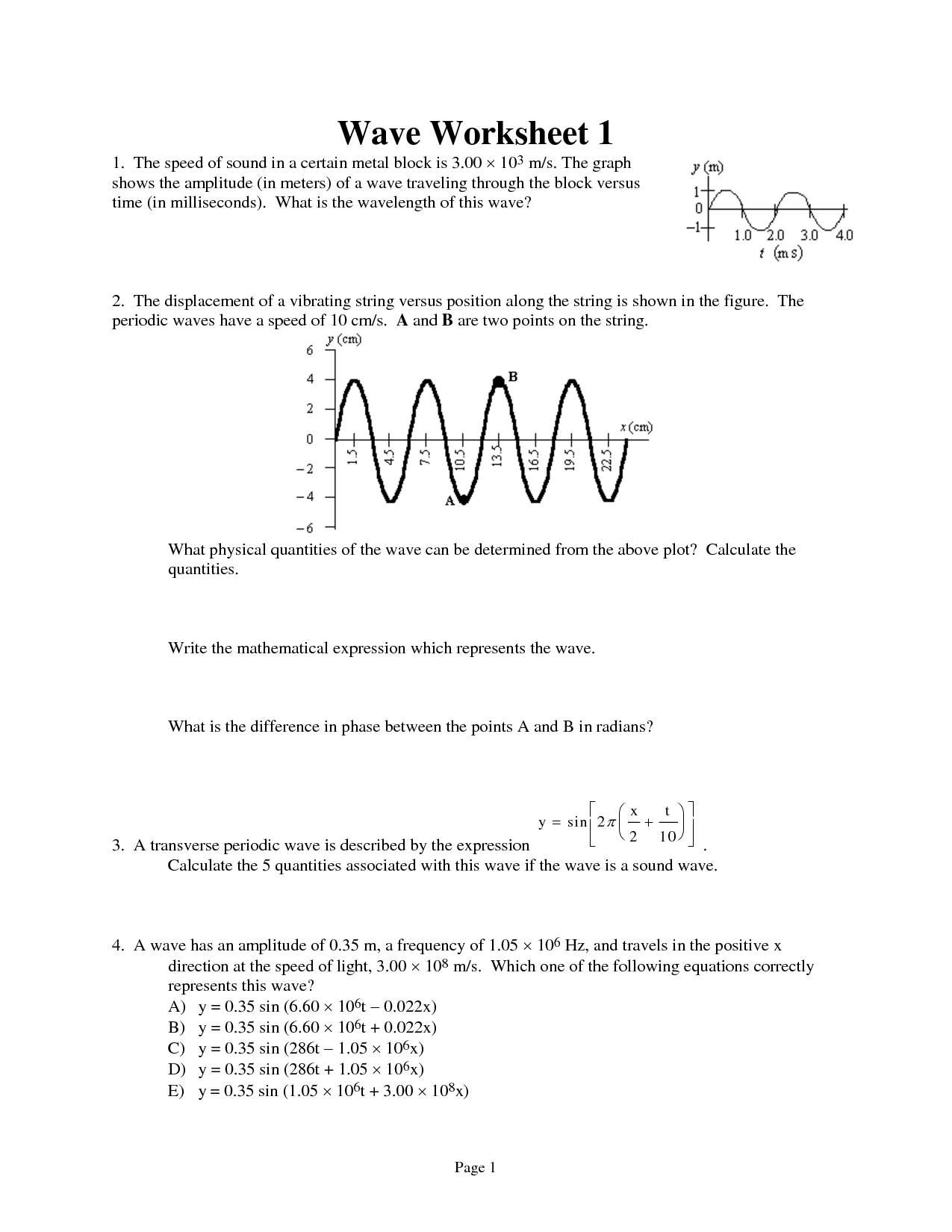
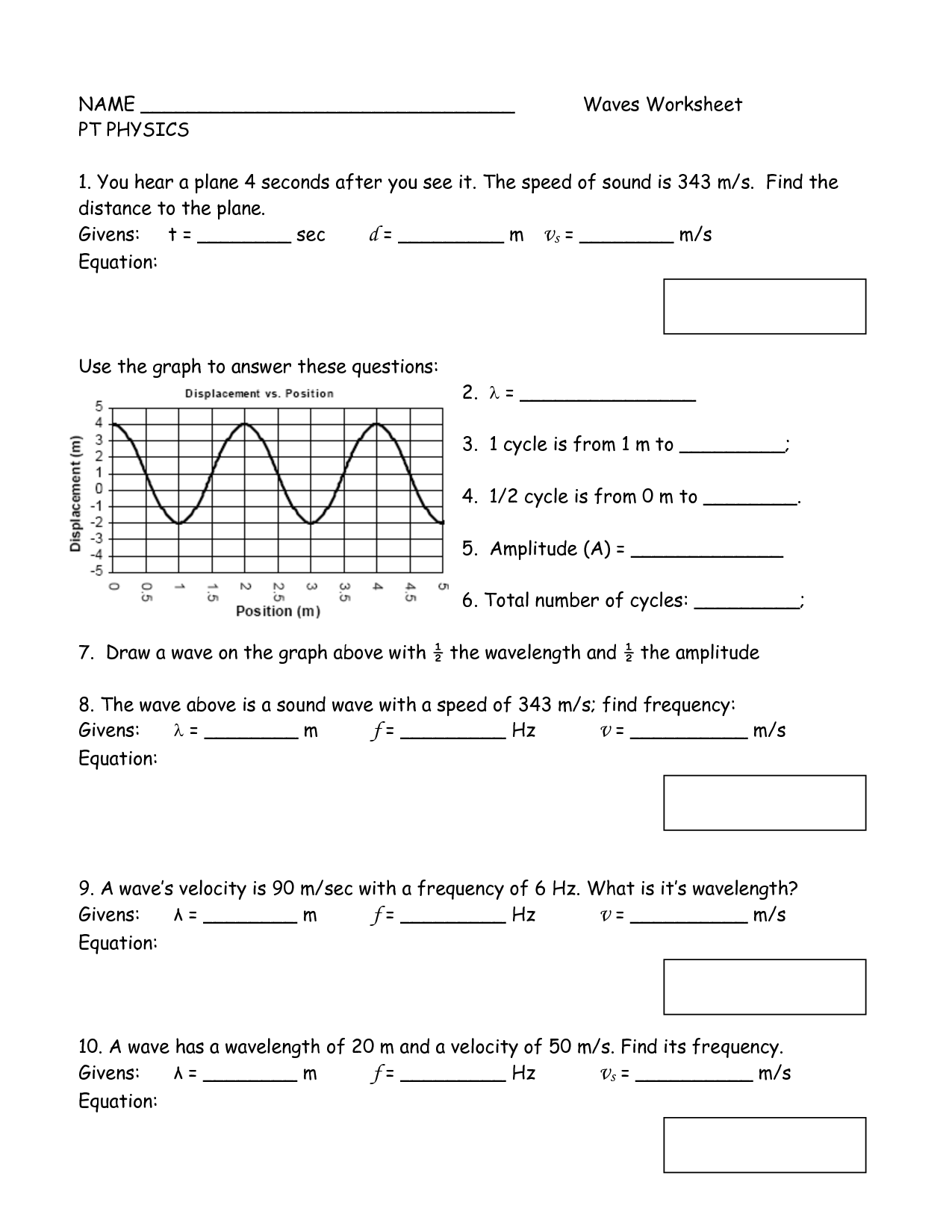
A wave profile refers to a visual representation of a wave's characteristics, such as its amplitude (height), wavelength (distance between two corresponding points on a wave), frequency (number of complete wave cycles passing a point in a given time), and speed. The shape and form of a wave can vary depending on these attributes, with different types of waves, like transverse or longitudinal waves, exhibiting distinct profiles.
How is the wavelength of a wave defined?
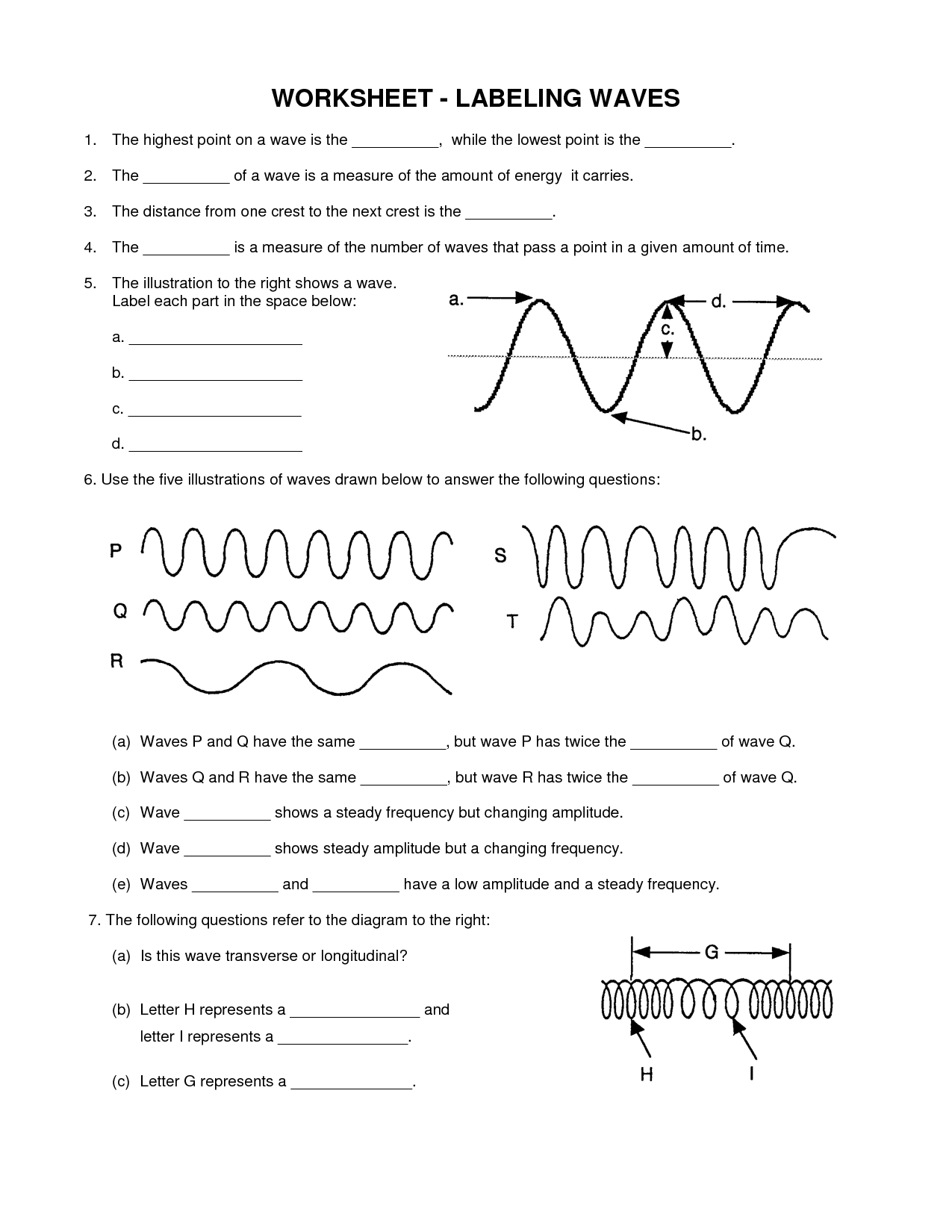
The wavelength of a wave is defined as the distance between two consecutive points on a wave that are in phase, such as the distance between two crests or two troughs. It is usually represented by the Greek letter lambda (λ) and is measured in units of length, such as meters, centimeters, or nanometers, depending on the type of wave.
Describe the amplitude of a wave.
The amplitude of a wave is the maximum displacement of a wave from its equilibrium position. It represents the height of the wave from the midpoint to its peak or trough. A larger amplitude indicates a more intense or powerful wave, while a smaller amplitude signifies a weaker one. Amplitude is a crucial component of waves as it affects the energy and intensity of the wave.
What units are used to measure the frequency of a wave?
The units used to measure the frequency of a wave are hertz (Hz), where one hertz is equal to one cycle per second.
Explain how the period of a wave is related to its frequency.
The period of a wave is inversely related to its frequency. The period of a wave is the time it takes for one complete cycle of the wave to occur, whereas the frequency of a wave is the number of complete cycles that occur in a given time period. Mathematically, the relationship between the period (T) and frequency (f) of a wave can be expressed as T = 1/f, where T is the period in seconds and f is the frequency in hertz (cycles per second). This means that as the frequency of a wave increases, the period decreases, and vice versa.
How can you determine the speed of a wave?
The speed of a wave can be determined by calculating the product of the wavelength and the frequency of the wave. This relationship is described by the formula: speed = wavelength x frequency. By knowing either the wavelength or the frequency of the wave, you can use this formula to calculate its speed.
Define the phase of a wave.
The phase of a wave refers to the position of a point on the wave cycle in relation to a reference point. It is usually measured in degrees or radians and indicates whether the wave is at a peak, trough, or any other point in its oscillation cycle. Phase plays a crucial role in determining interference patterns, wave interactions, and the behavior of waves in various physical systems.
Describe the relationship between the wavelength and frequency of a wave.
The relationship between the wavelength and frequency of a wave is inverse and proportional to each other. This means that as the wavelength of a wave increases, its frequency decreases, and vice versa. Mathematically, this relationship can be expressed as wavelength = speed of the wave / frequency, where the speed of the wave remains constant. This fundamental relationship is a key aspect of wave behavior in various fields, such as physics and telecommunications.
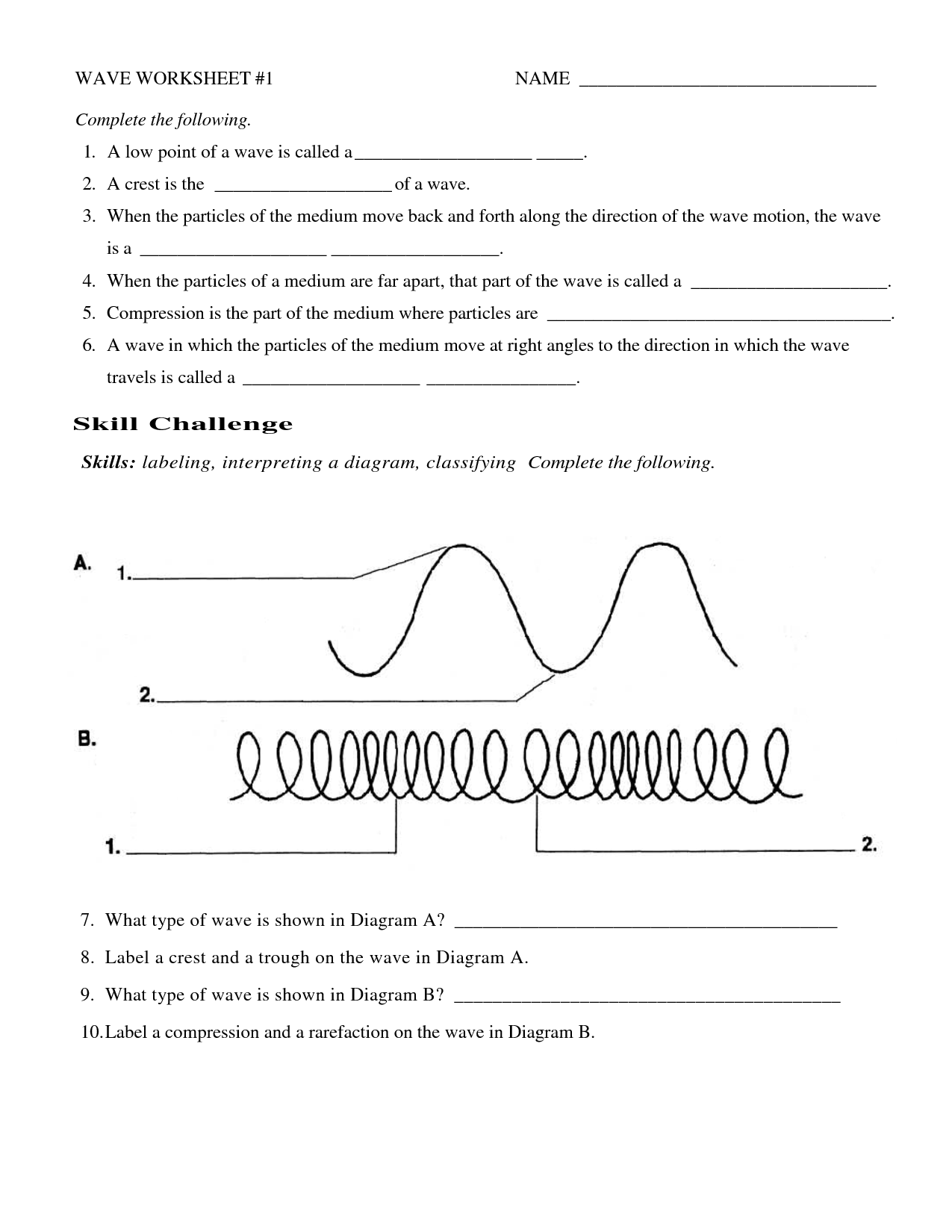
What is a transverse wave?
A transverse wave is a type of wave where the oscillations or vibrations are perpendicular to the direction in which the wave is traveling. This means that the particles of the medium through which the wave is moving move up and down, side to side, or in a circular motion as the wave passes through them. Examples of transverse waves include electromagnetic waves such as light waves and water waves on the surface of a pond.
Compare and contrast longitudinal and transverse waves.
Longitudinal waves have vibrations in the same direction as the wave propagation, like sound waves, while transverse waves have vibrations perpendicular to the wave propagation, like light waves. Longitudinal waves' particles move parallel to the wave motion while transverse waves' particles move perpendicular. Both types transfer energy, but transverse waves exhibit characteristics like polarization while longitudinal waves demonstrate compression and rarefaction. Generally, longitudinal waves are seen in gases and liquids, whereas transverse waves are typical in solid mediums.
Have something to share?
Who is Worksheeto?
At Worksheeto, we are committed to delivering an extensive and varied portfolio of superior quality worksheets, designed to address the educational demands of students, educators, and parents.

























Comments