Printable Science Worksheets Matter
If you're looking for a comprehensive resource to help your students understand the concept of matter, you've come to the right place. Our printable science worksheets on matter are designed to provide a clear and engaging learning experience for students of all levels. With a focus on key topics and a wide range of exercises, these worksheets are an excellent tool for teachers and parents looking to reinforce understanding and enhance critical thinking skills in their students.
Table of Images 👆
- Elementary Science Worksheets
- States of Matter Worksheets 2nd Grade
- Light and Heat Energy Worksheets
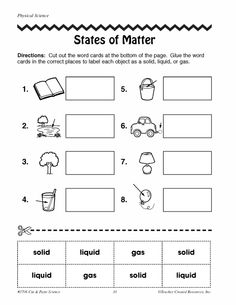
- States of Matter Worksheets
- Solid-Liquid Gas Graphic Organizer
- Worksheet On Science Materials
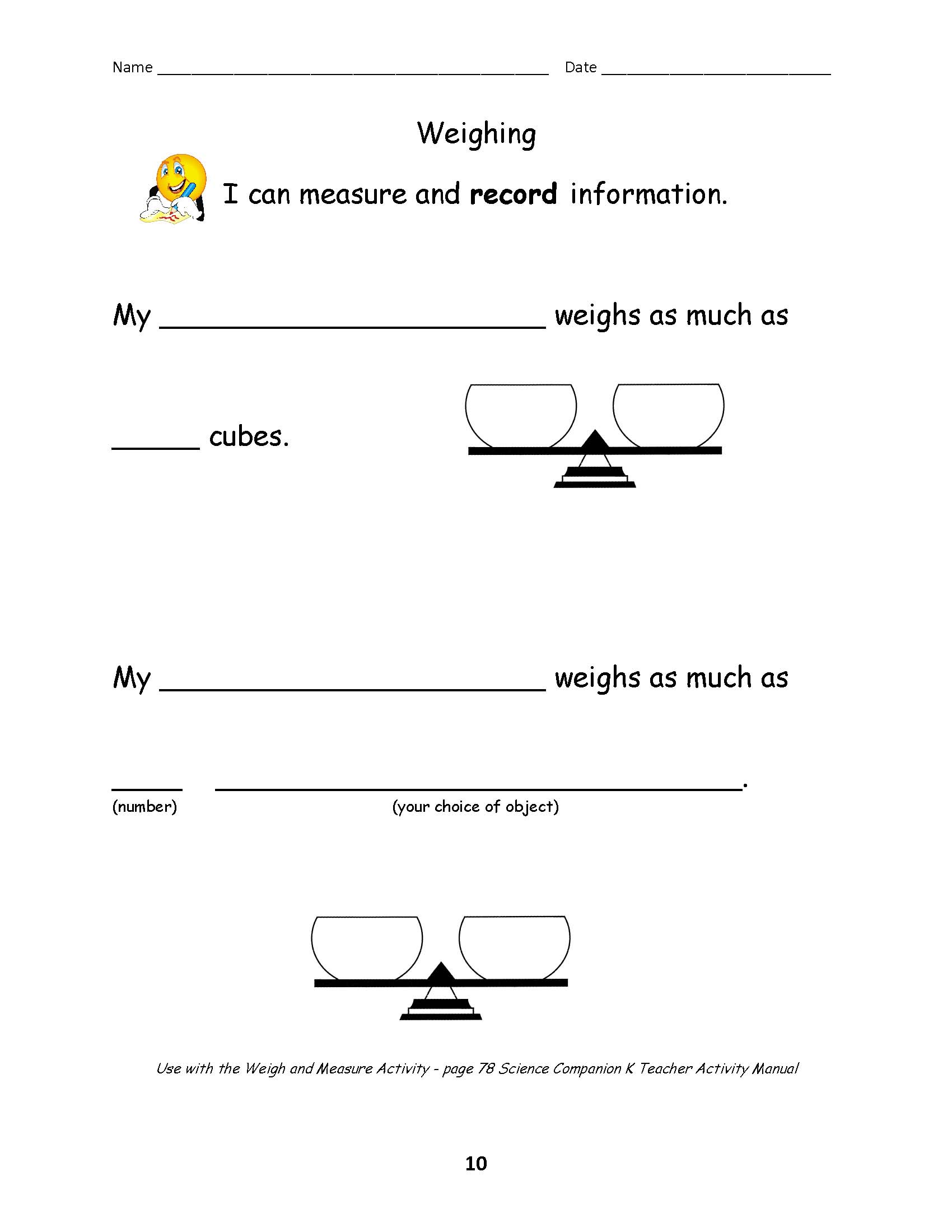
- 3rd Grade Science Volume Mass Liquid
- States of Matter Solid-Liquid Gas
- Oobleck Science Worksheet
- Elements Compounds and Mixtures Worksheet Answers
- 1st Grade Science Worksheets Plants
- Needs and Wants Worksheet Kindergarten
- Science Lab Safety Word Search
- Food Chain Worksheets 4th Grade
- Chemistry Lab Safety Worksheet
- Coloring Map of South America Countries
- Printable Periodic Table Elements
- As Periodic Table of Elements
- Heat Energy Transfer Worksheet
More Science Worksheets
6 Grade Science WorksheetsScience Heat Energy Worksheets with Answer
Science Worksheets Light and Sound
1st Grade Life Science Worksheets
7th Grade Science Cells Worksheets
Worksheets Life Science Vocabulary
8th Grade Science Scientific Method Worksheet
Science Worksheets All Cells
5th Grade Science Mixtures and Solutions Worksheets
What is the definition of matter?
Matter is anything that occupies space and has mass, comprising elements, molecules, and substances that make up the physical world. It is made up of atoms, which are the basic building blocks of all matter, and can exist in different states such as solid, liquid, or gas.
What are the three states of matter?
The three states of matter are solid, liquid, and gas.
Describe characteristics of a solid.
Solids have a definite shape and volume, their particles are closely packed together in a fixed arrangement, and they are not easily compressible. They have strong intermolecular forces that hold the particles in place, giving them a rigid structure. Solids can also exhibit regular geometric patterns, such as crystals, and can have a high melting point.
Explain the behavior of particles in a liquid.
Particles in a liquid exhibit constant random motion due to continuous collisions with each other and the container walls. These particles have more freedom of movement compared to those in a solid, which allows the liquid to take the shape of its container. The cohesive forces between the particles keep them closely packed together while allowing them to slide past each other, giving liquids the ability to flow and take the shape of their container.
How does gas differ from solid and liquid?
Gas differs from solids and liquids in terms of their arrangement of molecules. In a gas, molecules are far apart and move freely at high speeds, resulting in a less organized structure compared to solids and liquids. Solids have densely packed molecules that vibrate in fixed positions, while liquids have molecules that are close together but can move around each other. Additionally, gases do not have a definite shape or volume, unlike solids and liquids which have distinct shapes and volumes.
Provide an example of a physical change in matter.
An example of a physical change in matter is the melting of ice. When solid ice is heated, it transitions into liquid water without altering its chemical composition. The molecules in the ice rearrange from a fixed, rigid structure to a more fluid and less ordered arrangement, resulting in a change in state from solid to liquid while maintaining the same chemical properties.
What is an element?
An element is a pure substance that cannot be broken down into simpler substances by chemical means. It is composed of atoms that all have the same number of protons in their nucleus, giving each element its unique chemical properties. Elements are organized in the periodic table based on their atomic number, and there are currently 118 known elements.
Describe the concept of chemical reactions in matter.
Chemical reactions in matter involve the breaking and making of chemical bonds between atoms, resulting in the transformation of substances into new ones with different chemical properties. These reactions can release or absorb energy, leading to changes in temperature, color, state, or other observable characteristics of the matter involved. The reactants are the initial substances that undergo the reaction, while the products are the new substances formed after the reaction. Chemical reactions follow the principles of conservation of mass and energy, with atoms rearranging but not being created or destroyed in the process.
What are the properties of a chemical compound?
Chemical compounds have distinct properties that are determined by their chemical composition and structure, such as melting point, boiling point, density, solubility, color, odor, and reactivity. These properties can help identify and characterize a compound, as well as predict how it will behave in different chemical reactions and environments.
How can matter be classified based on its physical and chemical properties?
Matter can be classified based on its physical and chemical properties by observing characteristics such as color, shape, density, melting point, boiling point, conductivity, and reactions with other substances. Physical properties describe how a substance looks or behaves without changing its composition, while chemical properties describe how a substance interacts with other substances to form new substances. By combining observations of both physical and chemical properties, scientists can categorize matter into different groups or types based on its behavior and characteristics.
Have something to share?
Who is Worksheeto?
At Worksheeto, we are committed to delivering an extensive and varied portfolio of superior quality worksheets, designed to address the educational demands of students, educators, and parents.































Comments