Plant Structure and Function Worksheet
Understanding the structure and function of plants is crucial for anyone looking to delve into the fascinating world of botany. Whether you are a student studying biology, a teacher looking for engaging educational resources, or simply someone curious about the wonders of the natural world, this Plant Structure and Function Worksheet is designed to enhance your knowledge and appreciation of plants.
Table of Images 👆
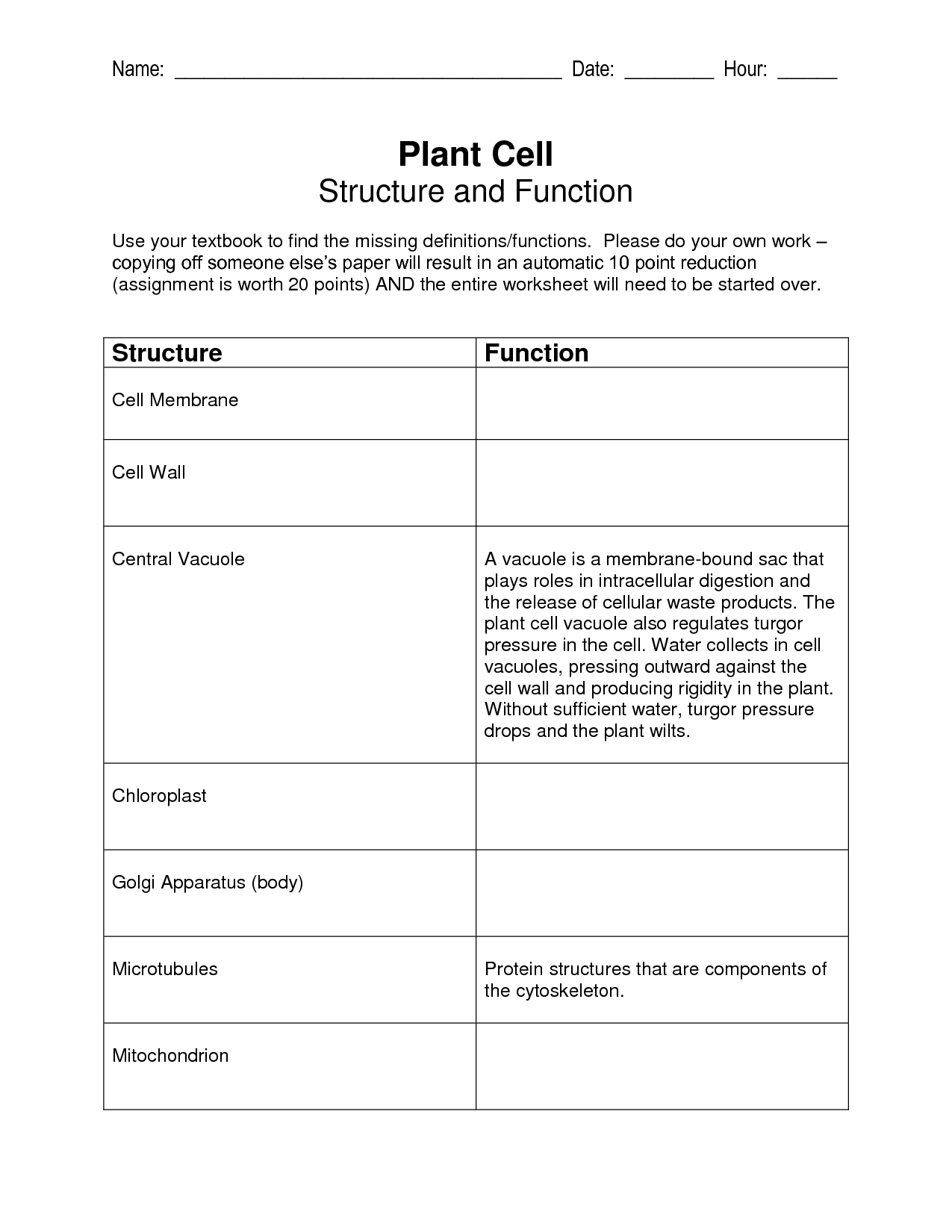
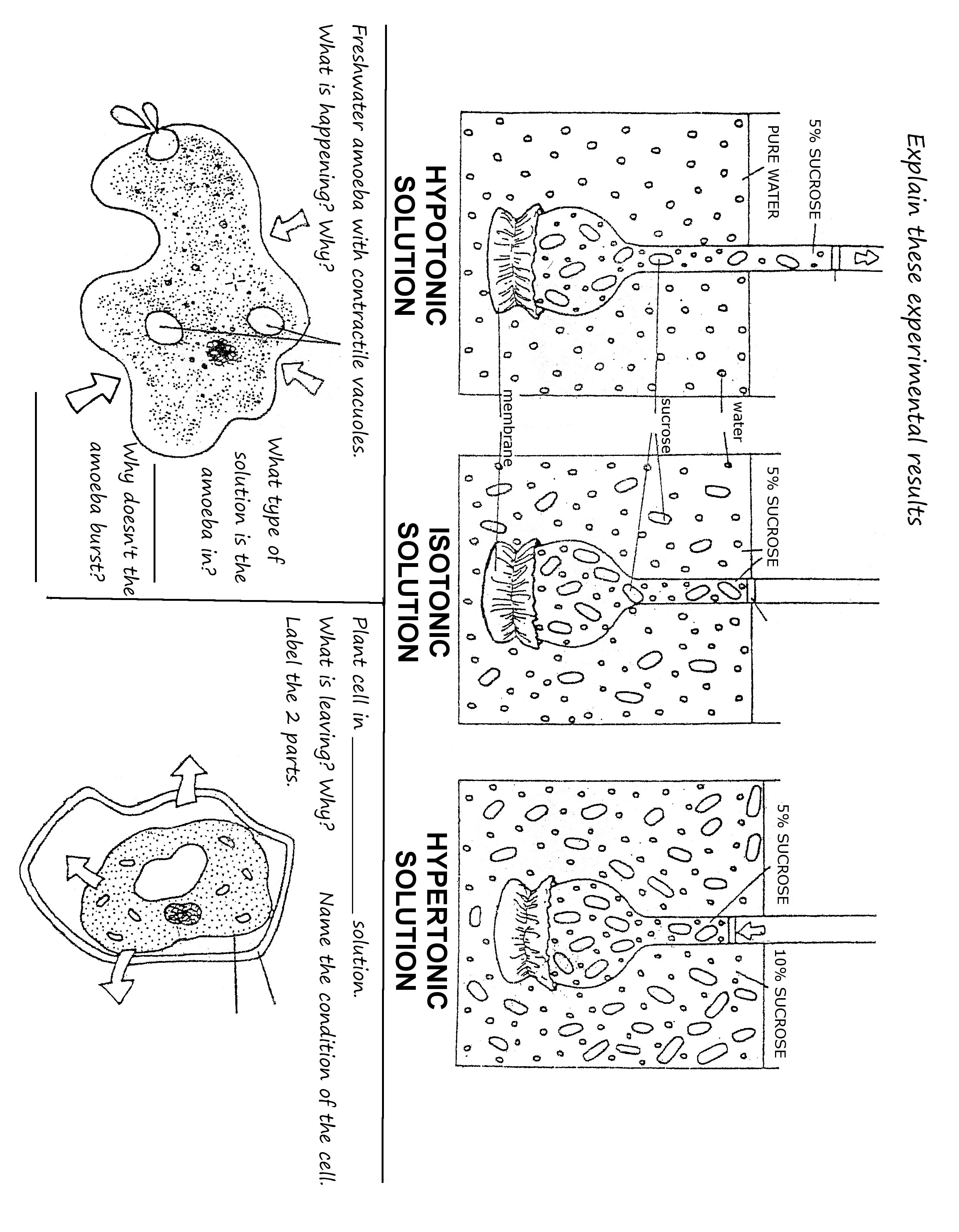
- Plant Cell Structure and Function Worksheet
- Plant Parts and Functions Worksheet
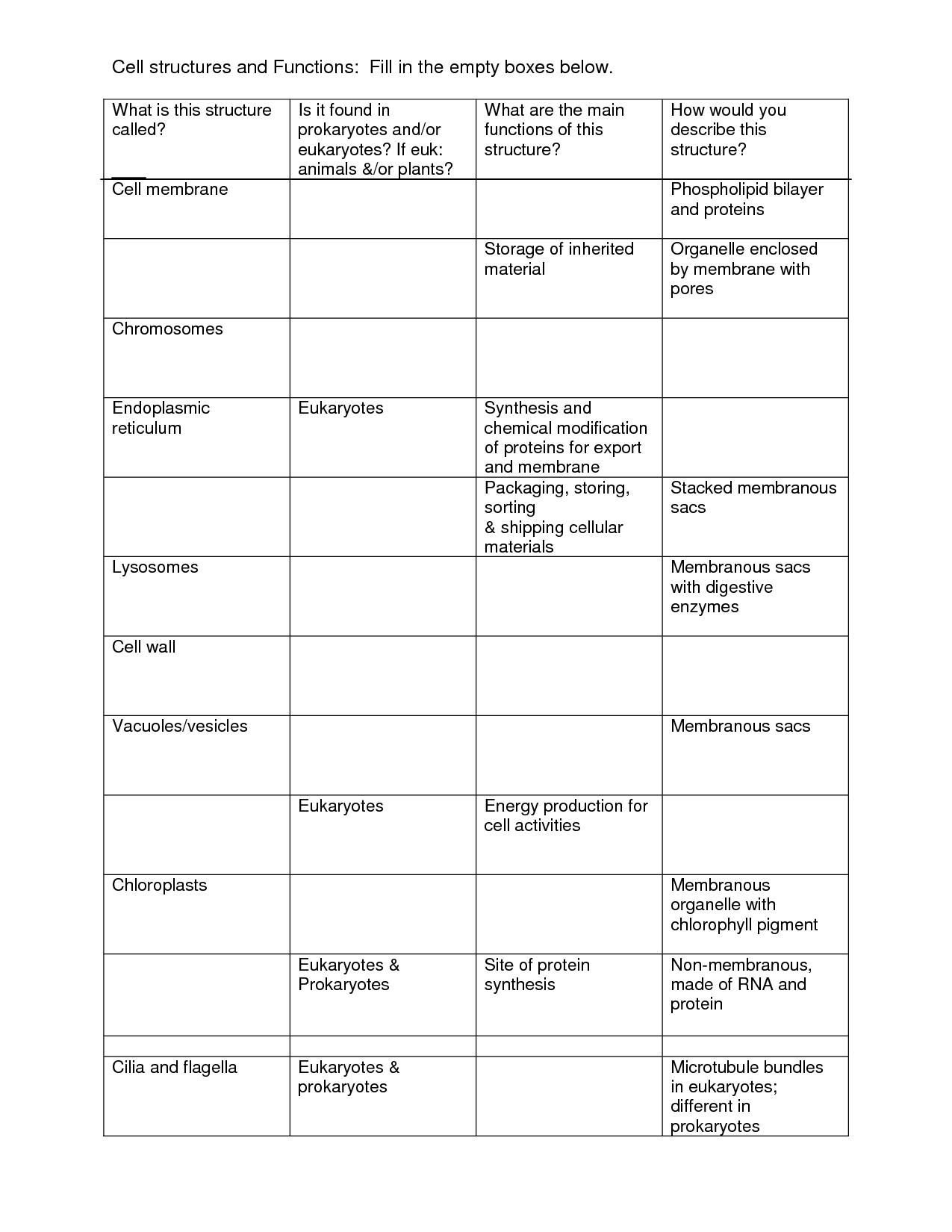
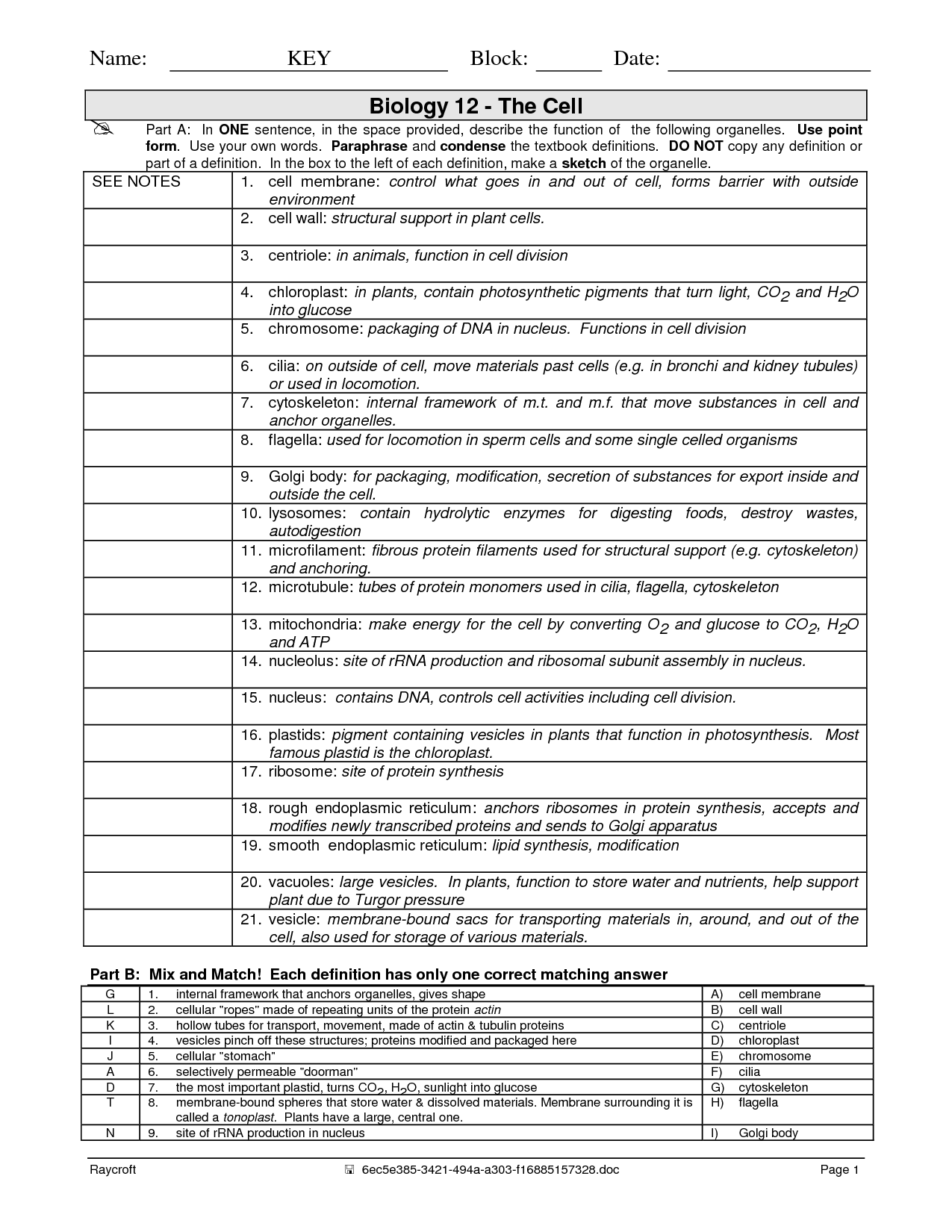
- Cell Structure and Function Worksheet Answers
- Plant Cell Structure and Function Worksheet
- Plant Cell Structure and Function Chart
- Cell Parts and Functions Worksheet
- Biology Cell Structure and Function Worksheet
- Plant Structure and Function Worksheet Answers
- Plant Cell Structure and Function Worksheet
- Root Structure and Function Worksheet
- Cells and Their Organelles Worksheet Answers
- Cell Structure and Function Worksheets Answer Key
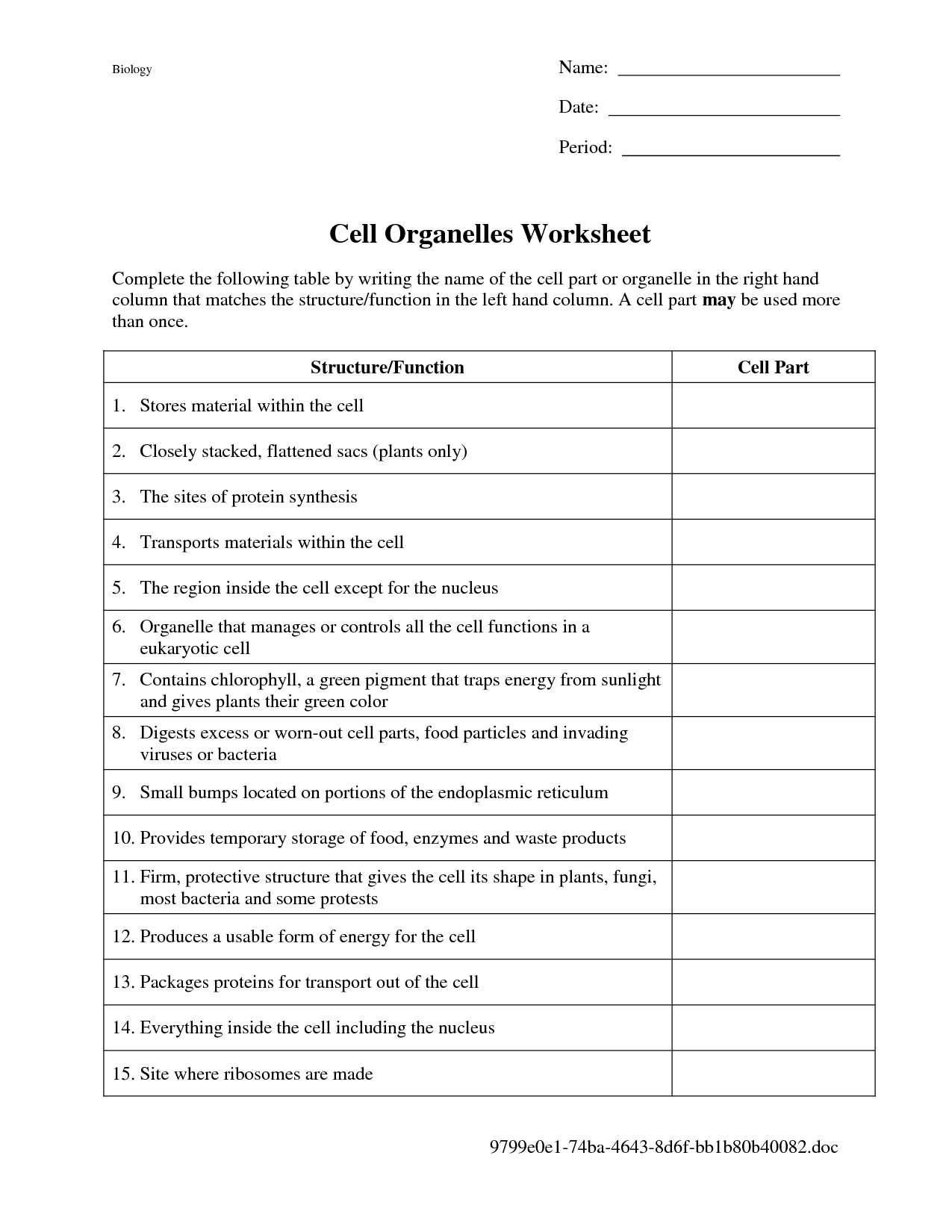
- Cell Organelles Worksheet Answer Key
- Cell Organelles Worksheet Answers
- Plant Anatomy and Physiology Worksheets
More Other Worksheets
Kindergarten Worksheet My RoomSpanish Verb Worksheets
Healthy Eating Plate Printable Worksheet
Cooking Vocabulary Worksheet
My Shadow Worksheet
Large Printable Blank Pyramid Worksheet
Relationship Circles Worksheet
DNA Code Worksheet
Meiosis Worksheet Answer Key
Rosa Parks Worksheet Grade 1
What is the function of the roots in a plant?
The main function of roots in a plant is to anchor the plant in the soil, absorb water and nutrients from the soil, and transport these resources up to the rest of the plant. Roots also store food reserves and provide support to the above-ground parts of the plant. Additionally, roots help to prevent soil erosion by holding the soil in place.
Describe the structure and function of the stem.
The stem is a vital part of a plant's anatomy that serves as a support system for the plant by holding up the leaves, flowers, and fruits. It also plays a crucial role in transporting water, nutrients, and sugars throughout the plant. The stem consists of different layers, including the epidermis, cortex, vascular bundles, and pith. Each layer has a specific function in maintaining the plant's structure and facilitating nutrient transport. Additionally, the stem can also store food and water reserves, enable plant growth and reproduction, and serve as a site for new leaf and flower growth.
How do leaves contribute to a plant's function?
Leaves play a crucial role in a plant's function by performing photosynthesis, a process where they absorb sunlight and carbon dioxide to produce glucose and oxygen, providing energy for the plant's growth and reproduction. Additionally, leaves also help regulate water evaporation, exchange gases with the atmosphere, and store nutrients for the plant's use, making them essential for the overall health and survival of the plant.
Explain the role of flowers in plant structure and function.
Flowers play a crucial role in the reproduction of plants as they are the reproductive organs that produce seeds. They are responsible for attracting pollinators such as bees, butterflies, and birds, which aid in the transfer of pollen between flowers for fertilization. Additionally, flowers contain male and female reproductive organs, namely stamens (male) and pistils (female), that facilitate the process of pollination and subsequent seed formation. Overall, flowers are essential for the reproductive success and genetic diversity of plants.
What are the different types of plant tissues and their functions?
Plant tissues can be categorized into three main types: dermal, vascular, and ground tissues. Dermal tissues, such as the epidermis, protect the plant from physical damage and pathogens. Vascular tissues, including xylem and phloem, are responsible for transporting water, nutrients, and sugars throughout the plant. Ground tissues, like parenchyma, collenchyma, and sclerenchyma cells, provide structural support, store nutrients, and carry out photosynthesis. Together, these tissues work in harmony to ensure the growth, development, and survival of the plant.
Describe the structure and function of xylem and phloem.
Xylem is a complex tissue in plants that transports water and minerals from the roots to the rest of the plant. Consisting of vessels, tracheids, and fibers, xylem provides structural support and helps in maintaining the plant's shape. Phloem, on the other hand, is responsible for transporting sugars, amino acids, and other organic substances produced during photosynthesis from the leaves to various parts of the plant. Comprised of sieve tube elements and companion cells, phloem is vital for distributing nutrients and energy throughout the plant. Both xylem and phloem work together to ensure proper nutrient transport and support plant growth and development.
What is the purpose of the cuticle and stomata in leaves?
The cuticle is a waxy layer on the surface of leaves that helps reduce water loss by preventing excessive evaporation. Stomata, on the other hand, are small openings on the surface of leaves that allow for the exchange of gases, such as carbon dioxide and oxygen, necessary for photosynthesis. Together, the cuticle and stomata help regulate water loss and gas exchange, allowing plants to efficiently perform photosynthesis while conserving water.
How do plants use photosynthesis to obtain energy?
Plants use photosynthesis to obtain energy by absorbing sunlight through their leaves and converting it into chemical energy. This process involves the consumption of water and carbon dioxide, which are used to produce glucose and oxygen. The glucose is then used by the plant as a source of energy for growth, reproduction, and other metabolic processes, while the oxygen is released into the atmosphere as a byproduct. In essence, photosynthesis allows plants to transform solar energy into a usable form of energy that sustains their life processes.
Explain how plant hormones regulate growth and development.
Plant hormones regulate growth and development by controlling various processes such as cell division, elongation, differentiation, and responses to environmental stimuli. Each hormone plays a specific role in plant growth, for example, auxins promote cell elongation and root initiation, cytokinins stimulate cell division and delay aging, gibberellins promote stem elongation and seed germination, abscisic acid regulates responses to stress and seed dormancy, ethylene controls fruit ripening and response to stress, and jasmonates regulate defense mechanisms against pathogens. These hormones interact with each other and with external factors to orchestrate the overall growth and development of a plant.
What is the role of meristems in plant structure and function?
Meristems are essential for plant growth and development as they are responsible for generating new cells that differentiate into various tissues and organs. They play a crucial role in plant structure by facilitating root and shoot growth, as well as enabling lateral growth for plants to increase in size. Without meristems, plants would not be able to continuously grow, adapt to changing environmental conditions, or repair damaged tissues, ultimately affecting their overall function and survival.
Have something to share?
Who is Worksheeto?
At Worksheeto, we are committed to delivering an extensive and varied portfolio of superior quality worksheets, designed to address the educational demands of students, educators, and parents.



























Comments