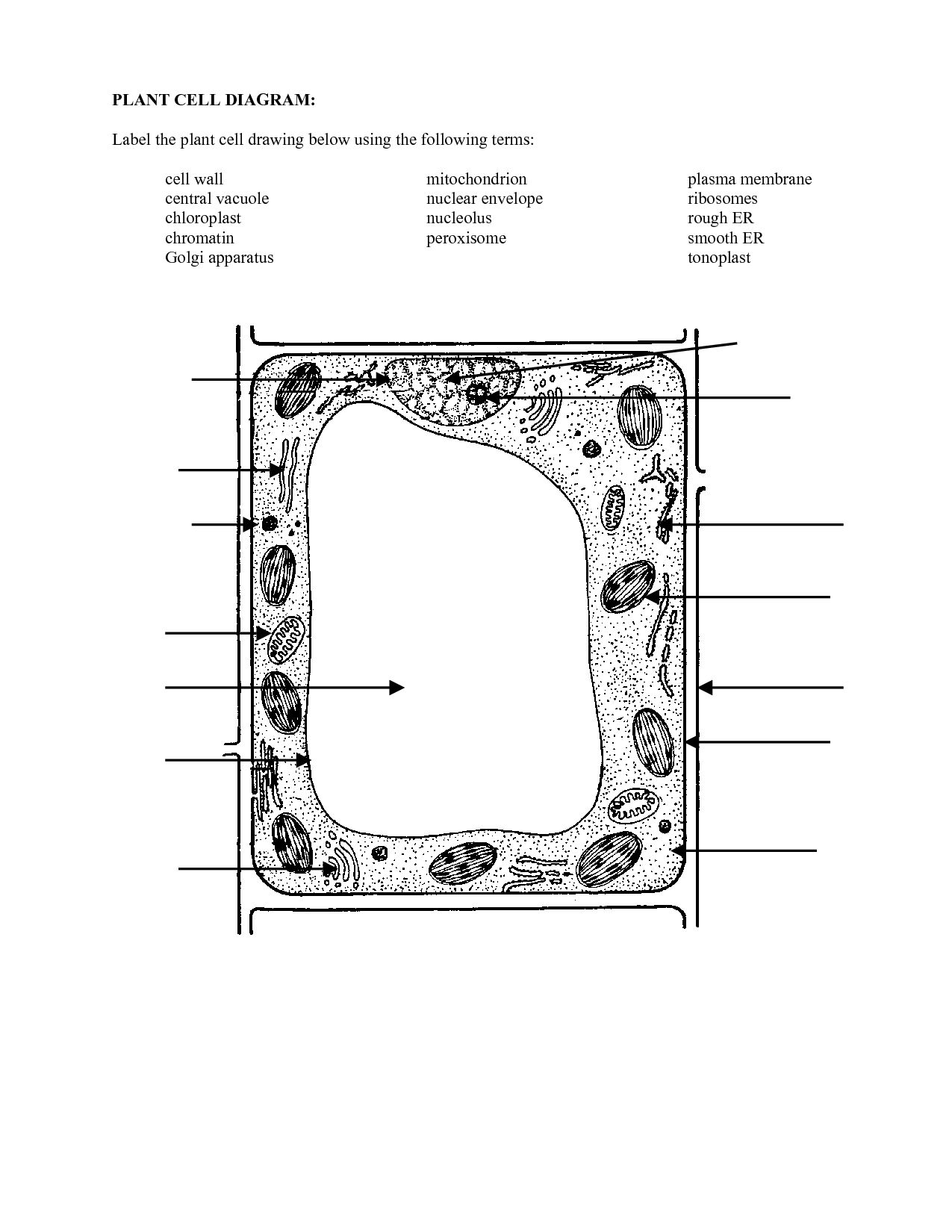
Plant Cell Parts Worksheet
Do you teach biology? If so, you may find this plant cell parts worksheet to be a helpful resource for your students. This worksheet provides a comprehensive overview of the different parts of a plant cell, allowing students to learn and identify each entity and subject within the cell.
Table of Images 👆
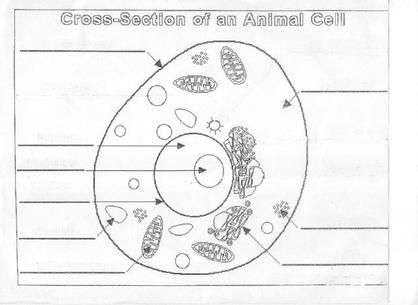
- Plant and Animal Cell Diagram Worksheet
- Plant and Animal Cell Labeling Worksheet
- Cell Parts and Functions Worksheet
- Plant Cell Structure and Function Worksheet
- Plant and Animal Cell Diagram Worksheet
- Plant Parts Worksheet 3rd Grade
- Plant and Animal Cell Worksheets 5th Grade
- Label Plant Parts Worksheet
- Plant Parts and Functions Worksheet
- Plant Cell Diagram Worksheet
- Blank Plant Cell Diagram
- Animal Cell Labeling Worksheet
- Plant Cell Diagram Worksheet
- Unlabeled Animal Cell Diagram Worksheet
- Animal Cell Parts Worksheet
- Blank Plant Cell Diagram Worksheet
More Other Worksheets
Kindergarten Worksheet My RoomSpanish Verb Worksheets
Healthy Eating Plate Printable Worksheet
Cooking Vocabulary Worksheet
My Shadow Worksheet
Large Printable Blank Pyramid Worksheet
Relationship Circles Worksheet
DNA Code Worksheet
Meiosis Worksheet Answer Key
Rosa Parks Worksheet Grade 1
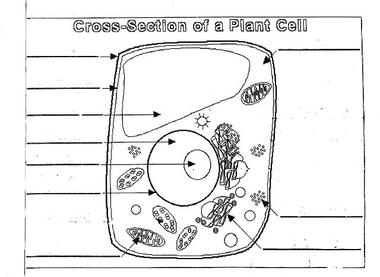
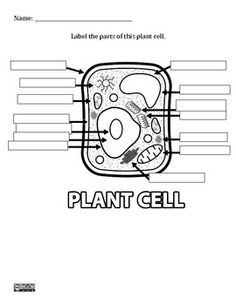
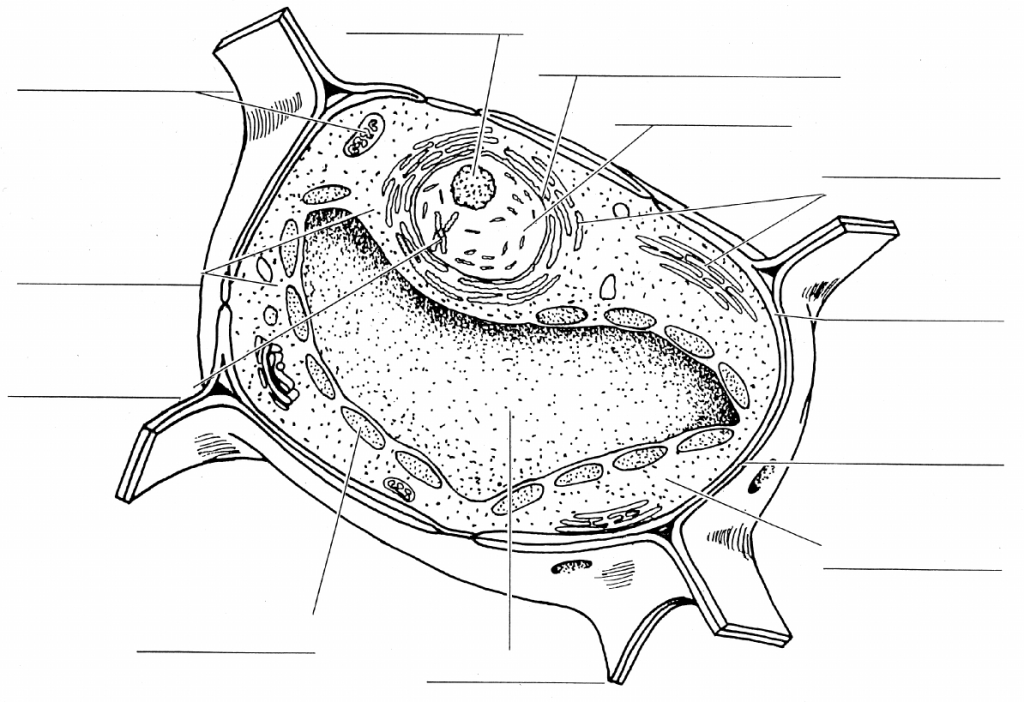
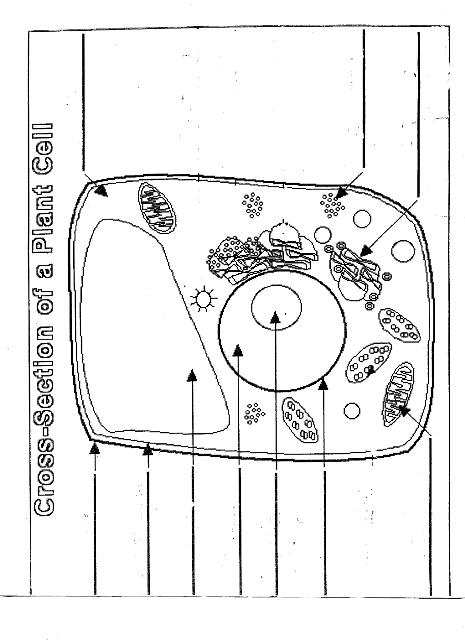
What is the function of the cell wall?
The cell wall provides structural support and protection for plant cells by maintaining the shape of the cell and preventing it from bursting due to osmotic pressure. It also acts as a barrier, regulating the movement of substances in and out of the cell. Additionally, the cell wall helps plants withstand environmental stresses such as drought and mechanical injury.
What is the main function of the plasma membrane?
The main function of the plasma membrane is to regulate the passage of substances in and out of the cell, thereby maintaining the cell's internal environment and allowing it to communicate with its external environment. Additionally, the plasma membrane also plays a role in cell signaling, cell adhesion, and cell recognition.
What is the role of the nucleus in a plant cell?
The nucleus in a plant cell plays a vital role in controlling cellular activities and storing genetic information in the form of DNA. It is responsible for regulating gene expression, cell growth, and reproduction. Additionally, the nucleus also houses the nucleolus, which is involved in ribosome synthesis and assembly.
What is the function of the mitochondria?
The function of the mitochondria is to generate energy for the cell through the process of cellular respiration, producing adenosine triphosphate (ATP), which is the main energy currency of the cell. Mitochondria are often referred to as the powerhouse of the cell due to their role in supplying the energy necessary for various cellular activities.
What are the chloroplasts responsible for in a plant cell?
Chloroplasts are responsible for photosynthesis in plant cells, the process by which sunlight energy is converted into chemical energy in the form of glucose. Chloroplasts contain chlorophyll, a pigment that captures light energy, and use it to produce food for the plant through photosynthesis.
What is the purpose of the vacuole?
The vacuole in a cell serves various functions, including storing nutrients, maintaining turgidity and pressure within the cell, storing waste products, and aiding in digestion and recycling of cellular components. In plant cells, the vacuole also plays a crucial role in maintaining the shape and structure of the cell, as well as storing pigments that provide color to flowers and fruits. Overall, the vacuole contributes to the overall health and functionality of the cell.
What are ribosomes responsible for in a plant cell?
Ribosomes in plant cells are responsible for protein synthesis, playing a crucial role in the translation of mRNA into functional proteins. Ribosomes are the cellular machinery where amino acids are assembled into polypeptide chains based on the instructions provided by the mRNA. These proteins are vital for various cellular functions, growth, and development of the plant.
What is the function of the endoplasmic reticulum?
The endoplasmic reticulum (ER) is a cell organelle that plays a crucial role in protein synthesis, folding, and transport within the cell. It also serves as a site for lipid synthesis and detoxification of harmful substances. The ER is divided into rough ER, which has ribosomes attached to its surface and is involved in protein synthesis, and smooth ER, which is responsible for lipid metabolism and detoxification processes. Overall, the endoplasmic reticulum is essential for maintaining cellular homeostasis and ensuring proper functioning of a variety of cellular processes.
What is the importance of golgi apparatus in a plant cell?
The Golgi apparatus in a plant cell plays a crucial role in processing and packaging various molecules, such as proteins and lipids, before they are transported to their appropriate destinations within or outside the cell. It is responsible for modifying, sorting, and packaging these substances into vesicles for secretion, transportation, or incorporation into cell membranes. This organelle is essential for maintaining the cell's structural integrity and function, as well as facilitating intercellular communication and regulating cellular processes.
What is the role of peroxisomes in plant cell metabolism?
Peroxisomes in plant cell metabolism play a crucial role in various metabolic pathways, including the beta-oxidation of fatty acids, the detoxification of harmful substances like hydrogen peroxide, and the synthesis of essential compounds such as lignin and phytoalexins. Additionally, peroxisomes are involved in the photorespiration process, where they aid in the breakdown of toxic byproducts produced during photosynthesis in plants. Overall, peroxisomes contribute significantly to maintaining a balanced cellular environment and supporting essential metabolic processes in plant cells.
Have something to share?
Who is Worksheeto?
At Worksheeto, we are committed to delivering an extensive and varied portfolio of superior quality worksheets, designed to address the educational demands of students, educators, and parents.




























Comments