Physical Science Worksheets On Atoms
Physical science worksheets on atoms are a valuable resource for students who are learning about the fundamentals of chemistry and physics. These worksheets provide an opportunity for students to explore the different properties of atoms, understand their structure, and learn about the periodic table. By using these worksheets, students can enhance their knowledge and comprehension of physical science concepts related to atoms.
Table of Images 👆
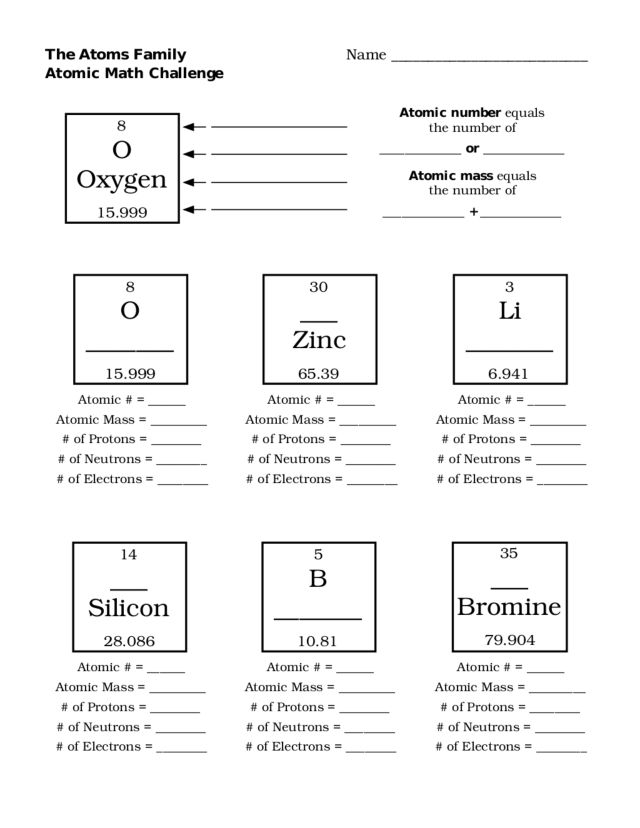
- Atoms Family Atomic Math Challenge Worksheet
- Atom Molecule Element Compound Worksheet
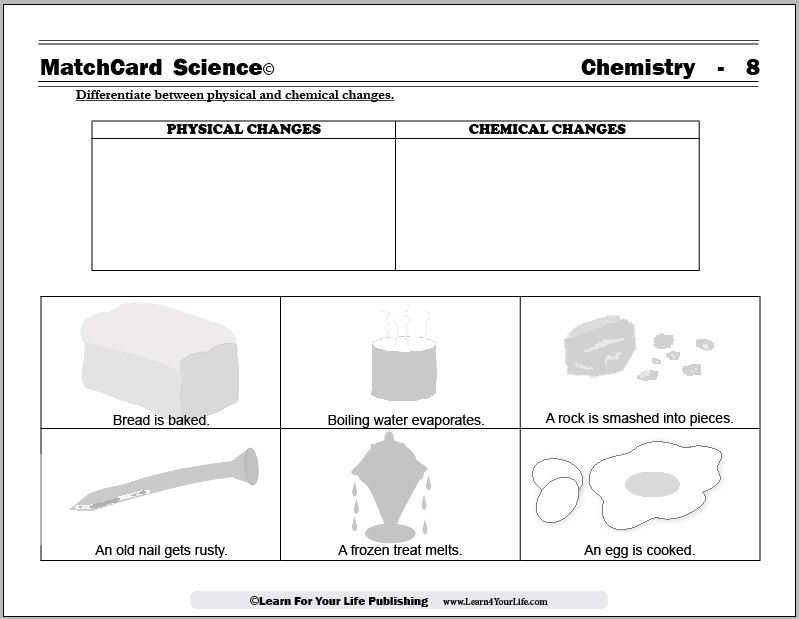
- Physical vs Chemical Change Worksheet
- Label Parts of an Atom Diagram
- 6th Grade Science Questions and Answers
- Physical and Chemical Changes Worksheets
- Label Parts of an Atom Diagram
- Bohr Model of the Atom Worksheet Answers
- Glencoe Physical Science
- Element Crossword Puzzle Answer Key
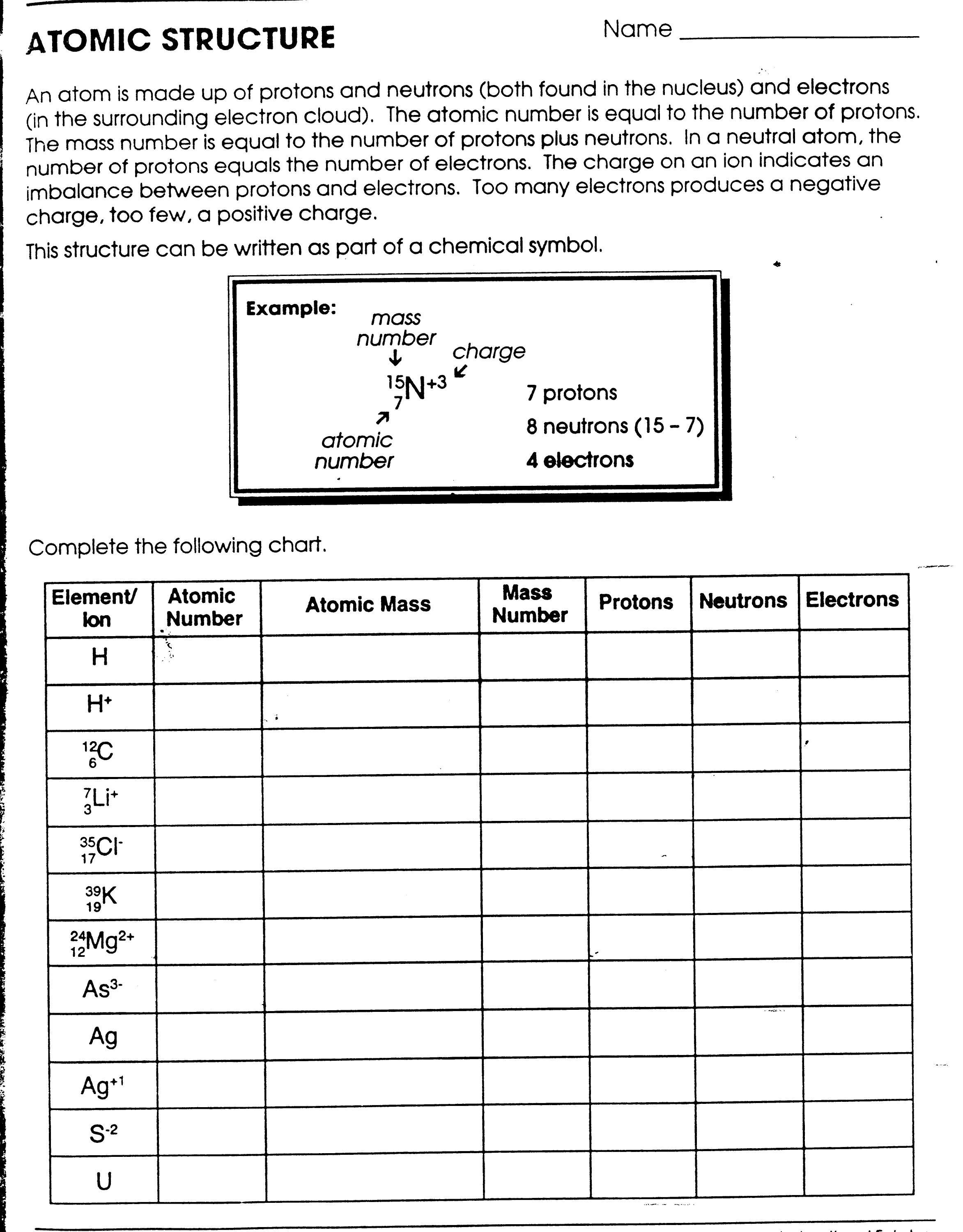
- Atomic Structure Worksheet Answers
- Chemistry Worksheet Answer Keys
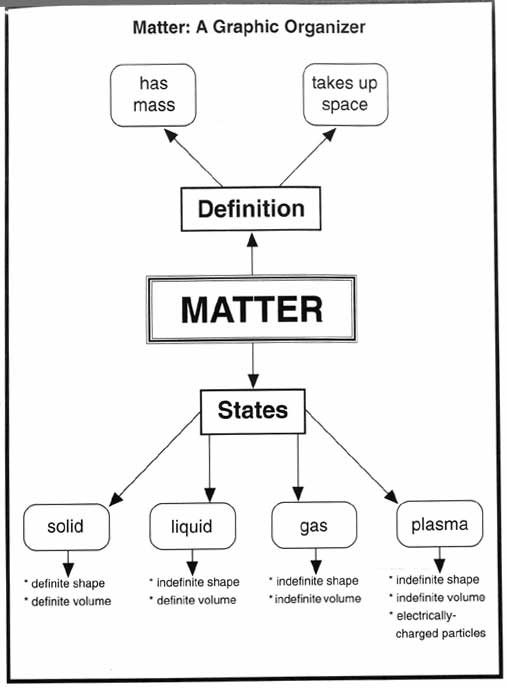
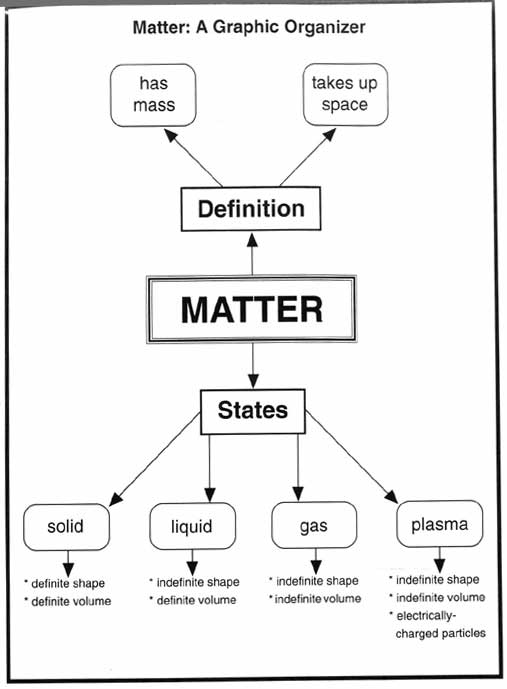
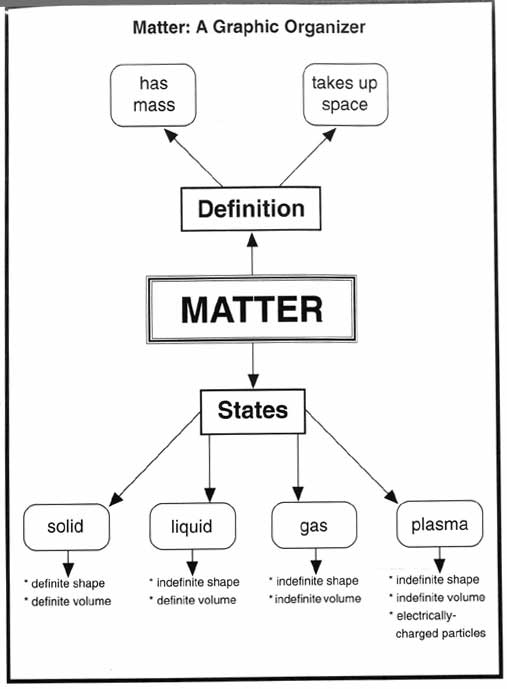
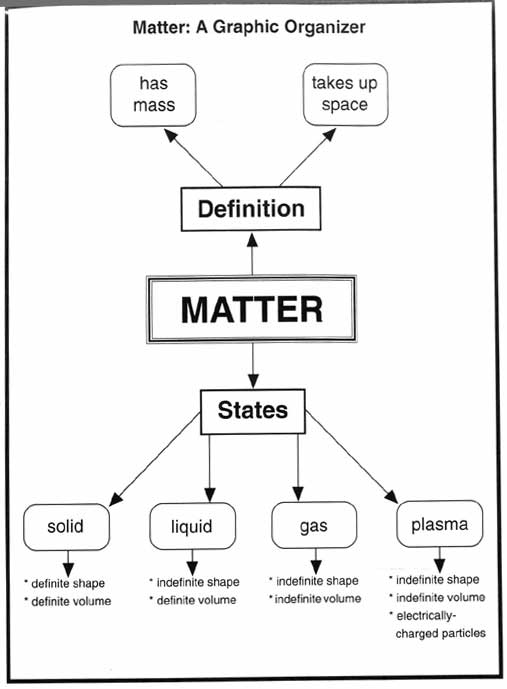
- Matter Science Graphic Organizers
- Matter Science Graphic Organizers
- Matter Science Graphic Organizers
- Matter Science Graphic Organizers
More Science Worksheets
6 Grade Science WorksheetsScience Heat Energy Worksheets with Answer
Science Worksheets Light and Sound
1st Grade Life Science Worksheets
7th Grade Science Cells Worksheets
Worksheets Life Science Vocabulary
8th Grade Science Scientific Method Worksheet
Science Worksheets All Cells
5th Grade Science Mixtures and Solutions Worksheets
What is an atom?
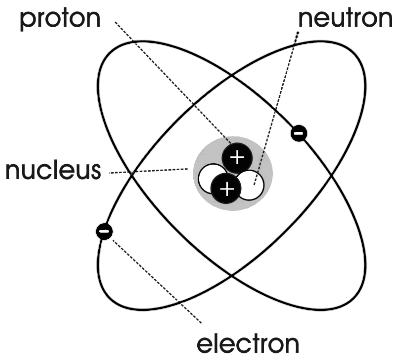
An atom is the smallest unit of matter that retains the properties of an element. It consists of a nucleus, containing protons and neutrons, surrounded by electrons that orbit the nucleus. The number of protons in the nucleus determines the element's identity, while the number of protons and neutrons combined determine the atom's mass.
What are the three main components of an atom?
The three main components of an atom are protons, neutrons, and electrons. Protons carry a positive charge, neutrons are uncharged, and electrons carry a negative charge. Protons and neutrons make up the nucleus of an atom, while electrons orbit around the nucleus in electron shells.
Describe the structure of an atom.
An atom consists of a nucleus at its center, which is composed of protons and neutrons. Surrounding the nucleus are electrons that orbit in shells or energy levels. The protons are positively charged, neutrons have no charge, and electrons are negatively charged. The number of protons in the nucleus determines the element's atomic number, while the sum of protons and neutrons gives the atomic mass. The electrons are distributed in different energy levels based on their energy and distance from the nucleus.
What is an atomic number?
An atomic number is the number of protons found in the nucleus of an atom. It uniquely identifies each element and determines its position on the periodic table. The atomic number essentially defines the chemical properties of an element and is essential for understanding its behavior in chemical reactions.
How is the atomic mass of an atom determined?
The atomic mass of an atom is determined by adding up the mass of protons and neutrons in its nucleus. Protons and neutrons have a consistent mass, so scientists can calculate the atomic mass by adding up the number of protons and neutrons in the nucleus of an atom. This value is typically given in atomic mass units (amu).
What are isotopes and how do they differ from each other?
Isotopes are atoms of the same element that have the same number of protons but different numbers of neutrons. This means isotopes have the same atomic number but different atomic masses. The differences in the number of neutrons give each isotope unique properties such as stability, radioactivity, and chemical behavior.
What is the difference between an element and a compound?
An element is a pure substance that cannot be broken down into simpler substances by chemical reactions, consisting of only one type of atom. In contrast, a compound is a substance composed of two or more elements that are chemically bonded together in fixed proportions, forming a new substance with properties different from those of its constituent elements.
Explain the concept of electron shells and their role in the behavior of atoms.
Electron shells are the different energy levels at which electrons orbit the nucleus of an atom. These shells are labeled with quantum numbers, and each shell can hold a specific number of electrons. The innermost shell is filled first, followed by outer shells. The arrangement of electrons in these shells determines an atom's chemical properties and reactivity. Atoms tend to react in ways that achieve a more stable electron configuration, typically by filling or emptying their outermost electron shell. This interplay of electron shells influences how atoms bond with each other to form molecules, impacting their behavior and chemical characteristics.
How do atoms combine to form molecules?
Atoms combine to form molecules through chemical bonds, where the outer shell electrons of the atoms interact with each other. This interaction can involve sharing electrons (covalent bonds) or transferring electrons (ionic bonds) between atoms. The specific type of bond formed depends on the type and number of atoms involved. Once the atoms have formed bonds, they are held together by these forces of attraction, creating a stable molecule with its own distinct properties.
Describe the process of radioactive decay and its effect on atoms.
Radioactive decay is the process by which unstable atomic nuclei lose energy by emitting radiation, such as alpha or beta particles. This process transforms the original atom into a different element or isotope, often resulting in a more stable configuration. Radioactive decay can change the mass number and atomic number of an atom, leading to the formation of a new element. The release of radiation during decay can have various effects on atoms, including causing damage to other atoms, changing their chemical properties, and potentially posing health risks to living organisms.
Have something to share?
Who is Worksheeto?
At Worksheeto, we are committed to delivering an extensive and varied portfolio of superior quality worksheets, designed to address the educational demands of students, educators, and parents.





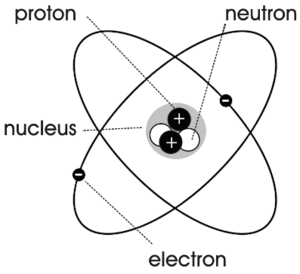


















Comments