Physical Science Worksheets Elementary
Physical science worksheets are an effective tool for elementary school students to expand their knowledge and understanding of key scientific concepts. Designed to engage young learners, these worksheets provide a structured approach to learning about various entities and subjects within the field of physical science. By encouraging children to explore and interact with different scientific principles, these worksheets help foster a love for learning and build a solid foundation for future scientific endeavors.
Table of Images 👆
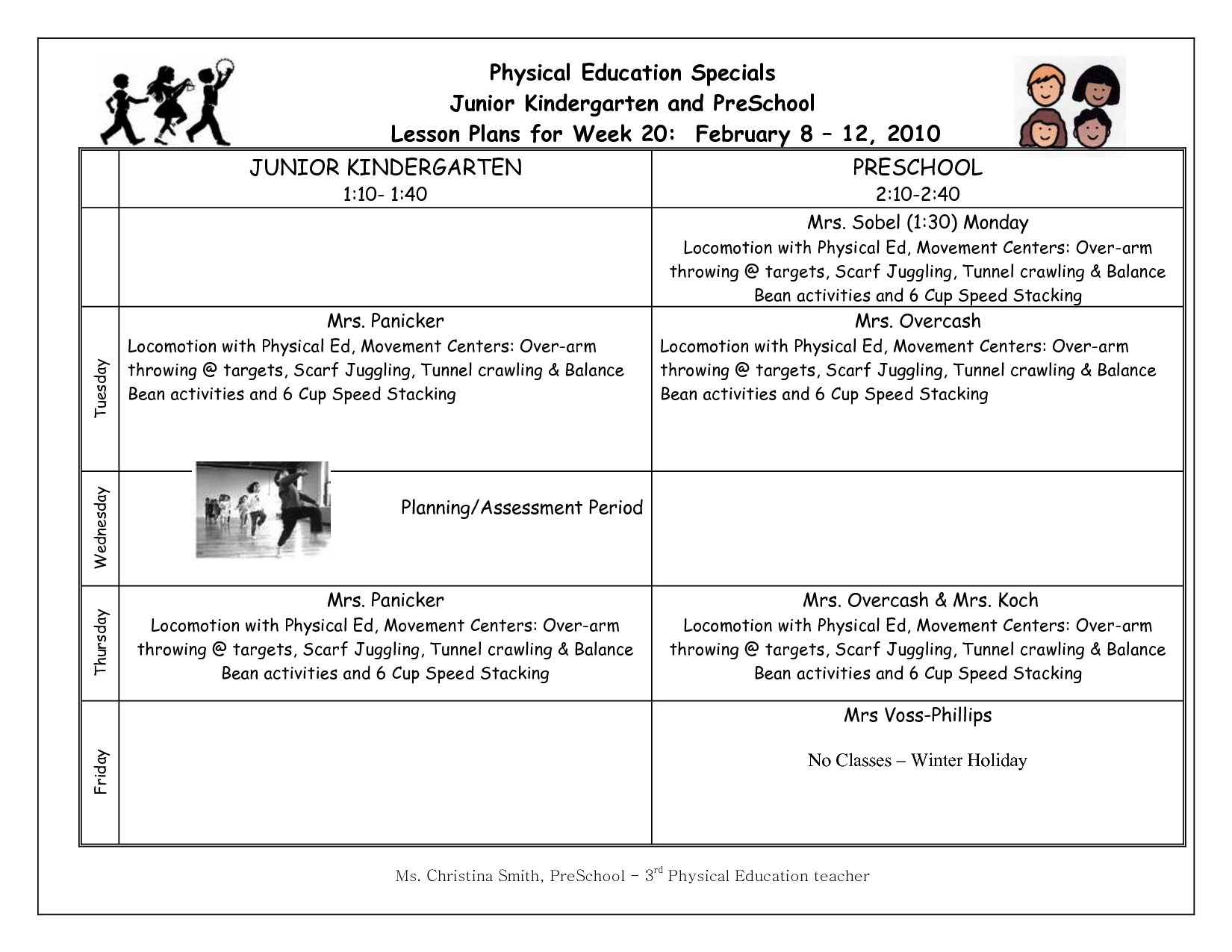
- Elementary Physical Education Lesson Plans
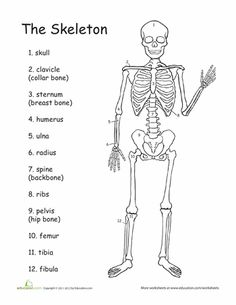
- Human Body Worksheets 4th Grade
- Life Science Worksheets 4th Grade
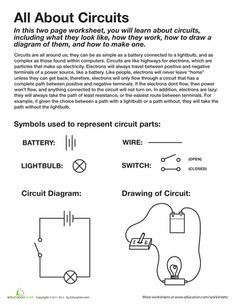
- Simple Circuit Worksheets 4th Grade
- Anti-Bullying Worksheets
- Station Key Science Worksheet
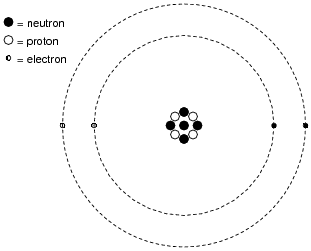
- Chemistry Atomic Structure Worksheet Answers
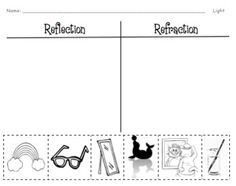
- Absorption Reflection and Refraction for Kids
- Physical vs Chemical Change Worksheet
- 4th Grade Map Skills Worksheets
- Printable Blank Lesson Plan Templates
- Crime Scene Sketches Examples
- Inside the Atom Worksheet
- Lion Animal Coloring Pages
More Science Worksheets
6 Grade Science WorksheetsScience Heat Energy Worksheets with Answer
Science Worksheets Light and Sound
1st Grade Life Science Worksheets
7th Grade Science Cells Worksheets
Worksheets Life Science Vocabulary
8th Grade Science Scientific Method Worksheet
Science Worksheets All Cells
5th Grade Science Mixtures and Solutions Worksheets
What is a physical property?
A physical property is a characteristic of a substance that can be observed or measured without changing the substance's chemical composition. Examples of physical properties include color, density, melting point, boiling point, and conductivity. These properties help to identify and describe different substances and can be used to distinguish one substance from another.
Give an example of a solid, liquid, and gas.
An example of a solid is ice, a liquid is water, and a gas is steam.
What is the difference between mass and weight?
Mass is a measure of the amount of matter present in an object, measured in units like grams or kilograms, and is constant regardless of the location. Weight, on the other hand, is the force of gravity acting on an object's mass, measured in units like newtons or pounds, and varies depending on the strength of the gravitational field experienced at a particular location. In simpler terms, mass stays the same no matter where you are in the universe, but weight can change depending on the gravitational pull of a planet or celestial body.
How does temperature affect the states of matter?
Temperature plays a crucial role in determining the states of matter. When temperature increases, particles gain energy and move more rapidly, causing them to overcome their intermolecular forces and transition from one state to another. For example, a solid will melt into a liquid as temperature rises, and a liquid will vaporize into a gas at higher temperatures. Conversely, decreasing temperature will cause particles to slow down and eventually lead to the condensation of a gas into a liquid, and the solidification of a liquid into a solid.
What is an element?
An element is a pure substance that is made up of only one type of atom. It cannot be broken down into simpler substances by chemical means and is represented by its unique atomic number on the periodic table of elements. Each element has distinct chemical properties that determine its behavior and reactivity in chemical reactions.
How are mixtures different from compounds?
Mixtures are composed of two or more different substances that are physically combined and can be easily separated, while compounds are composed of two or more elements that are chemically bonded together in definite proportions and cannot be easily separated. Mixtures retain the properties of their individual substances, whereas compounds have unique properties distinct from their component elements.
What is the difference between physical and chemical changes?
Physical changes are changes in the appearance or state of a substance that do not alter its chemical composition, such as melting ice or boiling water. On the other hand, chemical changes involve the formation of new substances with different chemical compositions through chemical reactions, such as rusting of iron or burning wood.
How does energy transfer occur?
Energy transfer occurs when energy moves from one place or object to another. This transfer can happen through various mechanisms such as conduction, convection, and radiation. In conduction, energy is transferred through direct contact between objects. In convection, energy is transferred through the movement of fluids such as air or water. Radiation involves the transfer of energy through electromagnetic waves, such as light or heat. Overall, energy transfer is essential for maintaining balance in the natural world and powering various processes.
Explain the concept of buoyancy.
Buoyancy is the upward force exerted by a fluid that opposes the weight of an immersed object. According to Archimedes' principle, the buoyant force is equal to the weight of the fluid that the object displaces. When an object is more dense than the fluid it displaces, it will sink, but if the object is less dense, it will float. Objects that float displace an amount of fluid equal to their own weight, which allows them to stay afloat. Buoyancy plays a crucial role in various applications, such as designing ships, submarines, and hot air balloons.
How do magnets attract or repel each other?
Magnets attract or repel each other based on the orientation of their magnetic fields. Opposite poles - north and south - attract each other, while like poles - north and north, or south and south - repel each other. This interaction is governed by the force of magnetism, which is generated by the movement of electrons within the atoms of the magnetized materials, creating magnetic fields that interact with each other.
Have something to share?
Who is Worksheeto?
At Worksheeto, we are committed to delivering an extensive and varied portfolio of superior quality worksheets, designed to address the educational demands of students, educators, and parents.

























Comments