Phases of Meiosis Worksheet
Are you studying biology and looking for a comprehensive worksheet to help you understand the phases of meiosis? Look no further! This worksheet is designed to clearly explain the different phases of meiosis and help you strengthen your knowledge on this important biological process. Whether you're a high school student, college student, or simply interested in delving deeper into biology, this worksheet is the perfect tool for you. By walking you through each phase of meiosis, it will enhance your understanding of this complex topic and aid in your academic success.
Table of Images 👆
- Meiosis Stages Worksheet
- Meiosis Stages Worksheet
- Cut and Paste Meiosis Worksheet Answers
- Meiosis Matching Worksheet Answer Key
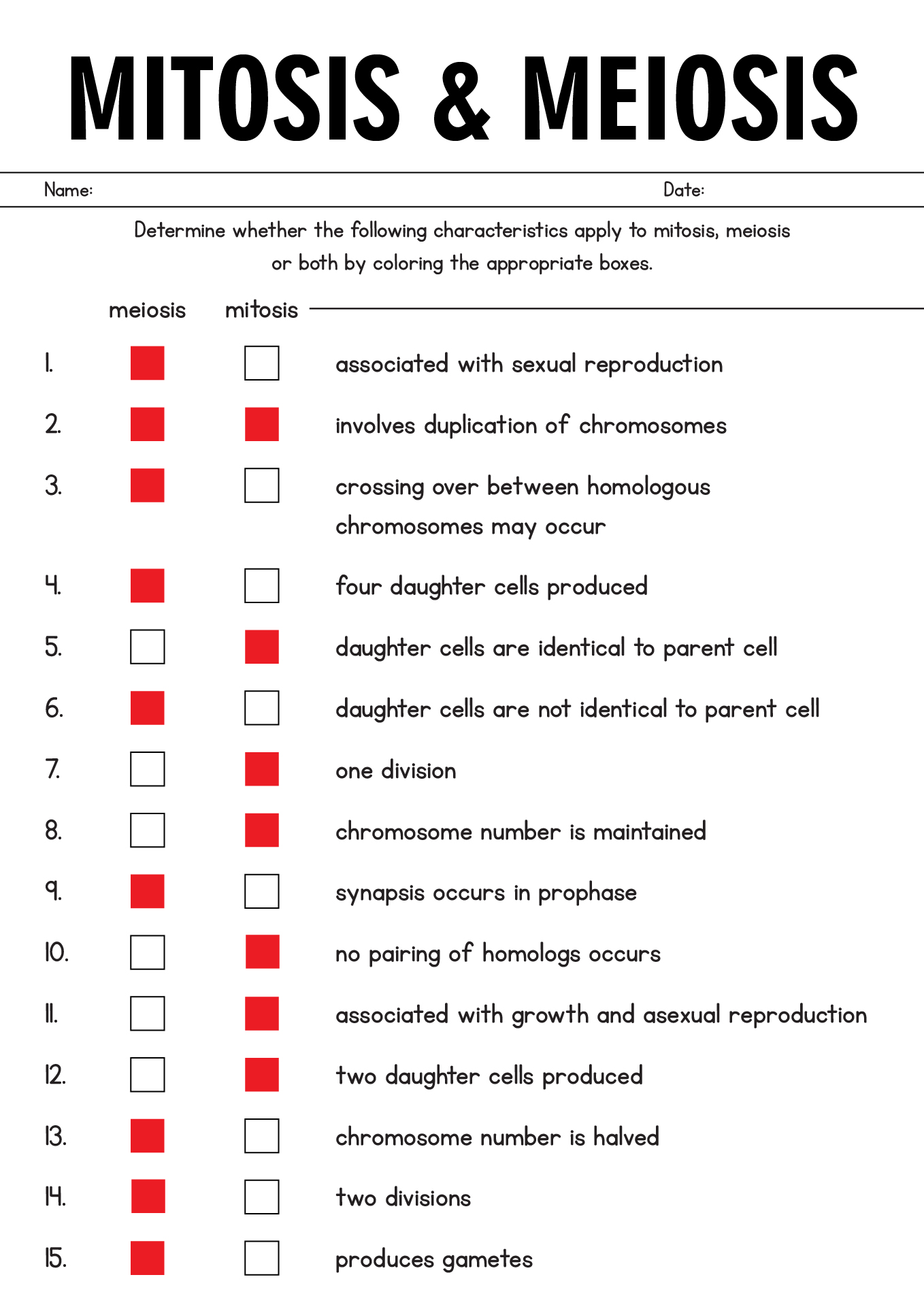
- Biology Meiosis Worksheet Answer Key
- Mitosis and Meiosis Coloring Worksheets
- Meiosis and Mitosis Worksheet Answers
- Mitosis and Meiosis Worksheet Answer Key
- Meiosis Drawing Worksheet
- Cell Cycle and Mitosis Worksheet Answers
- Cell Cycle and Mitosis Worksheet Answers
- Meiosis and Mitosis Worksheet Answers
- Meiosis and Mitosis Worksheet
- Fill in the Blank Mitosis Worksheet Answer Key
- Meiosis and Mitosis Worksheet Answers
- Cellsalive Meiosis Worksheet Answers
- Mitosis Coloring Worksheet

More Other Worksheets
Kindergarten Worksheet My RoomSpanish Verb Worksheets
Healthy Eating Plate Printable Worksheet
Cooking Vocabulary Worksheet
My Shadow Worksheet
Large Printable Blank Pyramid Worksheet
Relationship Circles Worksheet
DNA Code Worksheet
Meiosis Worksheet Answer Key
Rosa Parks Worksheet Grade 1
What is the purpose of meiosis?
The purpose of meiosis is to produce gametes, such as eggs and sperm, with half the number of chromosomes as the parent cell. This process is essential for sexual reproduction as it ensures genetic diversity in offspring by combining genetic material from two different parents. Additionally, meiosis also facilitates genetic recombination, leading to variations in the genetic makeup of offspring.
How many stages are there in meiosis?
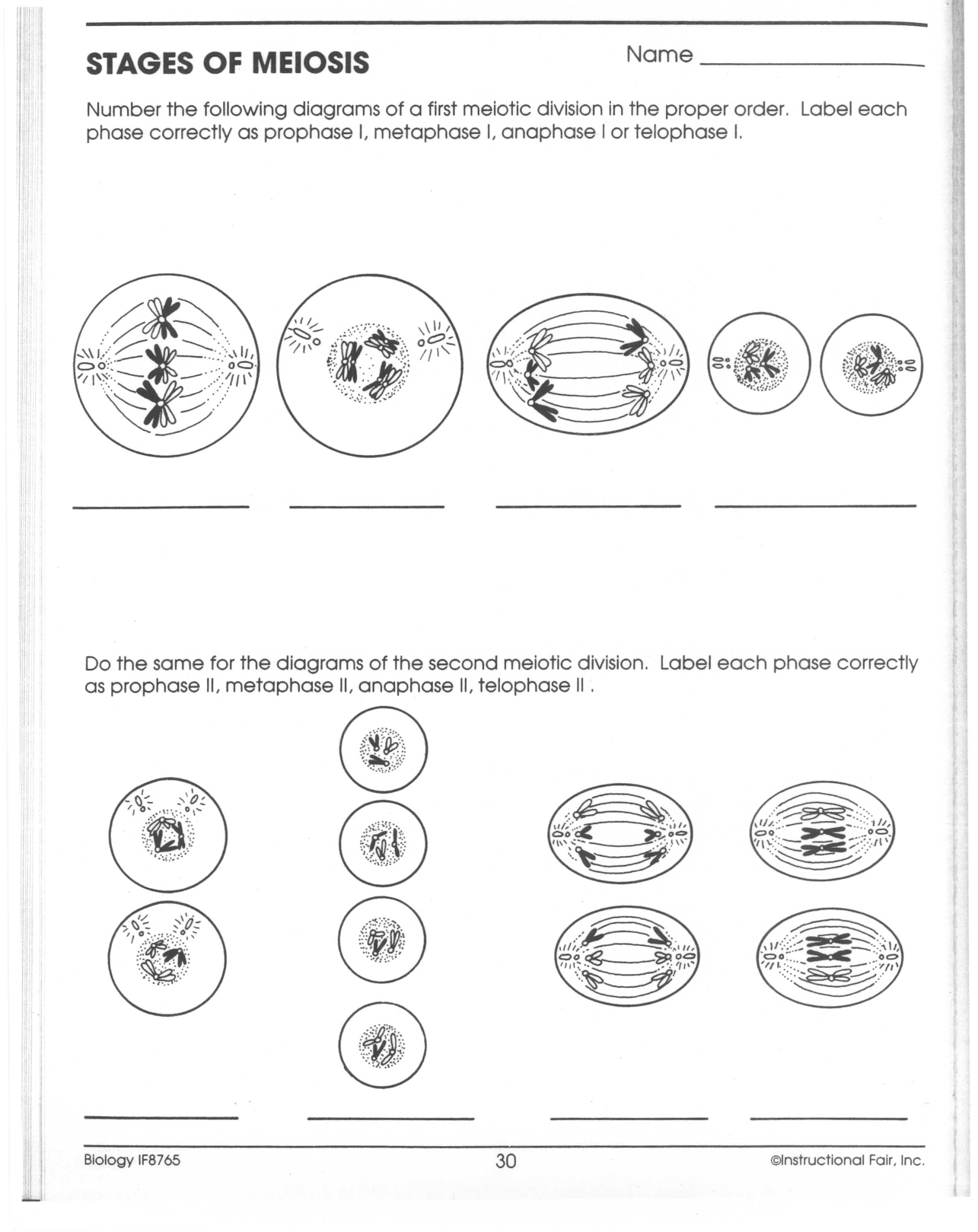
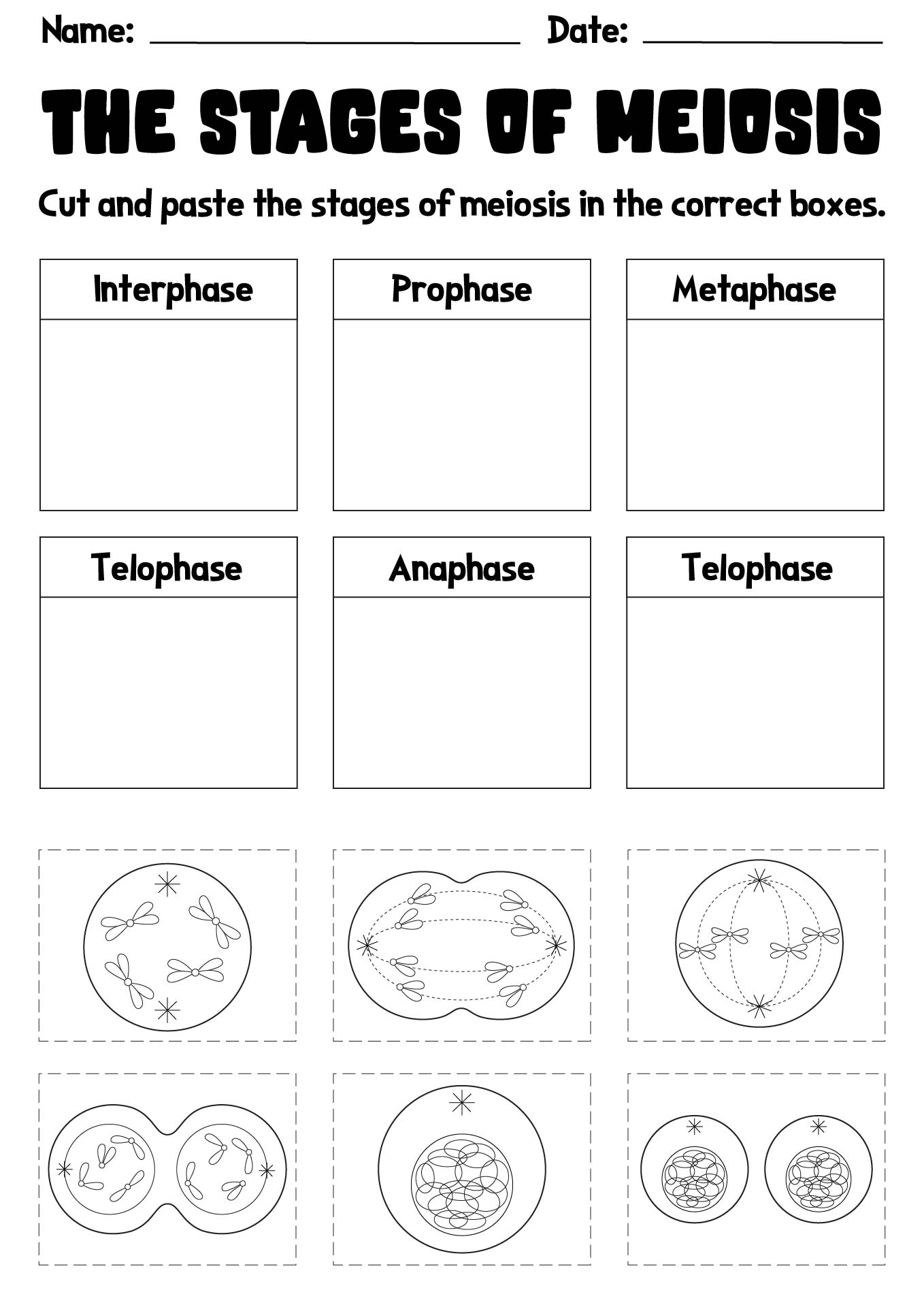
There are two stages in meiosis: meiosis I and meiosis II.
What happens in prophase I of meiosis?
In prophase I of meiosis, homologous chromosomes pair up and exchange genetic material through a process called genetic recombination or crossing over. This results in a shuffling of genetic information between chromosomes, promoting genetic diversity. Additionally, the nuclear envelope breaks down, and spindle fibers begin to form, preparing the cell for the subsequent stages of meiosis.
What is crossing over and when does it occur?
Crossing over is a process in genetics where homologous chromosomes exchange genetic material during meiosis. This occurs during prophase I of meiosis, specifically during the stage known as the pachytene. During crossing over, sections of the chromosomes are swapped, resulting in genetic recombination and the creation of new combinations of genes on the chromosomes.
Describe the events that take place during metaphase I.
During metaphase I of meiosis, homologous chromosomes line up at the equatorial plate of the cell and become attached to the spindle fibers. This alignment ensures that each homologous pair will separate correctly during anaphase I. Additionally, the crossing over of genetic material between homologous chromosomes that occurred during prophase I become visible as chiasmata, further increasing genetic diversity.
What is the significance of independent assortment during anaphase I?
Independent assortment during anaphase I is significant because it is the process by which homologous chromosomes line up independently at the metaphase plate and are randomly pulled apart to opposite poles during anaphase I of meiosis. This results in the creation of genetically diverse daughter cells with unique combinations of alleles from each parent, increasing genetic variation within a population and allowing for the possibility of new gene combinations that can lead to evolutionary changes or adaptation.
Explain what happens during telophase I and cytokinesis.
During telophase I of meiosis, the chromosome sets reach opposite ends of the cell, and a new nuclear membrane forms around each set. The chromosomes begin to decondense, and cytokinesis, the division of the cytoplasm, follows to create two haploid daughter cells. Each daughter cell has half the number of chromosomes as the original cell and is genetically distinct due to the crossing over and independent assortment that occurred during prophase I and metaphase I.
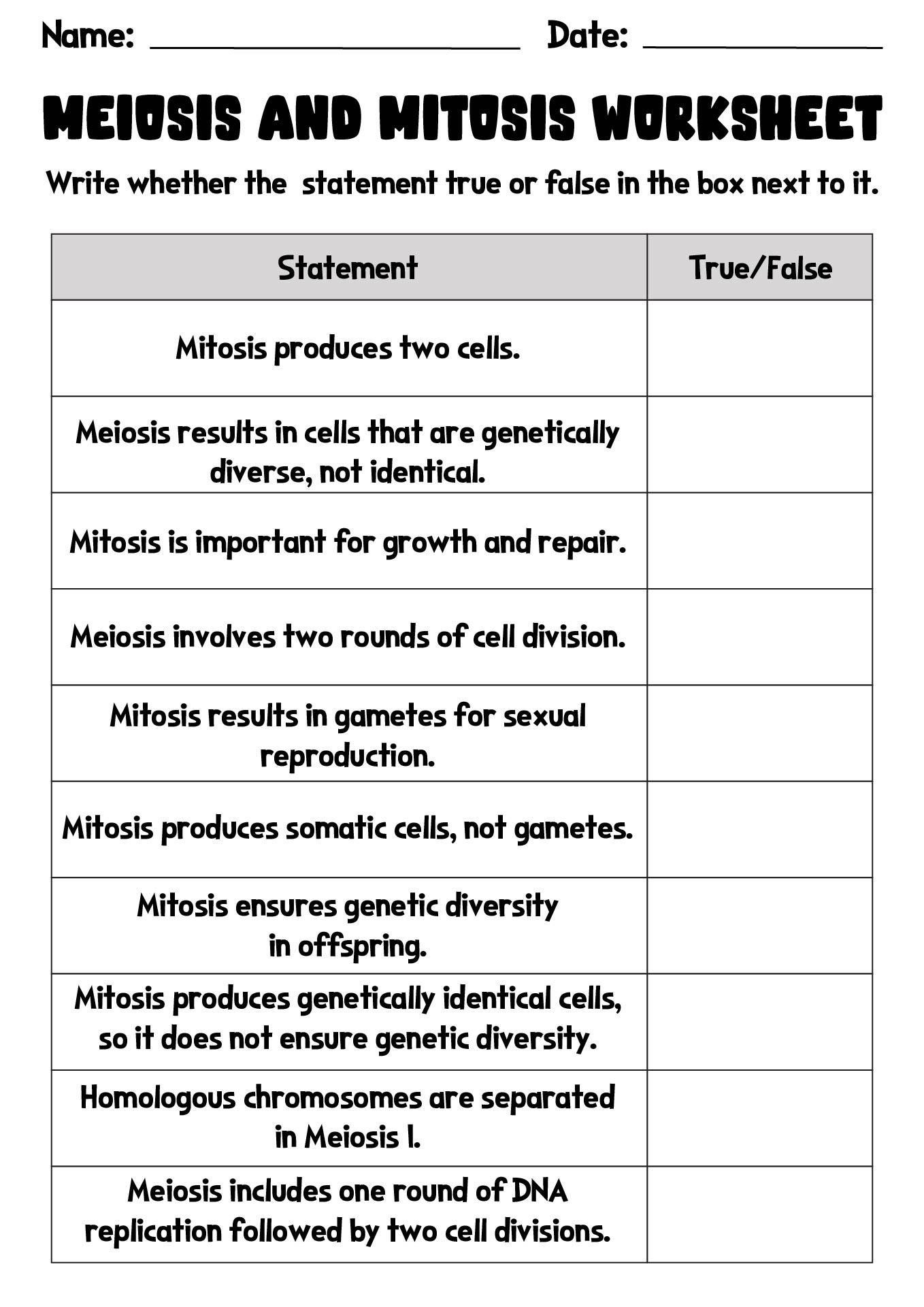
What is the main difference between meiosis I and meiosis II?
The main difference between meiosis I and meiosis II is that during meiosis I, homologous chromosomes pair up and exchange genetic material in a process called crossing over, leading to genetic diversity, while in meiosis II, sister chromatids separate into individual chromosomes without any further genetic exchange. Meiosis I is also responsible for reducing the chromosome number by half, whereas meiosis II primarily involves separating the sister chromatids to produce haploid cells.
Describe the events that occur during prophase II.
During prophase II, which is the first stage of the second meiotic division, the nuclear envelope breaks down, and the chromosomes condense. Each chromosome consists of two sister chromatids held together by a centromere. The centrioles move to opposite poles of the cell, and spindle fibers start to form. These spindle fibers will attach to the centromeres of the chromosomes and help move them to the metaphase II stage of meiosis.
How does meiosis contribute to genetic diversity?
Meiosis contributes to genetic diversity through several key mechanisms, including independent assortment, crossing over, and random fertilization. Independent assortment allows homologous chromosomes to randomly line up and segregate during meiosis I, leading to a unique combination of maternal and paternal chromosomes in each gamete. Crossing over, which occurs during prophase I, exchanges genetic material between homologous chromosomes, creating new combinations of alleles. Lastly, random fertilization involves the chance fusion of gametes during fertilization, further increasing genetic variability by combining different genetic material from each parent. These processes collectively increase genetic diversity among offspring, promoting evolutionary adaptation and genetic variability within a species.
Have something to share?
Who is Worksheeto?
At Worksheeto, we are committed to delivering an extensive and varied portfolio of superior quality worksheets, designed to address the educational demands of students, educators, and parents.




























Comments