Periodic Trends Worksheet Answers Key
Are you a high school or college student studying chemistry and struggling to understand periodic trends? Look no further! In this blog post, we will be providing the answers key for the periodic trends worksheet. This worksheet is designed to help you grasp the concept of periodic trends by focusing on the entity and subject. By providing the answers key, we aim to enhance your learning experience and make the process of understanding these trends easier for you.
Table of Images 👆
- Periodic Trends Worksheet Answer Key
- Periodic Table Trends Worksheet Answer Key
- Periodic Trends Worksheet Answer Key
- Periodic Table Trends Worksheet Answer Key
- Periodic Trends Worksheet Answer Key
- Periodic Trends Worksheet Answer Key
- Periodic Table Trends Worksheet Answer Key
- Periodic Trends Worksheet Answer Key
- Periodic Trends Worksheet Answer Key
- Periodic Trends Worksheet Answers
- Periodic Table Worksheet Answer Key
- Chemistry Periodic Table Trends Worksheet
- Periodic Trends Worksheet Answers
- Periodic Table Worksheet Answers
- Periodic Table Worksheet Answer Key
- Periodic Trends Worksheet Answers
- Periodic Table Trends Worksheet Answer Key
- Periodic Trends Worksheet
- Periodic Trends Worksheet Answer Key
- Periodic Table Basics Worksheet Answer Key
More Other Worksheets
Kindergarten Worksheet My RoomSpanish Verb Worksheets
Cooking Vocabulary Worksheet
My Shadow Worksheet
Large Printable Blank Pyramid Worksheet
Relationship Circles Worksheet
DNA Code Worksheet
Meiosis Worksheet Answer Key
Art Handouts and Worksheets
7 Elements of Art Worksheets
What are periodic trends?
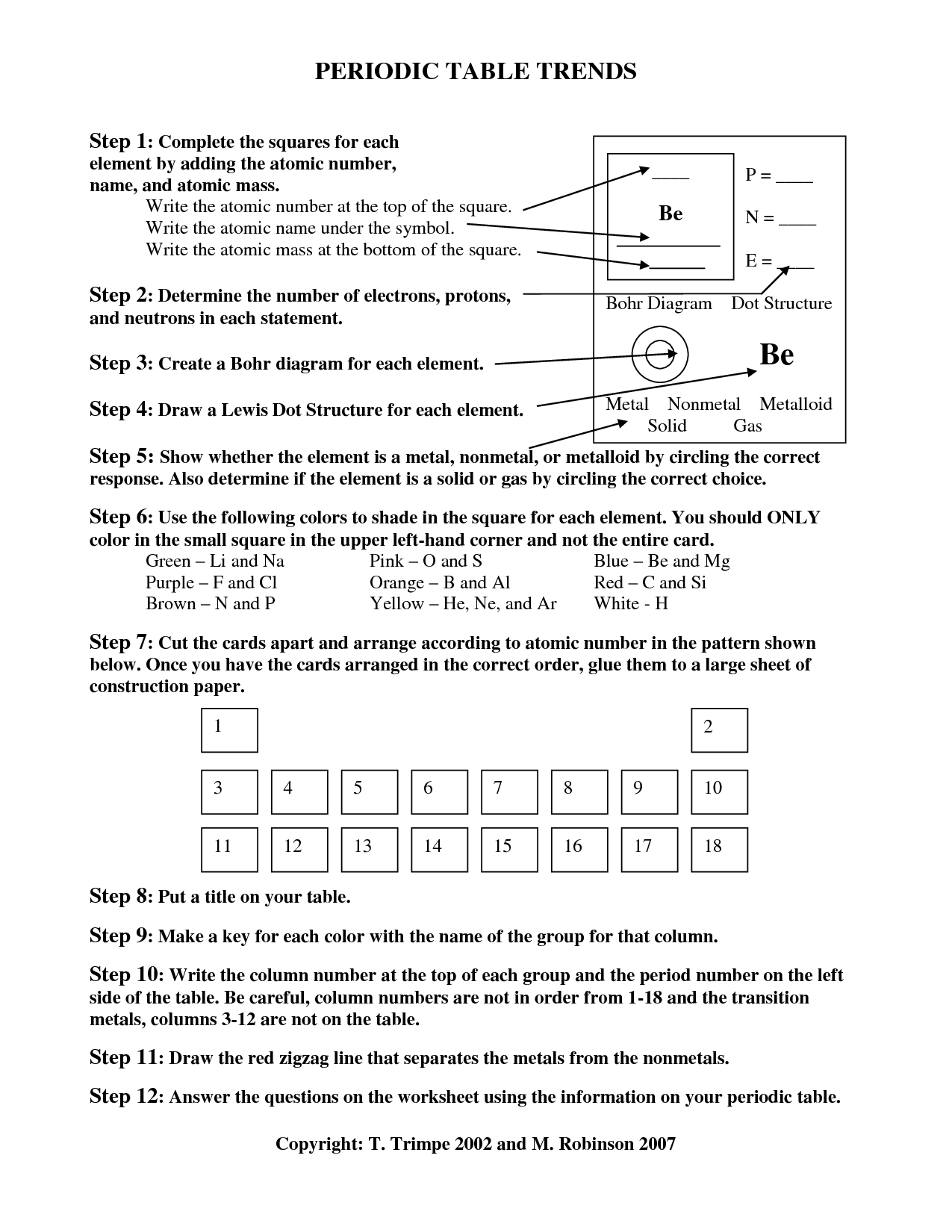
Periodic trends refer to the variations in properties of elements that occur as you move across or down the periodic table. These trends arise due to the increasing atomic number and changing electron configurations of elements. Some common periodic trends include atomic size, ionization energy, electron affinity, and electronegativity. By studying these trends, scientists can predict and explain the behavior and properties of elements within the periodic table.
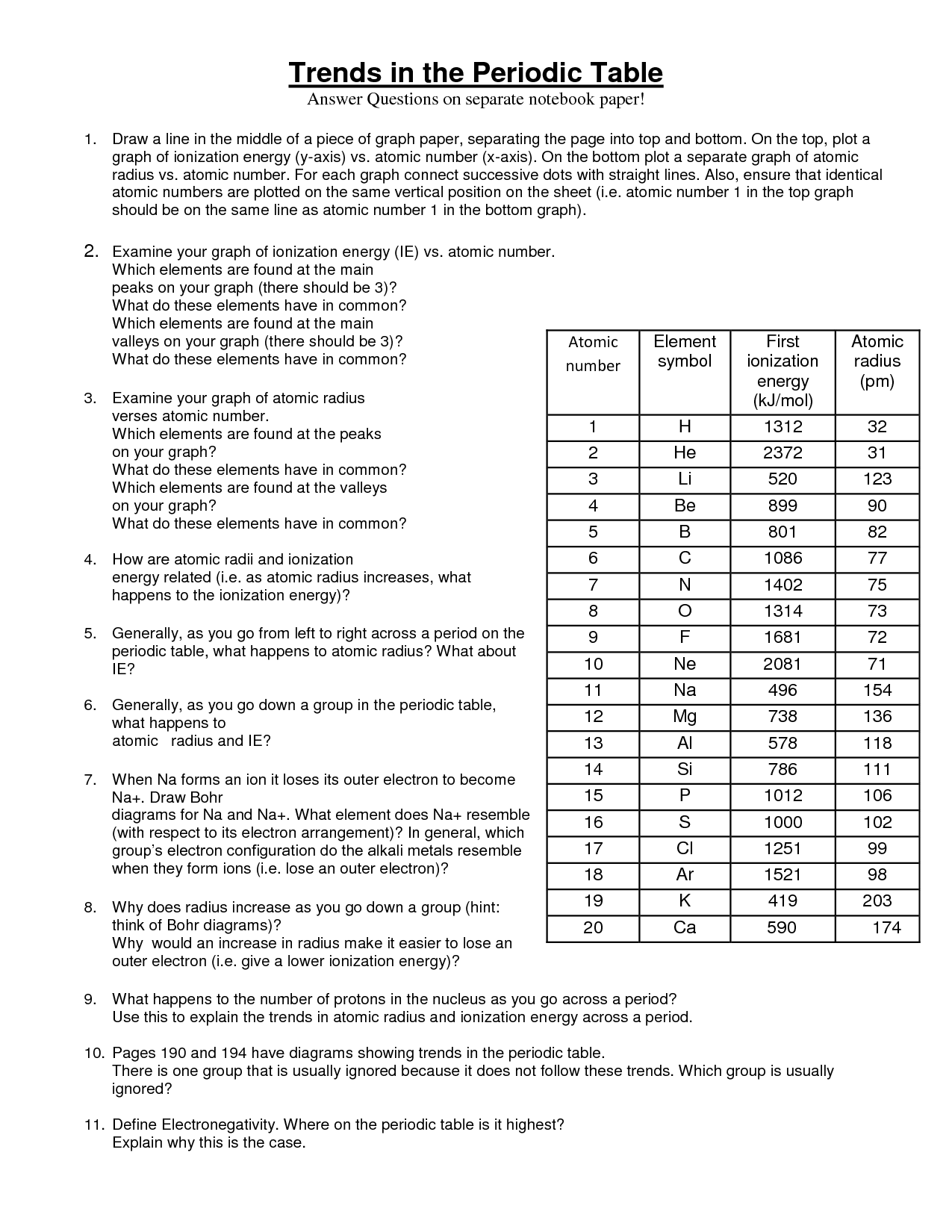
How do atomic radii change across a period?
In general, atomic radii decrease across a period from left to right. This is due to the increase in the number of protons in the nucleus, which exerts a stronger pull on the electrons in the same energy level, leading to a tighter electron cloud and smaller atomic radius. However, there may be slight fluctuations in atomic radii within a period due to factors such as electron-electron repulsions and electron shielding effects.
How do atomic radii change down a group?
Atomic radii generally increase as you move down a group in the periodic table. This is because as you move down a group, the number of electron shells or energy levels increases, leading to the electrons being further away from the nucleus. With the increase in the number of electron shells, the shielding effect increases, resulting in a decrease in the effective nuclear charge, which allows the outermost electrons to occupy larger orbitals and hence leads to an increase in the atomic radius.
What is ionization energy?
Ionization energy is the amount of energy required to remove an electron from an atom or ion in the gaseous state. It is a measure of how tightly an electron is held by an atom and is often used to predict the reactivity and chemical behavior of elements.
How does ionization energy change across a period?
Ionization energy tends to increase across a period from left to right. This is because as you move across a period, the number of protons in the nucleus increases, leading to a greater attractive force on the electrons in the outermost energy level. As a result, it becomes more difficult to remove an electron, resulting in higher ionization energy values.
How does ionization energy change down a group?
Ionization energy generally decreases down a group. This is because as you move down a group, the atomic size increases, and the valence electrons are located farther away from the nucleus. This results in weaker attraction between the nucleus and electrons, requiring less energy to remove an electron. Therefore, ionization energy decreases down a group as you move from top to bottom.
What is electronegativity?
Electronegativity is a measure of an atom's ability to attract and hold onto electrons in a chemical bond. It indicates how strongly an atom will pull shared electrons towards itself when forming a covalent bond with another atom. Elements with higher electronegativity values tend to attract electrons more strongly than elements with lower electronegativity values, leading to uneven distribution of charge in the molecule and influencing the overall chemical properties of the compound.
How does electronegativity change across a period?
Electronegativity generally increases across a period from left to right. This trend occurs because as the atomic number increases across a period, the nuclear charge of the atoms also increases, leading to a stronger pull on the shared electrons in covalent bonds. The increased electronegativity results in atoms being able to attract electrons more strongly, making them more likely to form negative ions or attract electrons in a chemical bond.
How does electronegativity change down a group?
Electronegativity generally decreases as you move down a group on the periodic table. This is because as you move down a group, the atomic size increases, which results in a weaker attraction between the nucleus and the outer electrons. As a result, the ability of an atom to attract and hold onto electrons decreases, leading to lower electronegativity values.
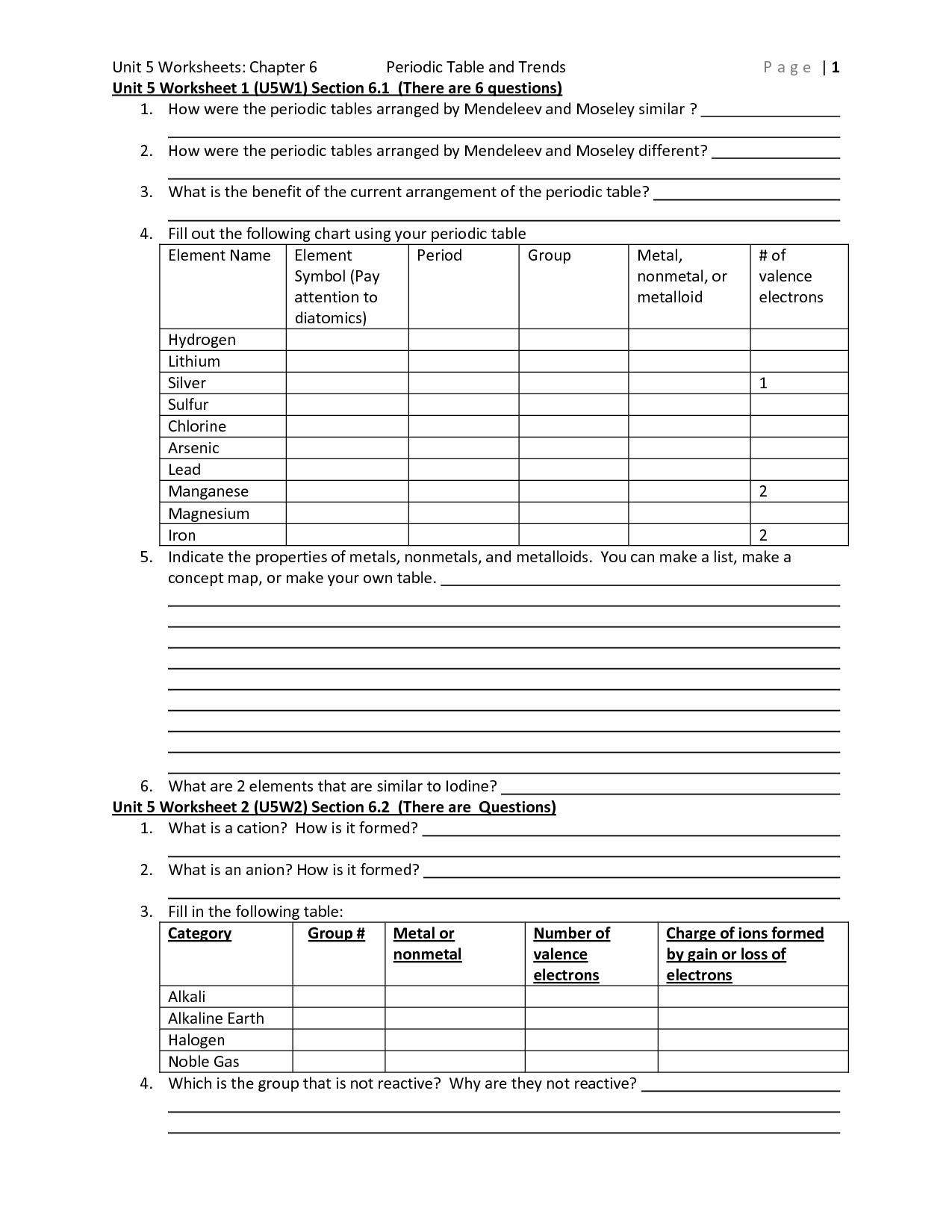
What are the trends in metallic character across the periodic table?
The metallic character increases as you move down a group in the periodic table and decreases as you move across a period from left to right. This is due to the increase in number of filled energy levels and shielding effect of inner electrons as you move down a group, leading to easier loss of electrons and increased metallic character. Conversely, as you move across a period from left to right, the increasing nuclear charge and decreasing atomic size result in stronger attraction between the nucleus and valence electrons, making it harder for them to be lost, leading to decreased metallic character.
Have something to share?
Who is Worksheeto?
At Worksheeto, we are committed to delivering an extensive and varied portfolio of superior quality worksheets, designed to address the educational demands of students, educators, and parents.



































Comments