Organic Macromolecules Worksheet Answer Key Packet
Are you a biology student looking for a reliable resource to reinforce your understanding of organic macromolecules? Look no further! In this blog post, we'll introduce you to an invaluable tool - the organic macromolecules worksheet answer key packet. Designed to provide comprehensive and accurate answers to the accompanying worksheet, this packet will help you master the concepts and principles related to organic macromolecules. Whether you are studying for exams or simply want to enhance your knowledge, this worksheet answer key packet is an essential asset.
Table of Images 👆
- Elements and Macromolecules in Organisms Answer Key
- Organic Molecules Worksheet Review Answers
- Elements and Macromolecules in Organisms Answer Key
- Elements and Macromolecules in Organisms Worksheet Answers
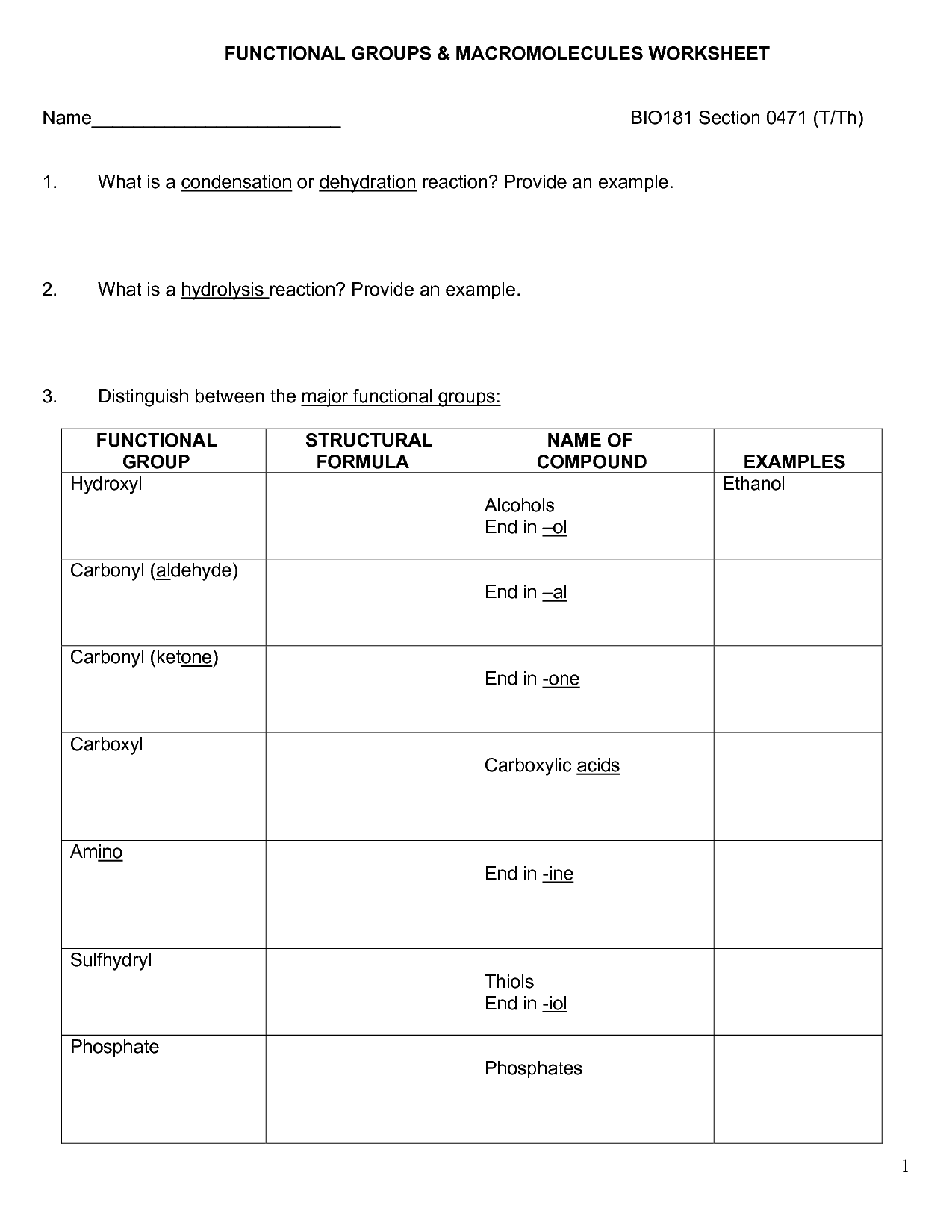
- Organic Macromolecules Worksheet Answers
- Rabbit Population By Season Gizmo Answer Key
- Macromolecule Worksheet Answer Key
- Molecules of Life Worksheet Answers
- Macromolecule Worksheet Answer Key
- Molecules and Atoms Worksheet Answer Key
- Macromolecules Worksheet Answers
- Carbohydrates Worksheet Answers
- Graphic Organizer Rubrics Assessment
- DNA the Molecule of Heredity Worksheet Answer Key
- Organic Molecules Worksheet Review Answer Key
- Section 12 4 Mutations Answer Key
More Other Worksheets
Kindergarten Worksheet My RoomSpanish Verb Worksheets
Cooking Vocabulary Worksheet
My Shadow Worksheet
Large Printable Blank Pyramid Worksheet
Relationship Circles Worksheet
DNA Code Worksheet
Meiosis Worksheet Answer Key
Art Handouts and Worksheets
7 Elements of Art Worksheets
What are organic macromolecules?
Organic macromolecules are large, carbon-based compounds found in living organisms, such as carbohydrates, proteins, lipids, and nucleic acids. These molecules play essential roles in a variety of biological processes, from providing energy to supporting structure and functioning as genetic material. They are characterized by their complex structures and the presence of carbon-carbon and carbon-hydrogen bonds.
What are the four major types of organic macromolecules?
The four major types of organic macromolecules are carbohydrates, lipids, proteins, and nucleic acids. Carbohydrates are a source of energy and include sugars and starches; lipids serve as energy storage and include fats and oils; proteins are involved in structural support and biochemical reactions; and nucleic acids store and transmit genetic information, such as DNA and RNA.
What is the main function of carbohydrates?
Carbohydrates are primarily used by the body as a source of energy. They are broken down into glucose, which is then used by cells as fuel to carry out various metabolic processes and provide energy for physical activities and bodily functions. Additionally, carbohydrates play a role in supporting brain function, facilitating digestion, and aiding in the storage and transport of nutrients within the body.
What are the two types of nucleic acids?
The two types of nucleic acids are DNA (deoxyribonucleic acid) and RNA (ribonucleic acid). DNA carries the genetic information of an organism and is responsible for inheritance, while RNA is involved in protein synthesis and various cellular functions. Both DNA and RNA are essential molecules for the storage and transmission of genetic information in living organisms.
What is the primary function of proteins?
Proteins serve a wide variety of functions in the body, but their primary function is to act as building blocks for tissues and organs, as well as to regulate and catalyze biochemical reactions in the body. Proteins are essential for growth, repair, and maintenance of cells, and they also play a vital role in the immune system, muscle contractions, and transporting molecules within the body.
What is the structural formula for glucose?
The structural formula for glucose is C6H12O6, which represents its six carbon, twelve hydrogen, and six oxygen atoms arranged in a specific configuration.
What is the difference between saturated and unsaturated fats?
Saturated fats are solid at room temperature and usually come from animal sources, while unsaturated fats are usually liquid at room temperature and mostly come from plant sources. Saturated fats have single bonds between carbon atoms in their fatty acid chains, making them rigid, while unsaturated fats have double bonds, which introduce kinks in their structure, making them more flexible. This difference affects how these fats are metabolized in the body and can impact health outcomes such as heart disease risk.
What is the structure of a nucleotide?
A nucleotide is composed of a nitrogenous base (either adenine, guanine, cytosine, or thymine in DNA; or adenine, guanine, cytosine, or uracil in RNA), a five-carbon sugar (either deoxyribose in DNA or ribose in RNA), and a phosphate group. This three-part structure forms the building blocks of DNA and RNA molecules, which are essential for genetic information storage and protein synthesis in living organisms.
What are the monomers of proteins called?
The monomers of proteins are called amino acids.
What is the function of enzymes in biological reactions?
Enzymes are biological catalysts that accelerate chemical reactions by lowering the activation energy required for the reaction to occur. They facilitate the conversion of substrate molecules into products, ultimately speeding up the rate of biological reactions. Enzymes are highly specific in their actions, binding to specific substrates and promoting specific reactions, contributing to the regulation and efficiency of various biochemical processes in living organisms.
Have something to share?
Who is Worksheeto?
At Worksheeto, we are committed to delivering an extensive and varied portfolio of superior quality worksheets, designed to address the educational demands of students, educators, and parents.
































Comments