Organic Compounds Worksheet
Are you searching for a helpful tool to reinforce your understanding of organic compounds? Look no further. This blog post introduces a comprehensive and engaging organic compounds worksheet designed specifically for students seeking to solidify their knowledge and enhance their learning experience in chemistry.
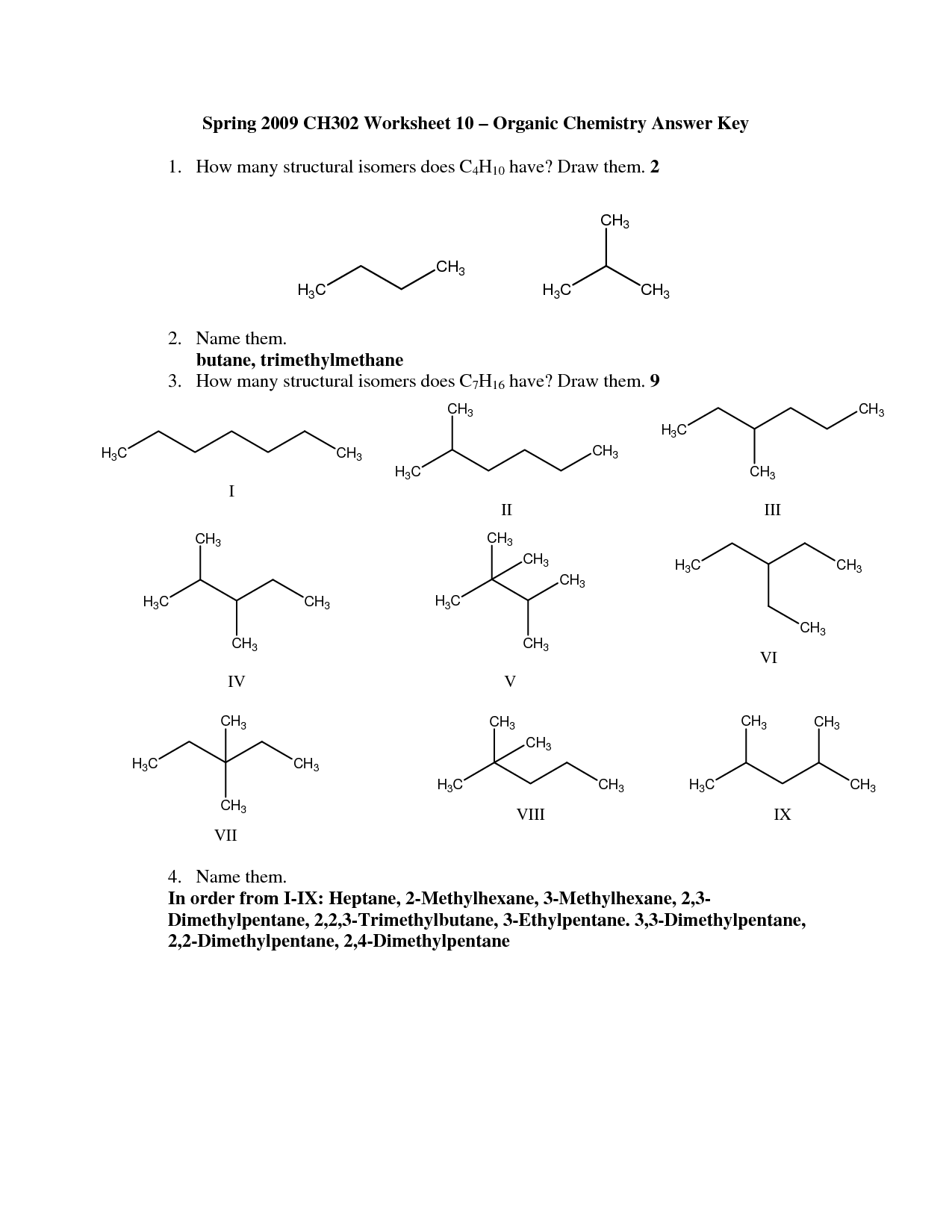
Table of Images 👆
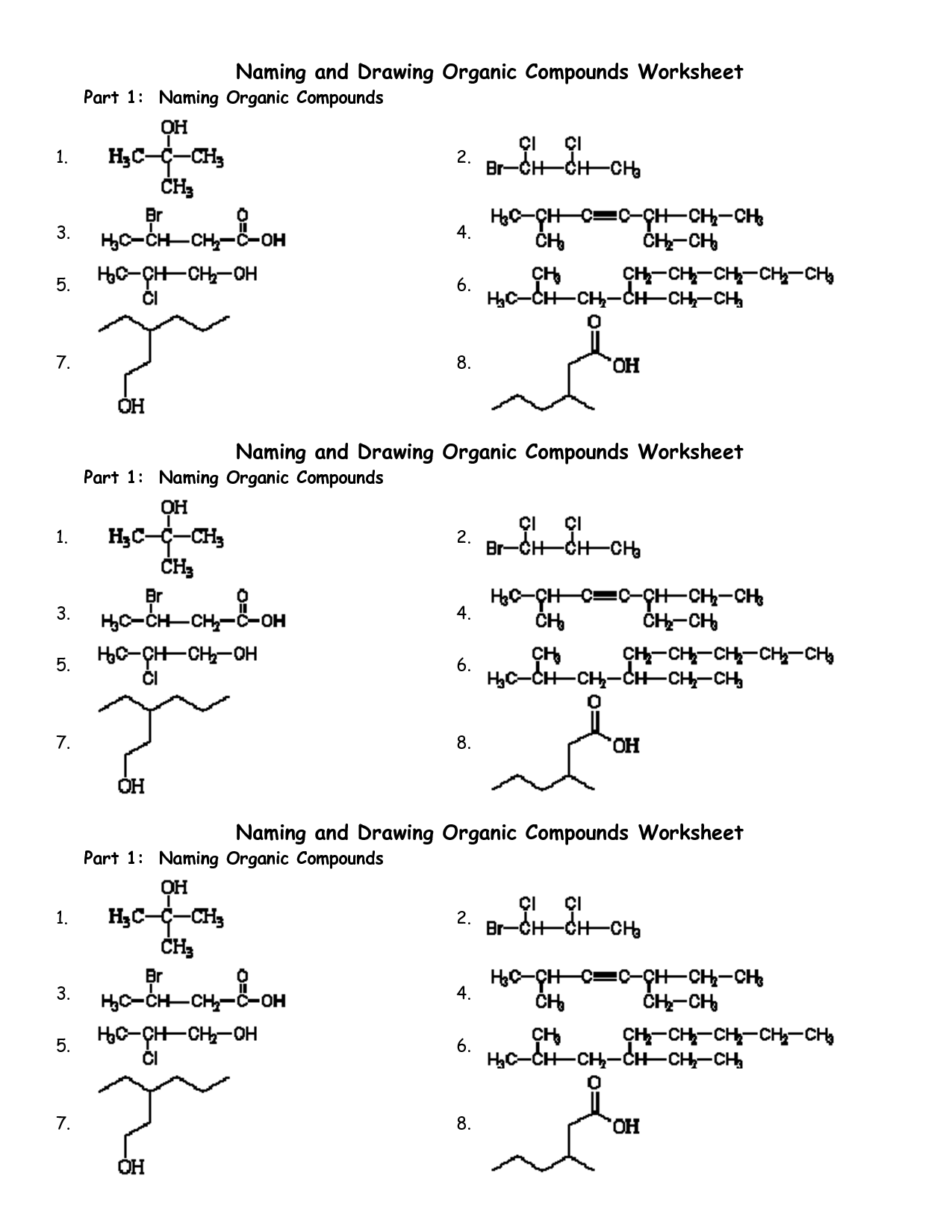
- Naming Organic Compounds Worksheet
- Molecular Compounds Worksheet
- Chemistry Organic Compounds Worksheets
- Naming Organic Compounds Practice Worksheet
- Organic Functional Groups Worksheet
- Naming Covalent Compounds Worksheet
- Naming Organic Compounds Practice Worksheet
- Organic and Inorganic Compounds Worksheet
- Naming Organic Compounds Worksheet
- Drawing Organic Compounds Worksheet
- Organic vs Inorganic Compounds Worksheet Answers
- Organic Chemistry Worksheets
- Organic vs Inorganic Compounds Worksheet
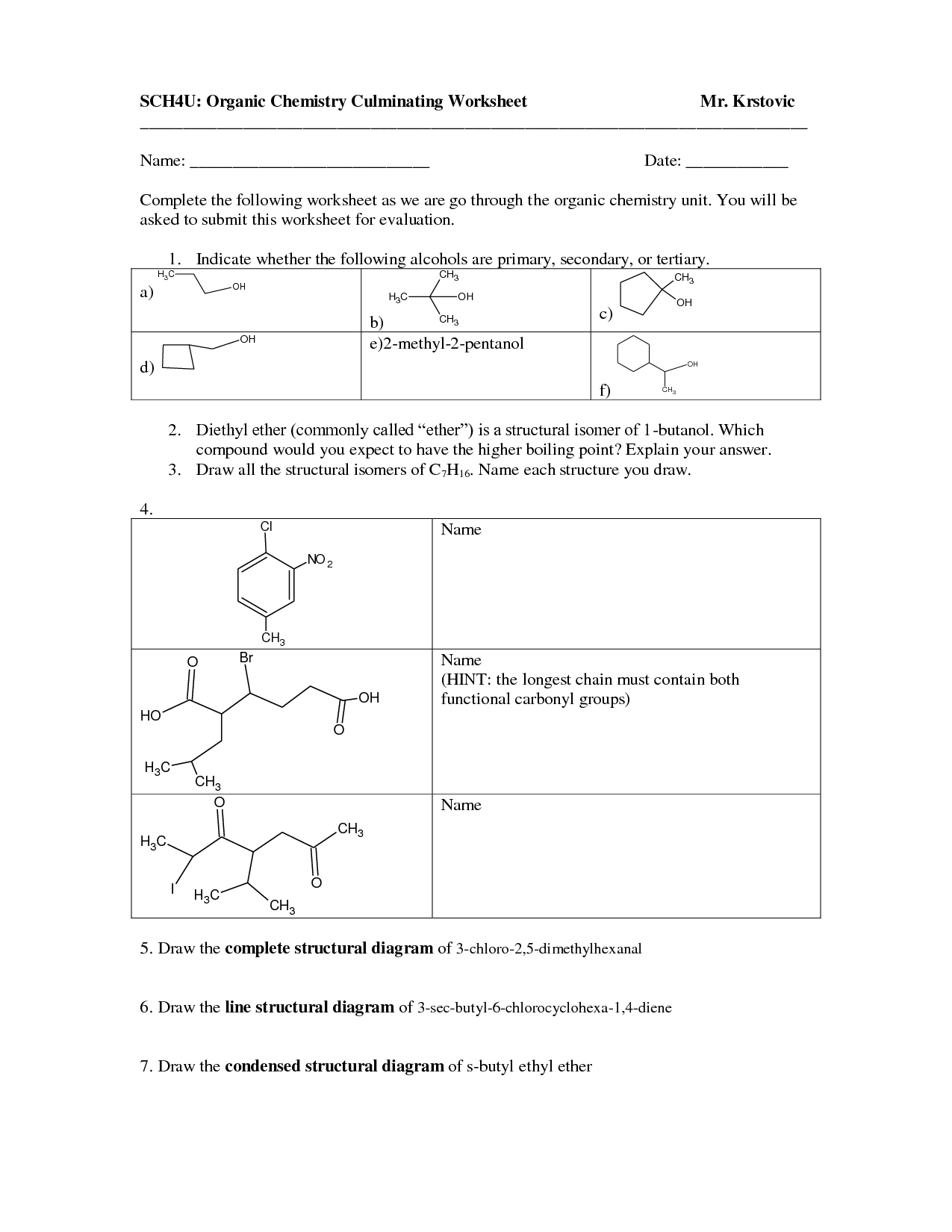
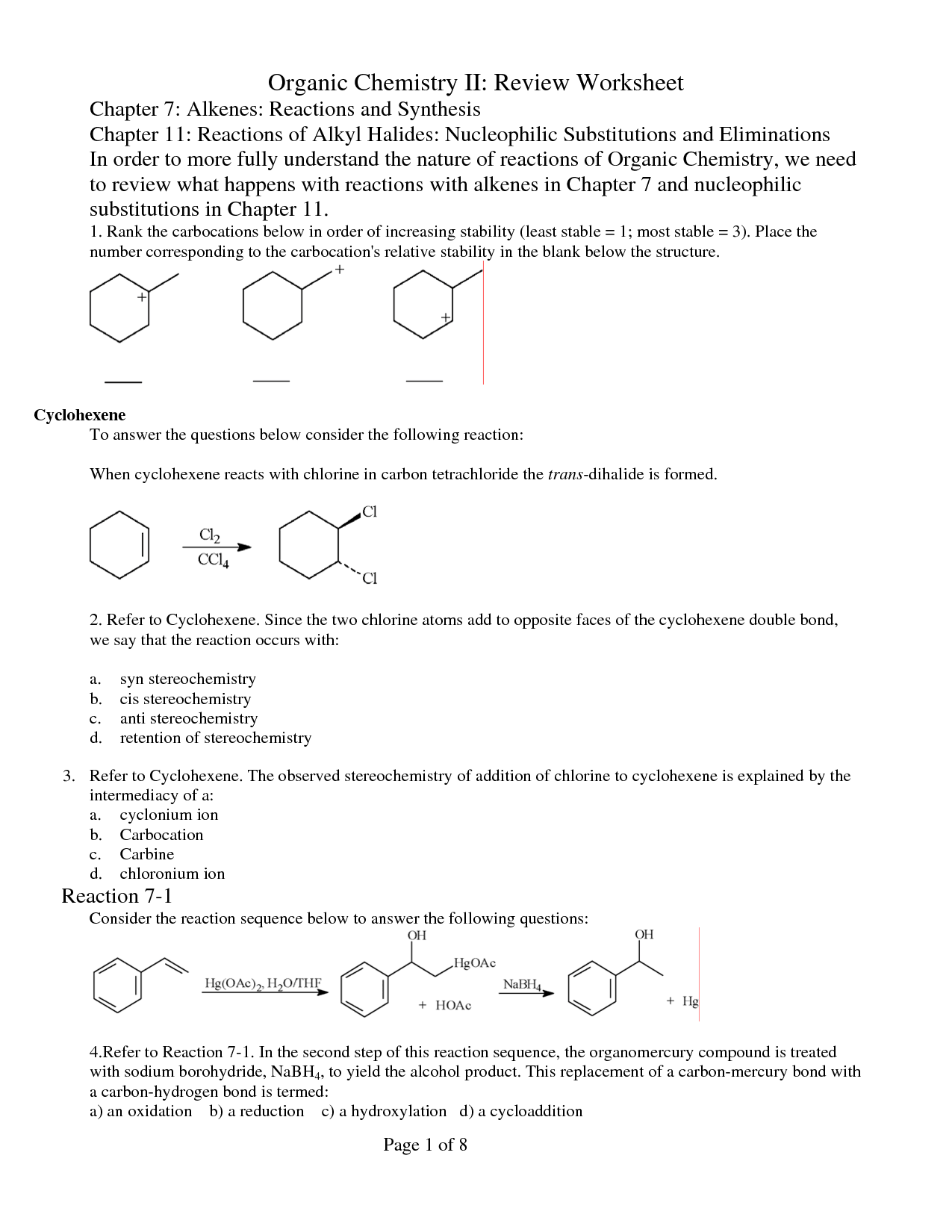
- Organic Chemistry Review Worksheets
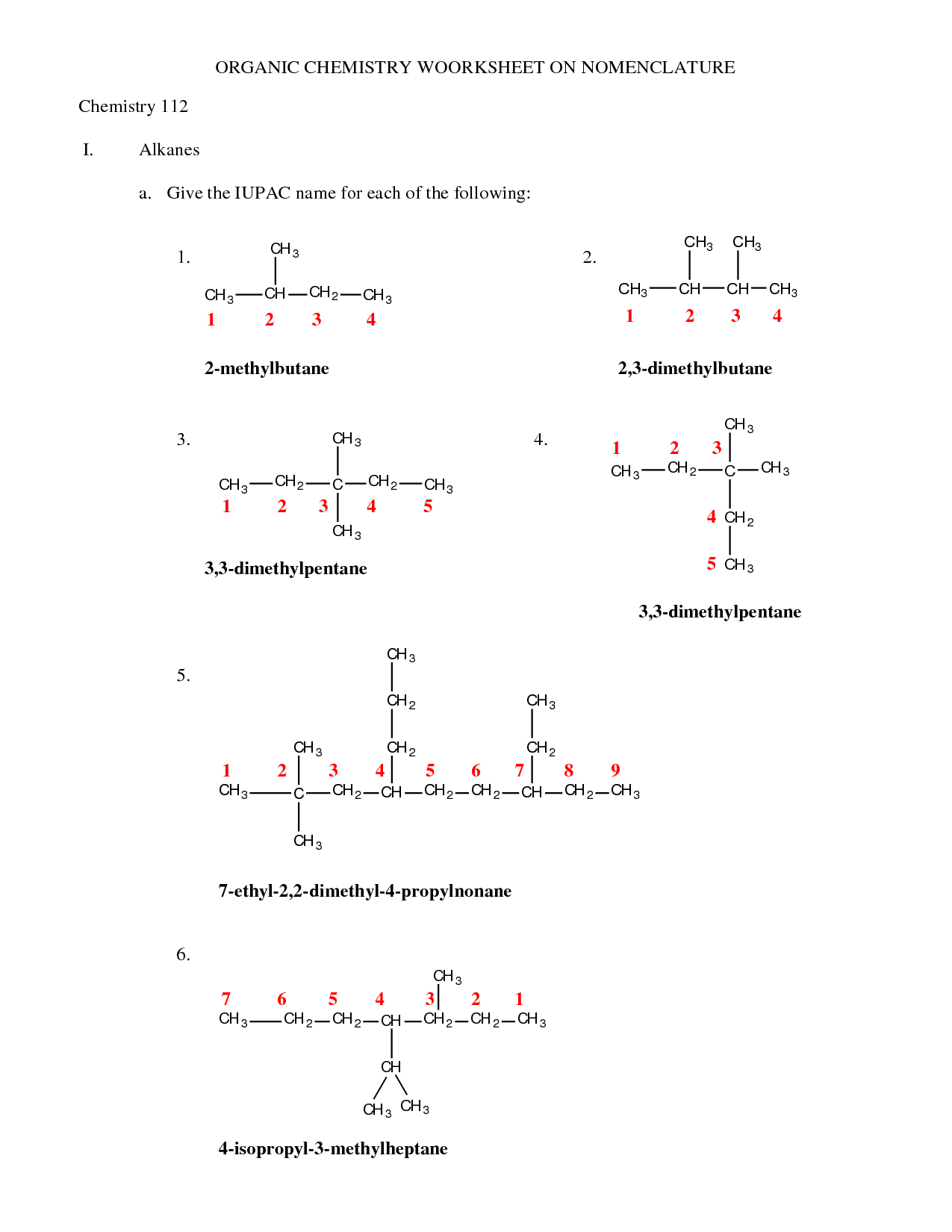
- Organic Chemistry Nomenclature Worksheets with Answers
- Organic Chemistry Worksheets Answers
- Organic Compounds Structure Worksheet
More Other Worksheets
Kindergarten Worksheet My RoomSpanish Verb Worksheets
Cooking Vocabulary Worksheet
My Shadow Worksheet
Large Printable Blank Pyramid Worksheet
Relationship Circles Worksheet
DNA Code Worksheet
Meiosis Worksheet Answer Key
Art Handouts and Worksheets
7 Elements of Art Worksheets
What are organic compounds?
Organic compounds are compounds that contain carbon atoms bonded to other elements such as hydrogen, oxygen, nitrogen, sulfur, and halogens. They are the basis of all living organisms and play a crucial role in various biological processes. Organic compounds can range from simple molecules like methane to complex structures such as proteins and DNA. They are typically found in natural sources like plants, animals, and fossil fuels.
What is the general chemical formula for carbohydrates?
The general chemical formula for carbohydrates is (CH2O)n, where "n" represents the number of carbon, hydrogen, and oxygen atoms in the molecule.
Give an example of a monosaccharide.
Glucose is a commonly known monosaccharide, which is a simple sugar that serves as an essential energy source for living organisms.
What type of bond holds amino acids together in a protein?
A peptide bond holds amino acids together in a protein. This bond forms through a condensation reaction between the carboxyl group of one amino acid and the amino group of another amino acid, resulting in the release of a water molecule.
Name two examples of unsaturated fatty acids.
Linoleic acid and oleic acid are examples of unsaturated fatty acids.
What is the primary function of lipids in living organisms?
The primary function of lipids in living organisms is to store energy, provide insulation, and act as structural components of cell membranes. Lipids also play a crucial role in cell signaling, hormone production, and the absorption of fat-soluble vitamins.
Define the term "isomer" in relation to organic compounds.
Isomer refers to organic compounds that have the same molecular formula but different structural arrangements, leading to distinct chemical and physical properties. Isomers can be classified into different categories such as structural isomers, stereoisomers, and geometric isomers based on the nature of their differences in structure or spatial arrangement of atoms.
How are organic compounds different from inorganic compounds?
Organic compounds are characterized by containing carbon-hydrogen bonds and are typically derived from living organisms, while inorganic compounds lack carbon-hydrogen bonds and are not necessarily derived from living organisms. Organic compounds tend to be more complex and varied in structure compared to inorganic compounds, which often have simpler structures. Additionally, organic compounds are often associated with chemical processes in living organisms, while inorganic compounds play crucial roles in non-living systems such as rocks, minerals, and metals.
Provide an example of a steroid molecule.
One example of a steroid molecule is cholesterol. Cholesterol is a type of lipid that is found in cell membranes and is a precursor for the synthesis of hormones like estrogen and testosterone. It plays a crucial role in maintaining the structural integrity of cell membranes and is essential for proper cellular function.
What is the main difference between saturated and unsaturated hydrocarbons?
The main difference between saturated and unsaturated hydrocarbons lies in their chemical structures. Saturated hydrocarbons contain only single bonds between carbon atoms, while unsaturated hydrocarbons contain one or more double or triple bonds between carbon atoms. As a result, saturated hydrocarbons have the maximum number of hydrogen atoms bonded to carbon atoms, making them saturated with hydrogen, whereas unsaturated hydrocarbons have fewer hydrogen atoms due to the presence of double or triple bonds.
Have something to share?
Who is Worksheeto?
At Worksheeto, we are committed to delivering an extensive and varied portfolio of superior quality worksheets, designed to address the educational demands of students, educators, and parents.





























Comments