Nutrients Worksheets for High School
High school students looking to deepen their understanding of nutrients and their impact on the body can benefit from using worksheets as a valuable learning tool. These worksheets provide an engaging way to explore the essential nutrients, their sources, and their roles in maintaining a healthy body. By incorporating worksheets into their studies, high school students can enhance their knowledge on this crucial subject matter and further develop their understanding of proper nutrition.
Table of Images 👆
- 4th Grade Science Sound Worksheets
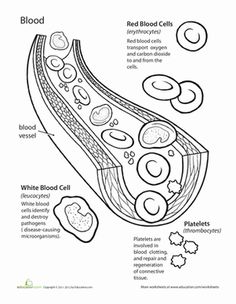
- Human Blood Cell Anatomy Worksheet
- Nutrition Food Groups Worksheets
- Glycolysis Cellular Respiration Lesson Plans
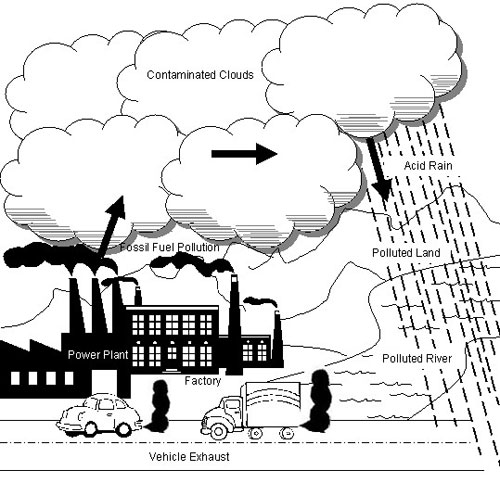
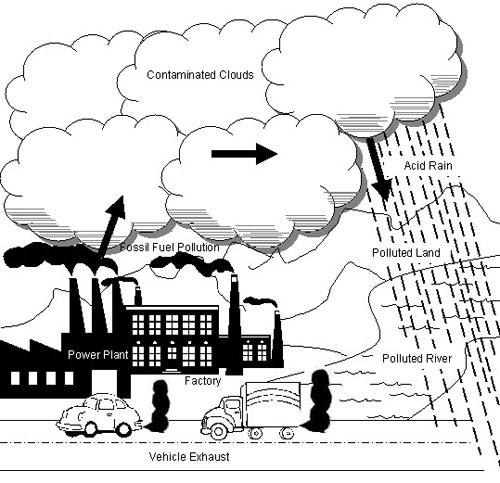
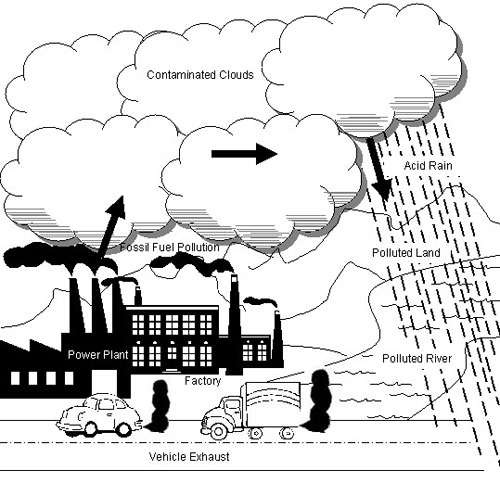
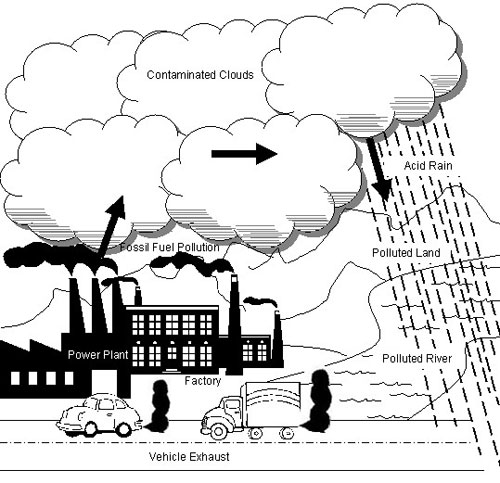
- Air Pollution for Kids Drawing
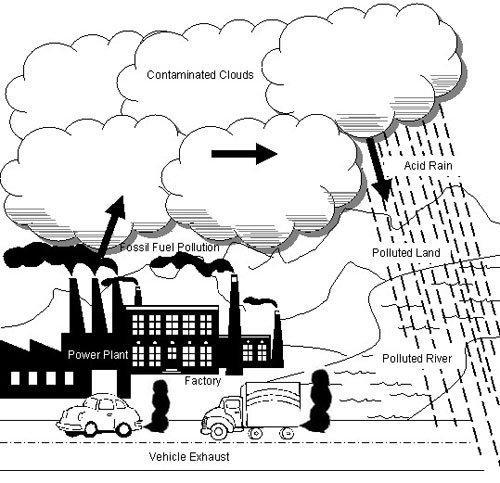
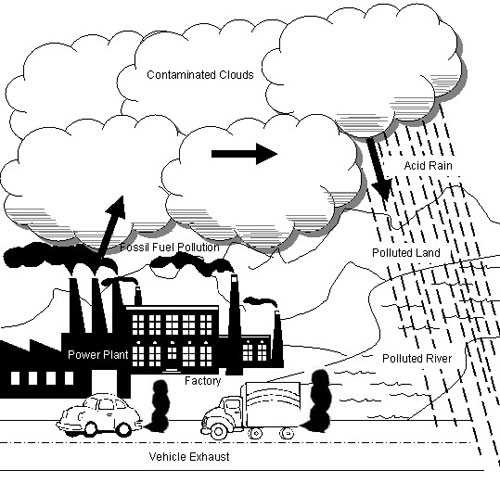
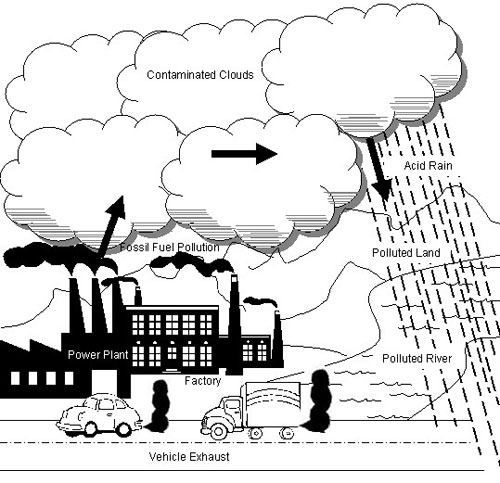
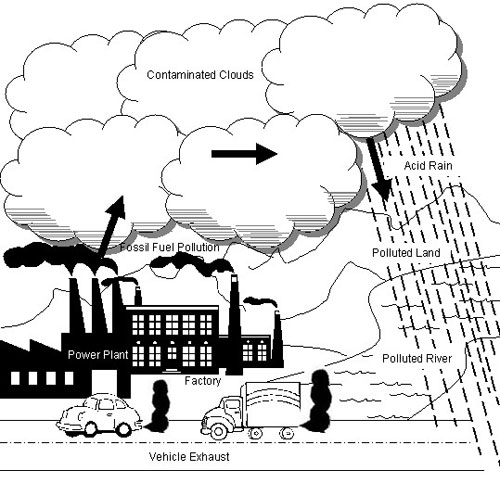
- Air Pollution for Kids Drawing
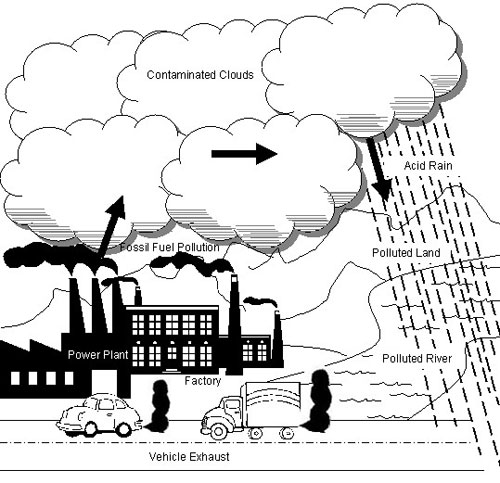
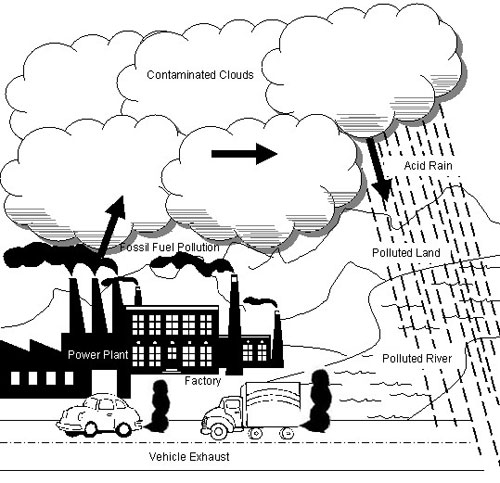
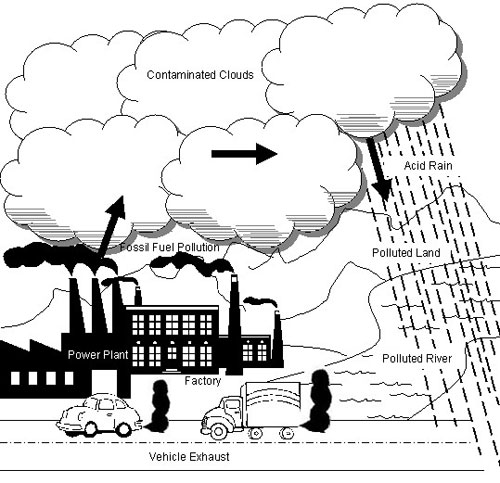
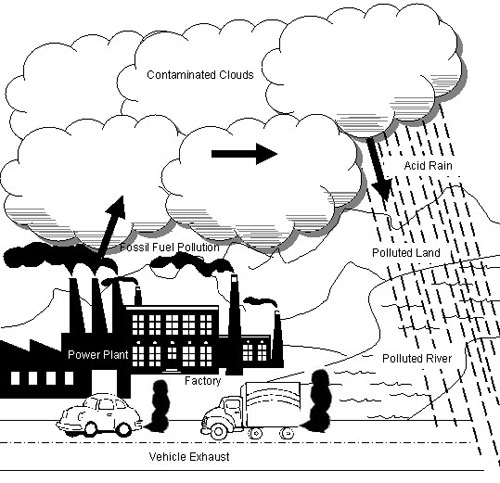
- Air Pollution for Kids Drawing
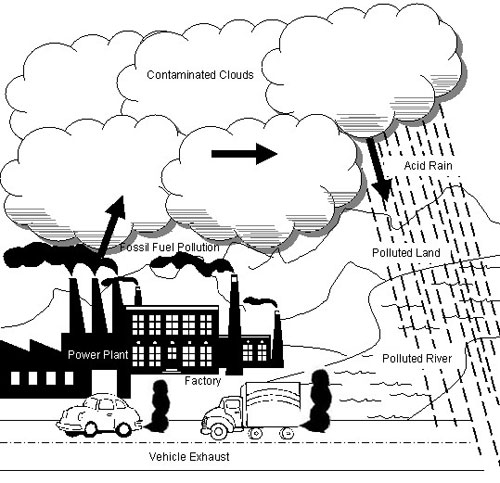
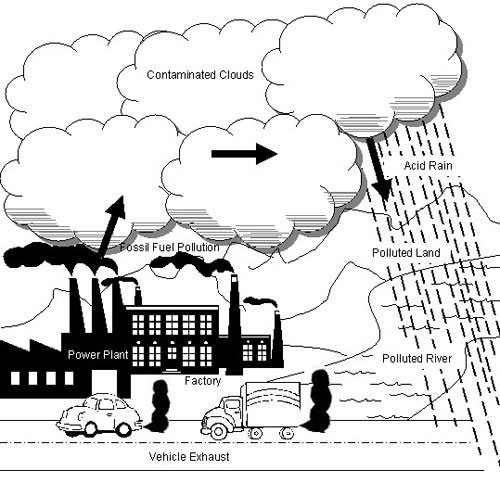
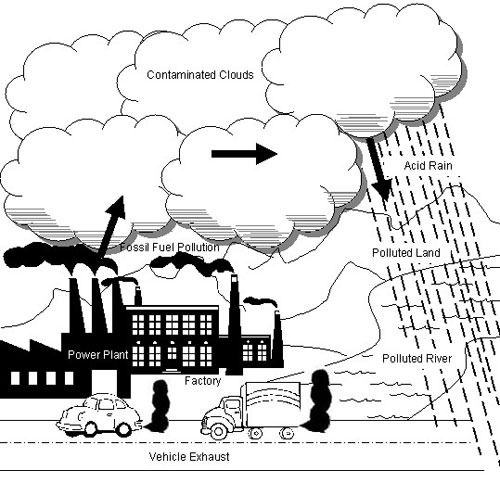
- Air Pollution for Kids Drawing
- Air Pollution for Kids Drawing
- Air Pollution for Kids Drawing
- Air Pollution for Kids Drawing
- Air Pollution for Kids Drawing
- Air Pollution for Kids Drawing
- Air Pollution for Kids Drawing
- Air Pollution for Kids Drawing
- Air Pollution for Kids Drawing
- Air Pollution for Kids Drawing
- Air Pollution for Kids Drawing
- Air Pollution for Kids Drawing
- Air Pollution for Kids Drawing
More Other Worksheets
Kindergarten Worksheet My RoomSpanish Verb Worksheets
Healthy Eating Plate Printable Worksheet
Cooking Vocabulary Worksheet
My Shadow Worksheet
Large Printable Blank Pyramid Worksheet
Relationship Circles Worksheet
DNA Code Worksheet
Meiosis Worksheet Answer Key
Rosa Parks Worksheet Grade 1
What are macronutrients?
Macronutrients are a group of essential nutrients that the body needs in large amounts to function properly. There are three main macronutrients: carbohydrates, proteins, and fats. Carbohydrates are our primary source of energy, proteins are important for building and repairing tissues, and fats play a key role in cell function and hormone production. Balancing the intake of macronutrients is crucial for overall health and well-being.
What is the role of carbohydrates in the body?
Carbohydrates serve as the primary source of energy for the body, providing fuel for metabolic processes and physical activities. They are broken down into glucose, which is then used by cells for energy production. Carbohydrates also play a key role in brain function, as the brain relies heavily on glucose for its energy needs. Additionally, carbohydrates contribute to the structure of cells and tissues, support the immune system, and help regulate protein and fat metabolism.
How does the body use proteins?
The body uses proteins for various essential functions, such as building and repairing tissues, creating enzymes and hormones, supporting the immune system, and serving as a source of energy. Proteins are made up of amino acids that are broken down and used by the body to maintain overall health and function properly.
What are the functions of lipids?
Lipids have several important functions in the body, including serving as a source of energy, providing insulation and protection for organs, aiding in the absorption of fat-soluble vitamins, acting as structural components of cell membranes, and playing crucial roles in cell signaling and communication. Additionally, lipids are involved in the production of hormones and are essential for overall cellular and physiological function.
What is the importance of water for our health?
Water is essential for maintaining proper hydration, regulating body temperature, aiding digestion, transporting nutrients and oxygen throughout the body, flushing out waste and toxins, and lubricating joints. Proper hydration is crucial for overall health, as it supports organ function, boosts energy levels, helps with concentration and cognitive performance, and promotes healthy skin. Inadequate water intake can lead to dehydration, which can cause a range of health issues such as fatigue, headaches, constipation, and even more serious conditions. Hence, staying adequately hydrated by consuming enough water daily is vital for optimal health and well-being.
How does the body metabolize vitamins?
The body metabolizes vitamins through various processes, including absorption in the digestive system, transport to target tissues, enzyme-catalyzed reactions for activation or breakdown, and excretion of excess through urine or bile. For instance, fat-soluble vitamins (A, D, E, K) are absorbed with dietary fats and stored in the liver and adipose tissue, while water-soluble vitamins (B-complex and C) are absorbed directly into the bloodstream and excess amounts are excreted in urine. Each vitamin has specific metabolic pathways and functions in the body to support essential processes like energy production, immune function, and cell repair.
What are minerals and why are they important?
Minerals are naturally occurring inorganic substances that are essential for the proper functioning of our bodies. They play a crucial role in various bodily functions such as bone health, nerve transmission, muscle function, and energy production. Minerals also support the immune system, help maintain a healthy pH balance, and assist in the absorption of vitamins. Without an adequate intake of minerals, our bodies may not be able to perform these functions efficiently, leading to various health issues.
What are the different types of dietary fibers and their benefits?
There are two main types of dietary fibers: soluble and insoluble fibers. Soluble fibers, such as pectins, gums, and psyllium, dissolve in water to form a gel-like substance that can help lower cholesterol levels, regulate blood sugar levels, and promote a feeling of fullness. Insoluble fibers, like cellulose, hemicellulose, and lignin, do not dissolve in water and add bulk to the stool, aiding in digestion and preventing constipation. Both types of fiber are important for maintaining a healthy digestive system and can contribute to overall health by reducing the risk of various chronic diseases such as heart disease and diabetes.
What are the consequences of micronutrient deficiencies?
Micronutrient deficiencies can lead to a range of negative health consequences including impaired immune function, decreased cognitive development, stunted growth, anemia, and increased risk of chronic diseases such as cardiovascular disease. Deficiencies in vitamins and minerals can have serious impacts on overall health and well-being, highlighting the importance of consuming a balanced diet rich in essential nutrients.
What are some examples of nutrient-dense foods?
Nutrient-dense foods are those that provide a high amount of nutrients relative to their calorie content. Some examples include leafy greens (such as kale and spinach), berries (like blueberries and strawberries), fatty fish (such as salmon and mackerel), nuts and seeds (like almonds and chia seeds), and whole grains (such as quinoa and brown rice). These foods are rich in vitamins, minerals, antioxidants, and other beneficial compounds that support overall health and well-being.
Have something to share?
Who is Worksheeto?
At Worksheeto, we are committed to delivering an extensive and varied portfolio of superior quality worksheets, designed to address the educational demands of students, educators, and parents.






















Comments