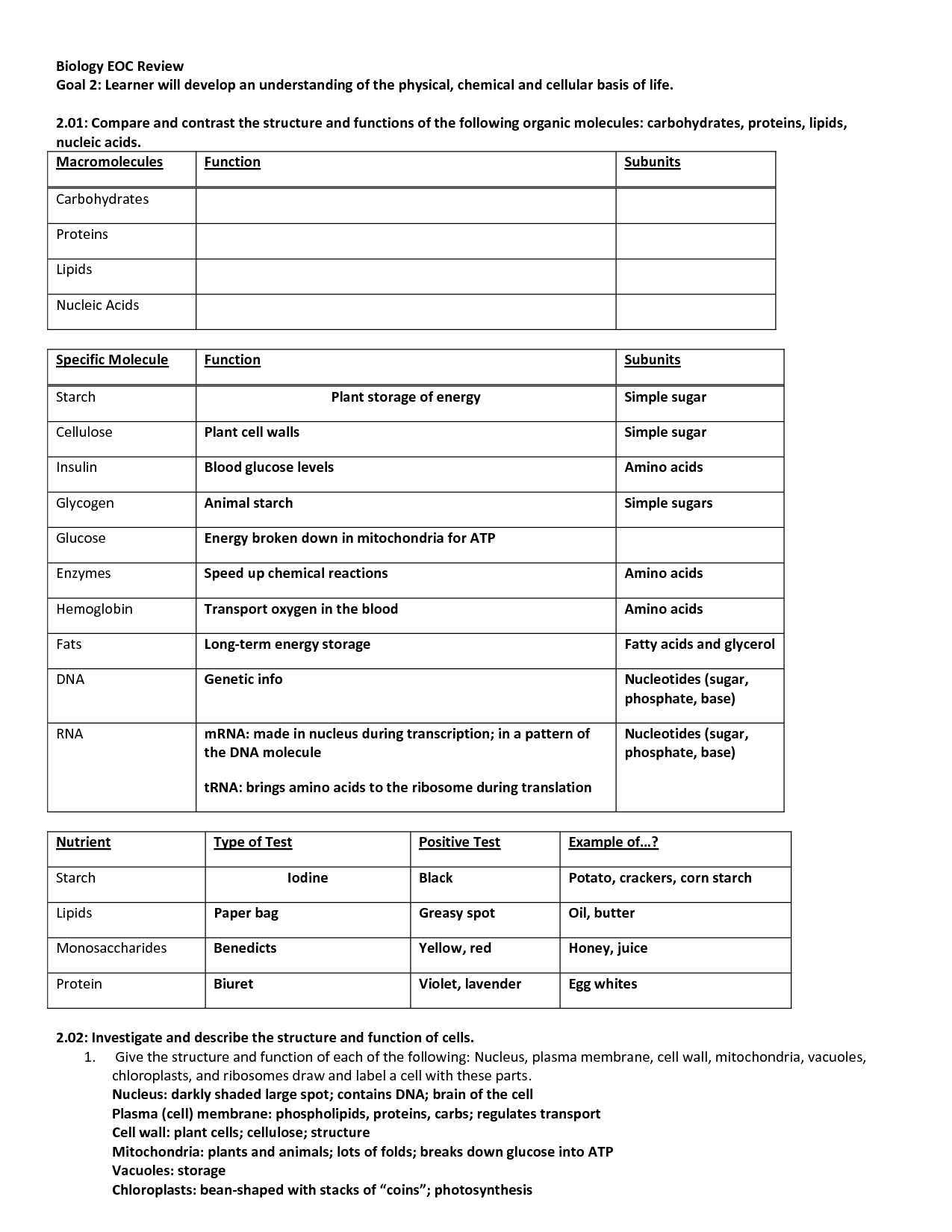
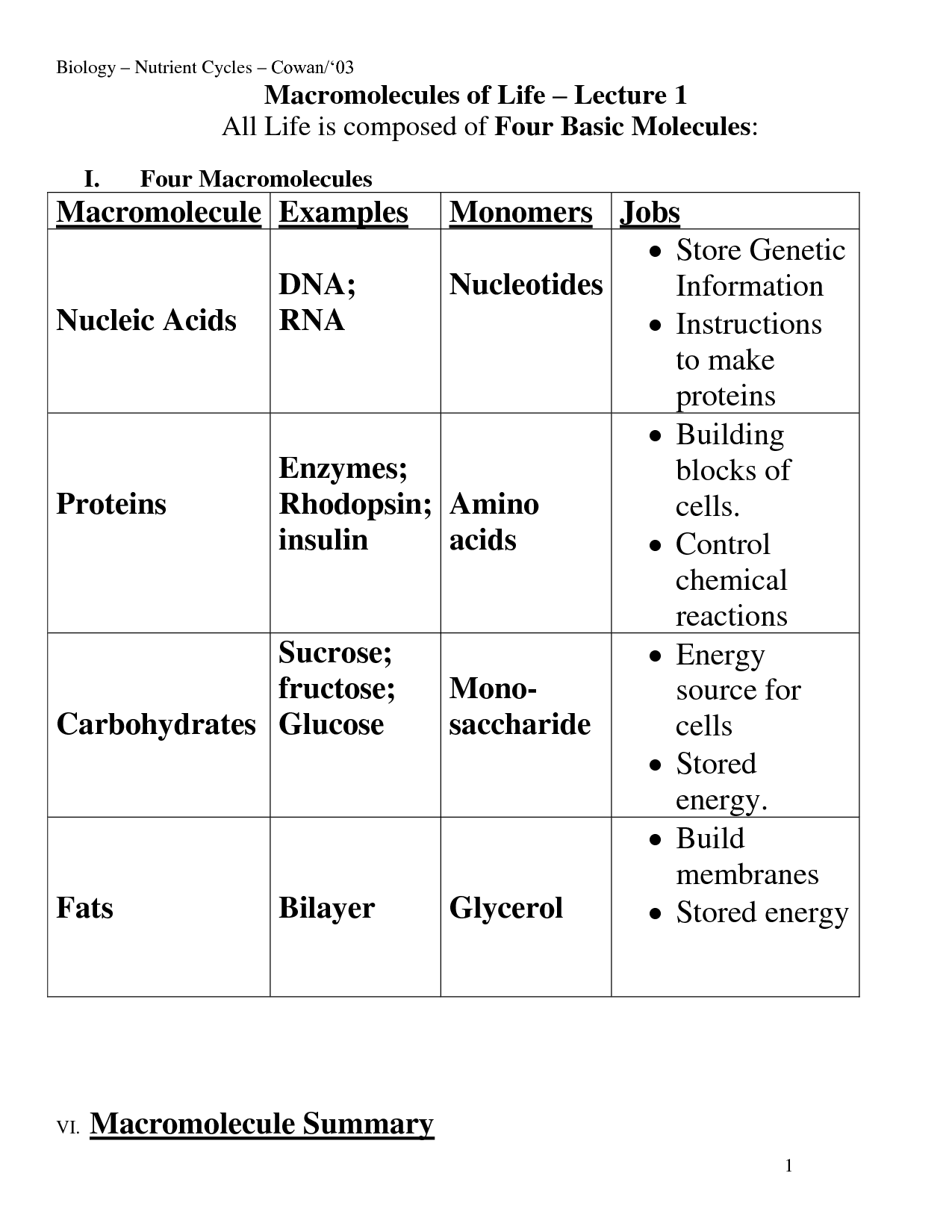
Nucleic Acids Worksheet
Understanding the structure and function of nucleic acids is crucial for students studying biology or biochemistry. With the Nucleic Acids Worksheet, learners can deepen their knowledge on this vital biological entity and subject. The worksheet provides a comprehensive overview of the different types of nucleic acids, their components, and their roles in cell processes. By exploring this worksheet, students can enhance their understanding of DNA, RNA, and the processes of replication, transcription, and translation.
Table of Images 👆
- Nucleic Acids Worksheet Answers
- Organic Molecules Worksheet Review Answer Key
- DNA Double Helix Coloring Worksheet Answers
- Macromolecule Worksheet Answer Key
- Carbohydrates Worksheet Answers
- Protein Synthesis Worksheet Answers
- DNA Protein Synthesis Worksheet Answers
- DNA and Protein Synthesis Study Guide Answers
- Biology Macromolecules Worksheets and Answers
- Amino Acids and Bases Worksheet
- Acids Bases and Salts Worksheet Answers
- Carbohydrates Lipids and Proteins Worksheet
- Nucleic Acids Worksheet Answer Key
- 4 Macromolecules and Their Functions
- Genetic Mutation Worksheet Answer Key
More Other Worksheets
Kindergarten Worksheet My RoomSpanish Verb Worksheets
Healthy Eating Plate Printable Worksheet
Cooking Vocabulary Worksheet
My Shadow Worksheet
Large Printable Blank Pyramid Worksheet
Relationship Circles Worksheet
DNA Code Worksheet
Meiosis Worksheet Answer Key
Rosa Parks Worksheet Grade 1
What are nucleic acids?
Nucleic acids are biomolecules that serve as the building blocks of genetic material in living organisms. They are made up of nucleotides, which consist of a sugar molecule, a phosphate group, and a nitrogenous base. There are two main types of nucleic acids: deoxyribonucleic acid (DNA) and ribonucleic acid (RNA). DNA carries genetic information and is responsible for the heredity and development of all living organisms, while RNA plays a crucial role in protein synthesis and other cellular functions.
What are the two main types of nucleic acids?
The two main types of nucleic acids are DNA (deoxyribonucleic acid) and RNA (ribonucleic acid). DNA carries genetic information and is mainly found in the cell nucleus, while RNA plays a role in protein synthesis and can be found in both the nucleus and cytoplasm of cells.
What are the monomers of nucleic acids?
The monomers of nucleic acids are nucleotides, which consist of a sugar molecule (either deoxyribose in DNA or ribose in RNA), a phosphate group, and a nitrogenous base (adenine, thymine/uracil, cytosine, or guanine).
What is the backbone of a nucleic acid made of?
The backbone of a nucleic acid is made of alternating sugar and phosphate molecules.
What are the four nitrogenous bases found in DNA?
The four nitrogenous bases found in DNA are adenine (A), thymine (T), cytosine (C), and guanine (G).
What are the four nitrogenous bases found in RNA?
The four nitrogenous bases found in RNA are adenine (A), guanine (G), cytosine (C), and uracil (U), which replaces thymine found in DNA.
How does DNA differ from RNA in terms of structure and function?
DNA contains a double helix structure with deoxyribose sugar, while RNA is single-stranded with ribose sugar. Additionally, DNA stores genetic information while RNA transfers genetic information from DNA to synthesize proteins. DNA is stable and long-lasting, while RNA is more dynamic and short-lived. In summary, DNA is the blueprint for life, while RNA helps carry out the instructions encoded in DNA to facilitate protein synthesis.
What is the role of nucleic acids in protein synthesis?
Nucleic acids, specifically mRNA, play a vital role in protein synthesis as they carry the genetic information from DNA molecules in the cell nucleus to the ribosomes in the cytoplasm where proteins are synthesized. During protein synthesis, mRNA serves as a template for the ribosomes to read the genetic code and assemble amino acids into specific sequences, ultimately forming proteins. This process, known as translation, is essential for the production of proteins that carry out various functions in the cell and organism.
How do nucleic acids store and transmit genetic information?
Nucleic acids, specifically DNA, store and transmit genetic information by encoding instructions for the synthesis of proteins. The sequence of nucleotide bases in DNA forms genes, which are transcribed into messenger RNA (mRNA) and then translated into proteins. Through this process, genetic information is passed on and expressed in the form of specific proteins that perform various functions in cells. Additionally, DNA can replicate itself to ensure transmission of genetic information to the next generation.
What are some common examples of nucleic acids in living organisms?
Some common examples of nucleic acids in living organisms include deoxyribonucleic acid (DNA) and ribonucleic acid (RNA). DNA carries genetic information and is responsible for storing and transmitting hereditary traits, while RNA is involved in protein synthesis and gene regulation. Both DNA and RNA are essential components of living cells and play critical roles in the functioning and maintenance of organisms.
Have something to share?
Who is Worksheeto?
At Worksheeto, we are committed to delivering an extensive and varied portfolio of superior quality worksheets, designed to address the educational demands of students, educators, and parents.






























Comments