Nitrogen Cycle Worksheet
Are you a science teacher or a student learning about the nitrogen cycle? Look at no further! In this blog post, we will discuss the importance of worksheets as an effective learning tool for understanding the intricate process of the nitrogen cycle. Worksheets provide a structured format for students to explore the different entities and subjects involved in this essential ecological process.
Table of Images 👆
- Parts of a Plant Cell Worksheet
- Food Chain Worksheets Free
- 4 Types of Bridges Worksheets
- Nitrogen Cycle Diagram Worksheet
- Rock Cycle Quiz Printable Worksheets
- Rocks and Minerals Worksheets
- Biogeochemical Cycles Worksheet
- Label Plant Parts Worksheet
- Water Carbon and Nitrogen Cycle Worksheet
- Sample Informed Consent Form Template
- Water Cycle Worksheets
- Nuclear Decay Worksheet Answer Key
- Nuclear Decay Worksheet Answer Key
- Nuclear Decay Worksheet Answer Key
- Nuclear Decay Worksheet Answer Key
- Nuclear Decay Worksheet Answer Key
- Nuclear Decay Worksheet Answer Key
More Other Worksheets
Kindergarten Worksheet My RoomSpanish Verb Worksheets
Healthy Eating Plate Printable Worksheet
Cooking Vocabulary Worksheet
My Shadow Worksheet
Large Printable Blank Pyramid Worksheet
Relationship Circles Worksheet
DNA Code Worksheet
Meiosis Worksheet Answer Key
Art Handouts and Worksheets
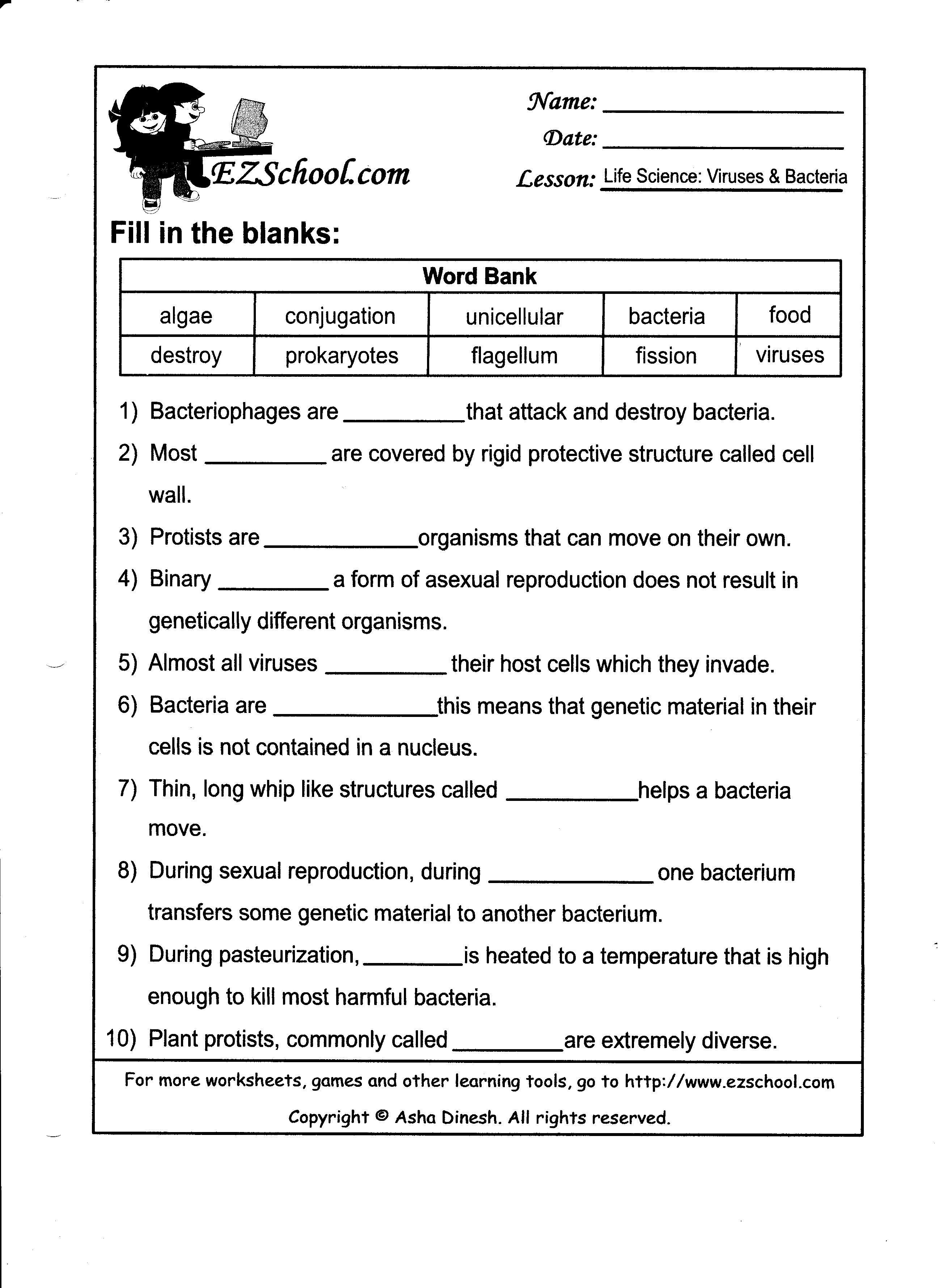
What is the nitrogen cycle?
The nitrogen cycle is a crucial biogeochemical process in which nitrogen is transformed and circulated between the atmosphere, soil, water, and living organisms. It involves various steps including nitrogen fixation by bacteria converting nitrogen gas into ammonia, nitrification where ammonia is converted into nitrites and then nitrates, assimilation by plants and animals, denitrification by bacteria returning nitrogen to the atmosphere, and ammonification where organic nitrogen is converted back into ammonia by decomposers. This cycle plays a vital role in maintaining the balance of nitrogen in ecosystems, ensuring the availability of this essential nutrient for living organisms.
What is the main source of nitrogen in the environment?
The main source of nitrogen in the environment is the atmosphere, as it comprises about 78% nitrogen gas (N2).
Describe the process of nitrogen fixation.
Nitrogen fixation is the biological process by which atmospheric nitrogen is converted into ammonia by certain microorganisms such as bacteria and archaea. These organisms have the enzyme nitrogenase, which is capable of breaking the strong triple bond of atmospheric nitrogen (N2) and combining it with hydrogen to form ammonia (NH3). This ammonia can then be used by plants and other living organisms to synthesize proteins and nucleic acids essential for their growth and development. Nitrogen fixation plays a crucial role in the global nitrogen cycle and is vital for maintaining the fertility of soil and the overall productivity of ecosystems.
Explain the role of nitrification in the nitrogen cycle.
Nitrification is an essential process in the nitrogen cycle where ammonia is converted into nitrite by ammonia-oxidizing bacteria, and then into nitrate by nitrite-oxidizing bacteria. This process helps in the transformation of nitrogen from organic forms that plants cannot readily use into inorganic forms that are easily absorbed by plants. Nitrate is a form of nitrogen that plants can utilize for growth, making it a crucial step in the cycling of nitrogen through the ecosystem. Additionally, nitrification also plays a role in regulating soil pH and reducing the environmental impact of excess ammonia in soil and water bodies.
What happens during the process of denitrification?
During denitrification, specialized bacteria convert nitrate (NO3-) and nitrite (NO2-) into nitrogen gas (N2) or nitrous oxide (N2O) under anaerobic conditions. This process helps to remove excess nitrogen from the environment, such as in waterlogged soils or aquatic environments, thus completing the nitrogen cycle and preventing the accumulation of harmful nitrate in ecosystems.
Describe the role of plants in the nitrogen cycle.
Plants play a vital role in the nitrogen cycle by acting as primary producers that take up nitrogen from the soil in the form of nitrates and ammonium. Through a process called nitrogen fixation, certain plants like legumes have symbiotic relationships with nitrogen-fixing bacteria that convert atmospheric nitrogen into a form that plants can use. Additionally, plants help return nitrogen back to the soil through decomposition when they die and are broken down by decomposers, releasing nitrogen compounds back into the environment for reuse by other plants. Overall, plants are essential in maintaining the balance of nitrogen in ecosystems and supporting the growth of all living organisms.
How do animals contribute to the nitrogen cycle?
Animals contribute to the nitrogen cycle by excreting waste containing nitrogen compounds like urea and uric acid. This waste is broken down by bacteria into ammonia, which can then be converted into nitrates and nitrites through nitrification. These nitrogen compounds are essential for plant growth and ultimately flow back into the food chain when animals consume plants or other animals, completing the cycle.
Explain the importance of decomposers in the nitrogen cycle.
Decomposers play a vital role in the nitrogen cycle by breaking down organic matter and returning nitrogen back into the soil in the form of ammonium through a process called ammonification. This recycled nitrogen is then made available for plants to uptake and use for growth and development. Without decomposers, organic matter would accumulate, and the nitrogen within it would remain locked up and unavailable for plants, disrupting the nutrient cycle essential for the functioning of ecosystems. Thus, decomposers are crucial in facilitating the recycling of nitrogen and sustaining the productivity of plant life.
Describe the impacts of human activities on the nitrogen cycle.
Human activities have significantly disrupted the nitrogen cycle by increasing the amount of nitrogen in the environment through activities such as industrial agriculture, fossil fuel combustion, and wastewater discharge. This excess nitrogen leads to issues like nutrient pollution in water bodies, which can cause algal blooms and oxygen-depleted dead zones. It also contributes to greenhouse gas emissions and smog formation, impacting both human health and the environment. Furthermore, the overuse of nitrogen-based fertilizers can lead to soil degradation and loss of biodiversity. Overall, human activities have disrupted the natural balance of the nitrogen cycle, leading to numerous environmental and societal consequences.
How does the nitrogen cycle contribute to ecosystem health and sustainability?
The nitrogen cycle is crucial for ecosystem health and sustainability as it recycles nitrogen from the atmosphere, soil, and living organisms. This cycle enables the conversion of atmospheric nitrogen into forms that can be used by plants for growth, thus supporting the productivity of ecosystems. Additionally, nitrogen-fixing bacteria play a key role in this cycle by converting atmospheric nitrogen into forms that plants can absorb. By facilitating the availability of essential nutrients for plants and influencing nutrient cycling, the nitrogen cycle helps to maintain biodiversity, soil fertility, and overall ecosystem functioning, ultimately promoting sustainability through the efficient use of resources.
Have something to share?
Who is Worksheeto?
At Worksheeto, we are committed to delivering an extensive and varied portfolio of superior quality worksheets, designed to address the educational demands of students, educators, and parents.






























Comments