Neuron Label Worksheet
If you're an anatomy student looking for a helpful tool to reinforce your understanding of neuron labels and their functions, you've come to the right place. Our neuron label worksheet provides a clear and concise layout that allows you to identify and comprehend the different elements of a neuron with ease and accuracy.
Table of Images 👆
More Other Worksheets
Kindergarten Worksheet My RoomSpanish Verb Worksheets
Healthy Eating Plate Printable Worksheet
Cooking Vocabulary Worksheet
My Shadow Worksheet
Large Printable Blank Pyramid Worksheet
Relationship Circles Worksheet
DNA Code Worksheet
Meiosis Worksheet Answer Key
Rosa Parks Worksheet Grade 1
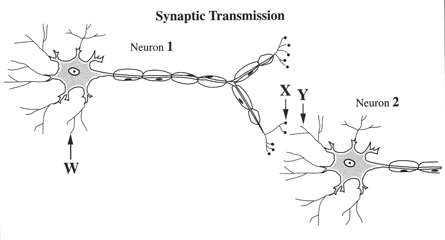
What is the function of a neuron?
The function of a neuron is to transmit electrical and chemical signals throughout the body, enabling communication between different parts of the nervous system and coordinating various bodily functions such as movement, sensation, and cognition. Neurons are specialized cells that process and transmit information by sending nerve impulses along their axons to other neurons, muscles, or glands, allowing for complex signaling and coordination within the body.
What are dendrites?
Dendrites are branched extensions of a neuron that receive signals from other neurons and transmit these signals toward the cell body, allowing for communication and integration of information within the nervous system.
What is the role of the cell body?
The cell body, also known as the soma, is responsible for maintaining the cell's structure, metabolism, and functions. It contains the nucleus which houses the cell's genetic material and controls cellular activities. The cell body also contains organelles such as mitochondria, endoplasmic reticulum, and Golgi apparatus, which are essential for cellular processes such as protein synthesis, energy production, and nutrient metabolism. In summary, the cell body plays a crucial role in the overall functioning and survival of the cell.
What is an axon?
An axon is a long, slender projection of a nerve cell that conducts electrical impulses away from the cell body to other cells, such as neurons, muscles, or glands. It is surrounded by a myelin sheath which helps to increase the speed of transmission of the electrical signals along the axon. Axons are essential for communication between different parts of the nervous system and play a vital role in transmitting information throughout the body.
What happens at the synapse?
At the synapse, which is the junction between two neurons, the electrical signal from one neuron is converted into a chemical signal in the form of neurotransmitters. These neurotransmitters are released into the synaptic cleft and bind to receptors on the receiving neuron, causing a new electrical signal to be generated and continue the transmission of information between neurons. This process is crucial for communication between neurons in the nervous system.
What is the purpose of myelin sheath?
The purpose of the myelin sheath is to insulate and protect nerve fibers, as well as to increase the speed and efficiency of electrical impulses traveling along the nerve cells. It acts as a fatty layer around nerve fibers, allowing for rapid transmission of signals and preventing signal loss or interference.
What are the two types of signals that a neuron can receive?
A neuron can receive two types of signals: excitatory signals, which increase the likelihood of the neuron firing an action potential, and inhibitory signals, which decrease the likelihood of the neuron firing an action potential. These signals ultimately determine whether the neuron will transmit information to other neurons.
What is an action potential?
An action potential is a brief electrical impulse that travels down the axon of a neuron, allowing for the transmission of information between neurons. It is caused by a change in the electrical potential across the neuron's cell membrane, leading to the rapid depolarization and repolarization of the membrane. This process is crucial for communication within the nervous system and is responsible for many physiological functions, such as muscle contraction and sensory perception.
What is the role of neurotransmitters?
Neurotransmitters are chemical messengers that transmit signals between neurons and other cells in the body. They play a crucial role in regulating various physiological processes, including mood, memory, cognition, and movement. By influencing the electrical activity and communication between neurons, neurotransmitters help to coordinate and control the functions of the nervous system.
What is the connection between neurons called?
The connection between neurons is called a synapse. At the synapse, electrical signals are transmitted from one neuron to another through the release and reception of chemical messengers called neurotransmitters. This communication between neurons is essential for the proper functioning of the brain and nervous system.
Have something to share?
Who is Worksheeto?
At Worksheeto, we are committed to delivering an extensive and varied portfolio of superior quality worksheets, designed to address the educational demands of students, educators, and parents.
























Comments