Net Force and Acceleration Worksheet
If you're seeking a resource that combines the topics of net force and acceleration in an engaging way, you've come to the right place. This worksheet provides an opportunity for students to delve into the concepts of net force and acceleration, allowing them to deepen their understanding of these fundamental physics principles.
Table of Images 👆
More Other Worksheets
Kindergarten Worksheet My RoomSpanish Verb Worksheets
Healthy Eating Plate Printable Worksheet
Cooking Vocabulary Worksheet
My Shadow Worksheet
Large Printable Blank Pyramid Worksheet
Relationship Circles Worksheet
DNA Code Worksheet
Meiosis Worksheet Answer Key
Rosa Parks Worksheet Grade 1
What is net force?
Net force is the combination of all forces acting on an object, taking into account their direction and magnitude. It is the overall force that influences the motion of an object, determining whether it accelerates, decelerates, or remains at a constant velocity. Mathematically, net force is calculated by adding or subtracting individual forces acting on an object in accordance with Newton's second law of motion.
How is net force calculated?
The net force is calculated by finding the vector sum of all the individual forces acting on an object. This involves adding up all the forces in the same direction and subtracting any forces acting in the opposite direction. The formula for calculating the net force is: Net Force = ΣF = F1 + F2 + F3 + ... Fn.
What are the units of net force?
The units of net force are Newtons (N).
What is acceleration?
Acceleration is the rate of change of velocity of an object over time. It can be in the form of speeding up, slowing down, or changing direction. Acceleration is a vector quantity, meaning it has both magnitude and direction, and is typically measured in meters per second squared (m/s^2).
How is acceleration calculated?
Acceleration is calculated by dividing the change in velocity by the time taken for the change to occur. The formula for acceleration is: acceleration (a) = (final velocity - initial velocity) / time. The unit of acceleration is meters per second squared (m/s^2).
What are the units of acceleration?
The units of acceleration are meters per second squared (m/s^2).
How are net force and acceleration related?
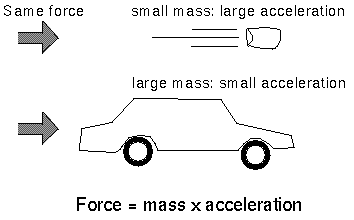
Net force and acceleration are directly proportional to each other according to Newton's second law of motion. This law states that the acceleration of an object is directly proportional to the net force acting on it and inversely proportional to its mass. This means that the greater the net force acting on an object, the greater its acceleration will be, provided its mass remains constant.
In which direction does an object accelerate if the net force applied is in the same direction as its motion?
If the net force applied to an object is in the same direction as its motion, the object will accelerate in that direction, causing its speed or velocity to increase.
In which direction does an object accelerate if the net force applied is in the opposite direction as its motion?
If the net force applied to an object is in the opposite direction as its motion, the object will decelerate. The negative force accelerates the object in the direction opposite to its initial motion, causing it to slow down or come to a stop, depending on the magnitude of the force.
How does increasing the net force affect an object's acceleration?
Increasing the net force acting on an object will lead to a higher acceleration of the object. According to Newton's second law of motion, the acceleration of an object is directly proportional to the net force applied to it and inversely proportional to its mass. Therefore, as the net force increases, the object's acceleration will also increase, assuming its mass remains constant.
Have something to share?
Who is Worksheeto?
At Worksheeto, we are committed to delivering an extensive and varied portfolio of superior quality worksheets, designed to address the educational demands of students, educators, and parents.




















Comments