Naming Covalent Compounds Worksheet
Are you struggling to understand how to name covalent compounds? If so, you're not alone! Many students find this topic challenging because it involves understanding the relationship between the elements in compounds and their chemical formulas. In this blog post, we will provide a helpful naming covalent compounds worksheet that will guide you through the process step by step. This worksheet is designed for high school chemistry students who are looking to improve their skills and gain a better understanding of this fundamental concept.
Table of Images 👆
- Practice Naming Ionic Compounds Worksheet Answers
- Behavior of Gases Worksheet Answers
- Organic vs Inorganic Compounds Worksheet Answers
- Transition Metal Ionic Compounds Worksheet and Answers
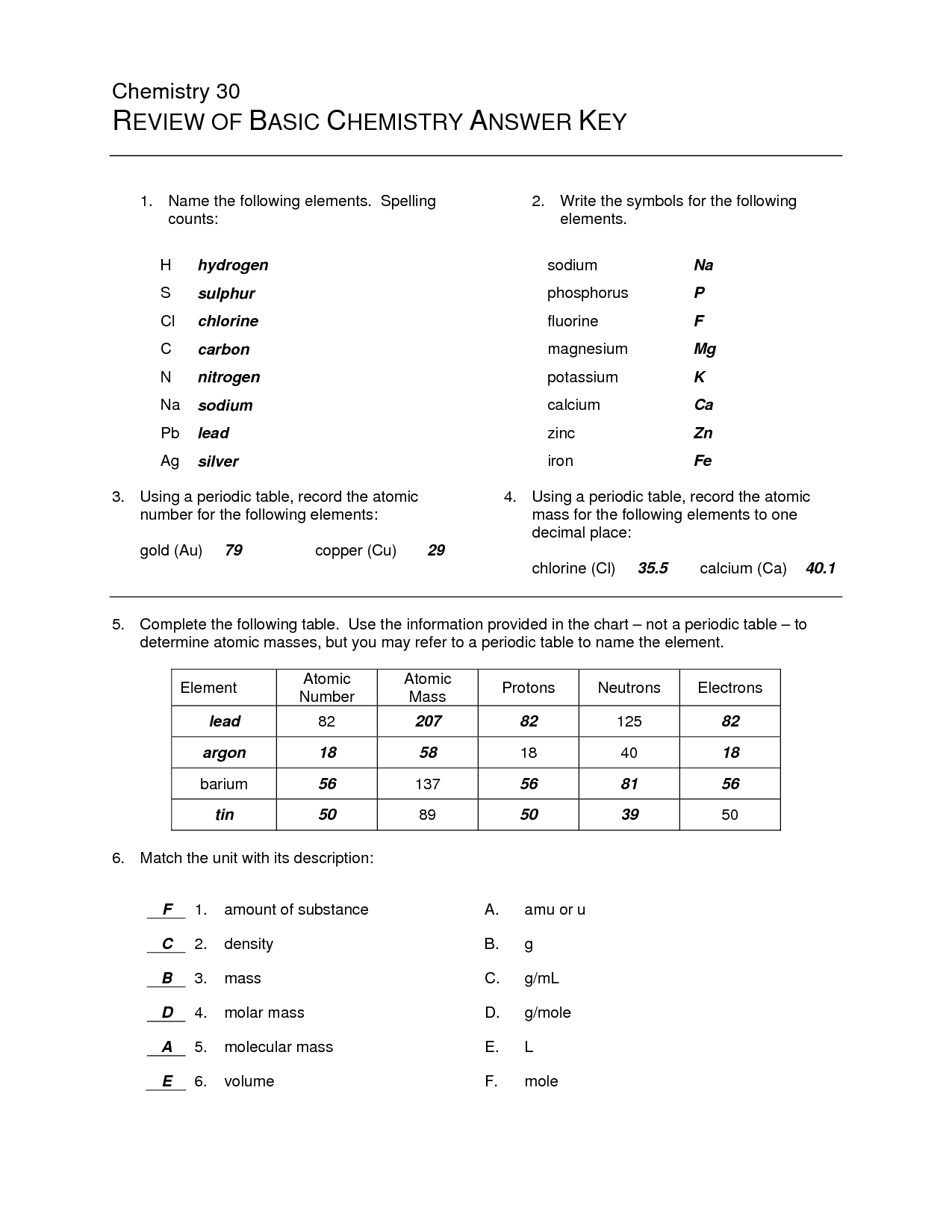
- Basics Chemistry Worksheet Answer Key
- Ionic and Covalent Bonds Worksheet
- Periodic Table
- Aluminum Compound Formula
- Balancing Chemical Equations Worksheet Answer Key
- Naming Ionic Compounds Worksheet Answer Key
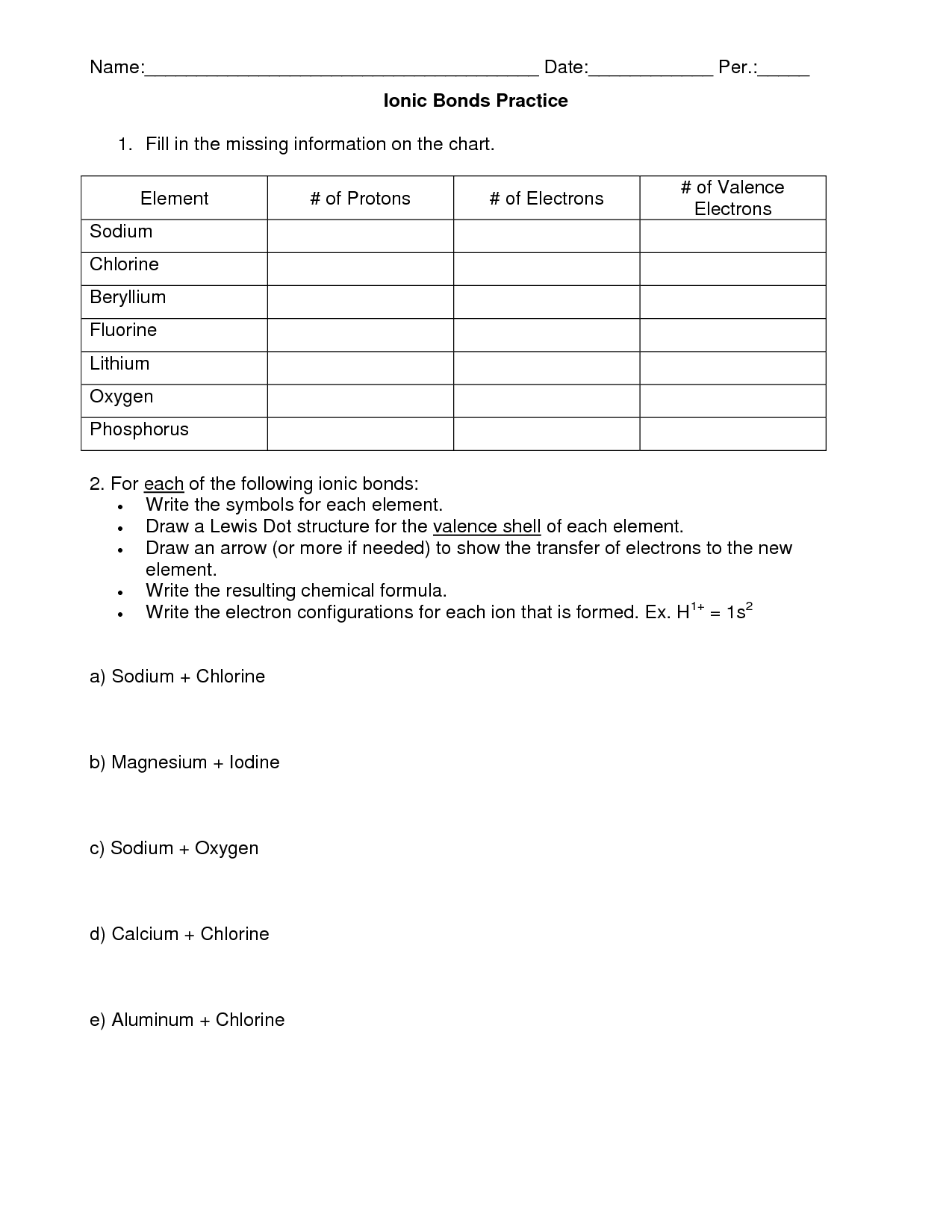
- Ionic Bond Practice Worksheet
- Naming Molecular Compounds Worksheet Answers
- 4th Grade Math Addition Worksheets
- High School English Grammar Worksheets
- High School English Grammar Worksheets
More Other Worksheets
Kindergarten Worksheet My RoomSpanish Verb Worksheets
Cooking Vocabulary Worksheet
My Shadow Worksheet
Large Printable Blank Pyramid Worksheet
Relationship Circles Worksheet
DNA Code Worksheet
Meiosis Worksheet Answer Key
Art Handouts and Worksheets
7 Elements of Art Worksheets
What are covalent compounds?
Covalent compounds are chemical compounds that are formed when two or more non-metal atoms share electrons in a covalent bond. These bonds are formed by the overlapping of electron orbitals between atoms, resulting in the atoms being held together by the shared pair of electrons. Covalent compounds typically have lower melting and boiling points compared to ionic compounds and do not conduct electricity in their solid state.
How are covalent compounds different from ionic compounds?
Covalent compounds are formed when two or more nonmetal atoms share electrons to achieve a stable octet, resulting in a molecule with a neutral charge. In contrast, ionic compounds form when a metal atom transfers electrons to a nonmetal atom, resulting in the formation of positively and negatively charged ions that are held together by electrostatic forces. Ionic compounds typically have higher melting and boiling points compared to covalent compounds, and they tend to be more soluble in water.
What are the rules for naming covalent compounds?
The rules for naming covalent compounds involve using prefixes to indicate the number of each type of atom present in the molecule. The first element in the compound is named as is, while the second element has an "-ide" suffix added to its name. The prefixes used include mono-, di-, tri-, tetra-, penta-, hexa-, hepta-, octa-, nona-, and deca-. Additionally, if the first element starts with a vowel, the prefix "mon-" is often dropped. It's important to note that the prefix "mono-" is never used for the first element.
How do you name binary covalent compounds?
Binary covalent compounds are named using a system of prefixes to indicate the number of each atom present in the molecule. The prefix "mono-" is used for the first element only if there is more than one of the second element present. The second element always uses a prefix to indicate its quantity, for example, "di-" for two atoms, "tri-" for three atoms, and so on. The second element also has its ending changed to "-ide.
What is the purpose of using prefixes in the naming of covalent compounds?
The purpose of using prefixes in the naming of covalent compounds is to indicate the number of each element present in the compound. These prefixes specify the quantity of atoms of each element, helping to correctly identify and represent the molecular structure of the compound.
What is the significance of the prefixes "mono" and "di" in covalent compound names?
The prefixes "mono" and "di" are used in covalent compound names to indicate the number of atoms of each element present in the molecule. "Mono" is used when there is only one atom of that element in the molecule, while "di" is used when there are two atoms of that element. This helps in accurately naming and representing the composition of covalent compounds, especially when there are multiple elements involved in the molecule.
How do you name covalent compounds with three or more elements?
To name covalent compounds with three or more elements, you use prefixes to indicate the number of atoms of each element in the compound. Start by identifying the elements present and their quantities, then use prefixes like di- (2), tri- (3), tetra- (4), penta- (5), etc., before the element name. The ending of the second element changes to "-ide." If the compound starts with mono- for the first element, you can drop the mono- prefix. Always write the full name of the compound without spaces or hyphens between the numerical prefix and the element name.
What is an example of a covalent compound with three elements?
An example of a covalent compound with three elements is sulfur trioxide, with the chemical formula SO3. This compound is composed of sulfur, represented by the symbol S, and three oxygen atoms, represented by the symbol O. It forms covalent bonds through the sharing of electrons between the atoms to achieve stability.
How do you write the chemical formula for a covalent compound given its name?
To write the chemical formula for a covalent compound given its name, you need to determine the number of each element present in the compound and then use subscript numbers to show the ratios of the elements. The prefixes in the compound's name indicate the number of atoms of each element in the compound. For example, in carbon dioxide (CO2), the prefix "di-" corresponds to two oxygen atoms. It's important to remember that you should simplify the ratio of elements by using the lowest possible whole numbers.
What is the importance of correctly naming covalent compounds?
Correctly naming covalent compounds is important because the name of a compound provides crucial information about the elements involved, their arrangement, and the ratio of atoms present. It allows scientists and chemists to communicate effectively and accurately about the chemical composition and structure of substances. Proper naming also helps in understanding the properties and behavior of the compounds, aiding in research, education, and various industrial applications. Furthermore, a systematic naming system ensures consistency and standardization in the field of chemistry.
Have something to share?
Who is Worksheeto?
At Worksheeto, we are committed to delivering an extensive and varied portfolio of superior quality worksheets, designed to address the educational demands of students, educators, and parents.





























Comments