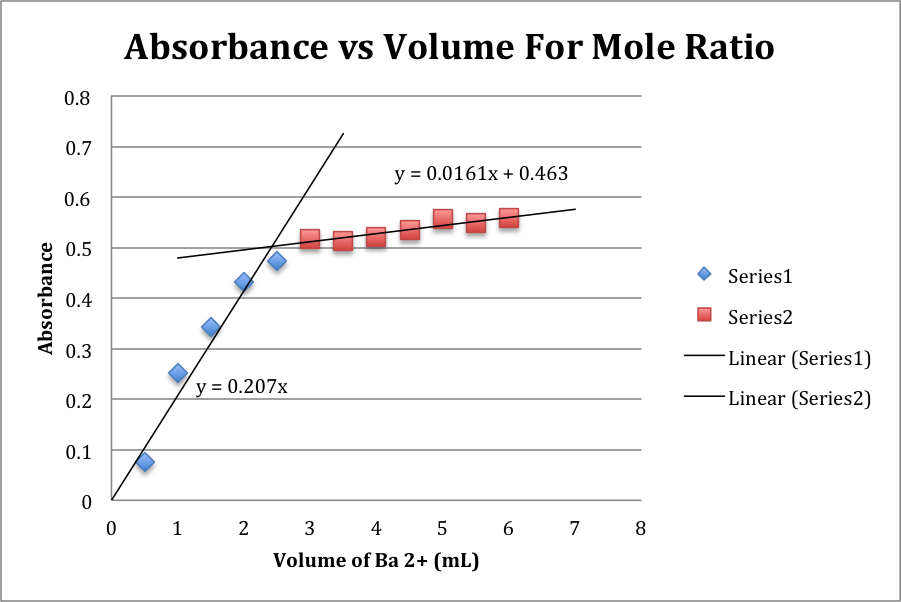
Mole Ratio Worksheet
Are you a student in a chemistry class struggling to understand mole ratios? Look no further! This blog post is designed to provide you with a comprehensive understanding of mole ratios and how they are used in chemical calculations. Whether you're new to the concept or need a refresher, this worksheet will guide you through the process step by step, allowing you to confidently tackle any mole ratio problem that comes your way.
Table of Images 👆
More Other Worksheets
Kindergarten Worksheet My RoomSpanish Verb Worksheets
Cooking Vocabulary Worksheet
My Shadow Worksheet
Large Printable Blank Pyramid Worksheet
Relationship Circles Worksheet
DNA Code Worksheet
Meiosis Worksheet Answer Key
Art Handouts and Worksheets
7 Elements of Art Worksheets
What is a mole ratio?
A mole ratio is a ratio between the number of moles of one substance to another in a balanced chemical equation. It is used to convert between amounts of reactants and products in a chemical reaction and is essential in stoichiometry calculations. The mole ratio is determined by the coefficients of the substances in the balanced equation.
How is a mole ratio used in chemical reactions?
A mole ratio is used in chemical reactions to determine the relative amounts of reactants and products involved in the reaction. It is the ratio of the coefficients in the balanced chemical equation, allowing chemists to calculate the amount of one substance needed to react with another or the amount of product that will be formed. Mole ratios are essential for stoichiometry calculations and for predicting the outcomes of chemical reactions in terms of quantities.
What does a mole ratio represent in a balanced chemical equation?
A mole ratio in a balanced chemical equation represents the ratio of moles of one substance to another substance involved in a chemical reaction, as determined by the coefficients in the balanced equation. It indicates the relative amounts of reactants and products that participate in the reaction, allowing for the calculation of quantities involved in the reaction.
How can you determine the mole ratio between two substances?
To determine the mole ratio between two substances, you first need to balance the chemical equation representing the reaction involving those substances. Once the equation is balanced, the coefficients in front of the substances indicate the mole ratio between them. For example, if the balanced equation is 2A + 3B → C, the mole ratio between A and B is 2:3. This ratio shows the relative number of moles of each substance involved in the reaction.
How does the stoichiometry of a reaction relate to mole ratios?
Stoichiometry of a reaction shows the quantitative relationship between reactants and products in a chemical reaction. This includes mole ratios, which are the coefficients of the balanced chemical equation representing the ratio of moles of reactants and products involved in the reaction. Mole ratios are important in determining the amounts of substances needed or produced in a reaction and help in calculating the quantities of reactants consumed or products formed. By understanding the stoichiometry of a reaction and the mole ratios, one can accurately predict and calculate the amounts of substances involved in a chemical reaction.
Why is it important to use mole ratios in calculations?
Mole ratios are crucial in calculations as they establish the relationship between the different reactants and products in a chemical reaction, enabling accurate stoichiometric calculations. By using mole ratios, one can determine the ideal amounts of reactants needed for a reaction, predict the amounts of products formed, and ensure that the reaction proceeds efficiently. This fundamental principle allows chemists to understand and control chemical reactions, aiding in the design and optimization of processes in various industries.
Are mole ratios always whole numbers? Why or why not?
Mole ratios are not always whole numbers. This is because mole ratios are determined by the coefficients in a balanced chemical equation, which can be fractions or decimals. The ratios can represent the relative number of moles of each substance involved in a reaction, and therefore they may not always be whole numbers.
Can mole ratios be used to predict the amounts of products or reactants in a chemical reaction?
Yes, mole ratios can be used to predict the amounts of products or reactants in a chemical reaction. By knowing the stoichiometry of the reaction and the mole ratios of the reactants and products, one can calculate the amounts of substances involved in the reaction or predict how much product will be formed from a given amount of reactants. This is a fundamental concept in stoichiometry and is crucial for understanding and quantifying chemical reactions.
How do mole ratios allow for the conversion between different units of measurement in a reaction?
Mole ratios allow for the conversion between different units of measurement in a reaction by providing a way to relate the amounts of reactants and products in a chemical reaction based on the coefficients in the balanced equation. By using mole ratios, one can convert between the amount of one substance to another in a reaction, allowing for the calculation of the amount of product produced or reactant needed in a given reaction.
Can mole ratios be used to determine the limiting reagent in a reaction?
Yes, mole ratios can be used to determine the limiting reagent in a reaction. By comparing the actual ratio of reactants present in a reaction to the balanced equation, you can identify which reactant will be completely consumed first and limit the amount of product that can be formed. This allows you to determine the limiting reagent and calculate the maximum amount of product that can be produced.
Have something to share?
Who is Worksheeto?
At Worksheeto, we are committed to delivering an extensive and varied portfolio of superior quality worksheets, designed to address the educational demands of students, educators, and parents.
























Comments