Molar Mass Practice Worksheet Answers
Are you a chemistry student in search of a reliable resource for practicing molar mass calculations? Look no further! In this blog post, we will provide you with the answers to a molar mass practice worksheet. Designed to reinforce your understanding of the concept, this worksheet focuses on calculating the molar mass of various compounds. Whether you're a high school student preparing for exams or a college student reviewing for a chemistry course, this worksheet will serve as an excellent tool to enhance your knowledge and sharpen your skills in determining the molar mass of different entities and subjects.
Table of Images 👆
- Mole Calculation Worksheet Answer Key
- Chemistry Mole Conversions Cheat Sheet
- Worksheet Mole Problems Answers
- Mole Conversion Worksheet Answer Key
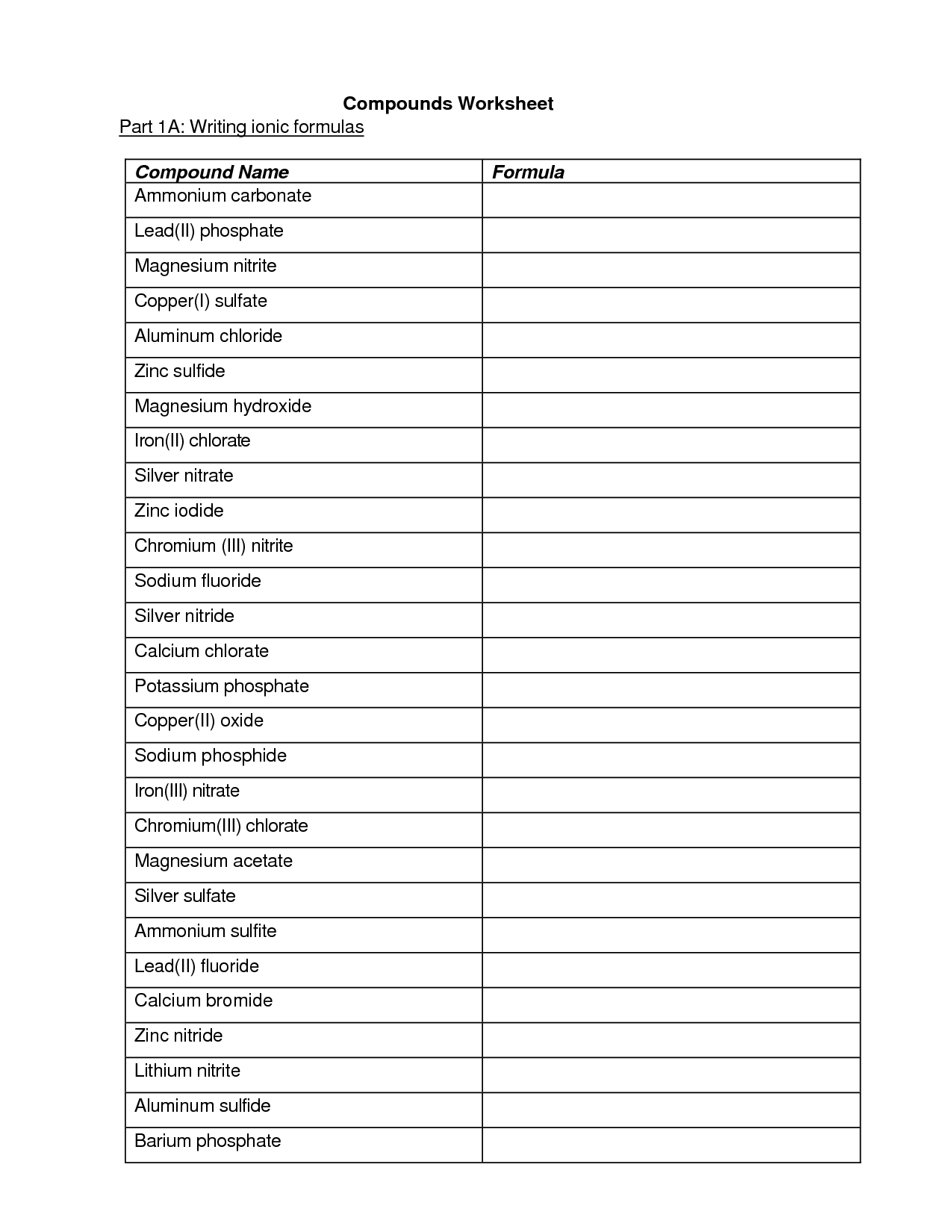
- Writing Ionic Compound Formula Worksheet
- Stoichiometry Worksheet Answers
- Molarity Worksheet Answer Key
- Gram Formula Mass Worksheet Answers
- Worksheets Answer Key
- Bonding Worksheet Answer Key
- Balancing Chemical Equations Worksheet Answer Key
- Balancing Chemical Equations Worksheet Answer Key
- Balancing Chemical Equations Worksheet Answer Key
- Balancing Chemical Equations Worksheet Answer Key
- Balancing Chemical Equations Worksheet Answer Key
More Other Worksheets
Kindergarten Worksheet My RoomSpanish Verb Worksheets
Cooking Vocabulary Worksheet
My Shadow Worksheet
Large Printable Blank Pyramid Worksheet
Relationship Circles Worksheet
DNA Code Worksheet
Meiosis Worksheet Answer Key
Art Handouts and Worksheets
7 Elements of Art Worksheets
What is molar mass?
Molar mass is the mass of a given substance (chemical element or chemical compound) divided by the amount of that substance, measured in moles. It is expressed in units of grams per mole (g/mol). Molar mass is used in chemistry to convert between mass and moles of a substance in various chemical calculations, such as determining the amount of a substance needed for a reaction or calculating the concentration of a solution.
How is molar mass calculated?
Molar mass is calculated by adding up the atomic masses of each atom in a chemical compound, as specified in the periodic table of elements. The mass of each atom is typically measured in atomic mass units (amu). By summing up the atomic masses of all the atoms present in the compound, the molar mass in grams per mole can be determined.
What is the molar mass of an element?
The molar mass of an element is the mass of one mole of atoms of that element, expressed in grams per mole. It is calculated by adding up the atomic masses of the individual atoms within a single molecule or formula unit of the element.
What is the molar mass of a compound?
The molar mass of a compound is the mass of one mole of that compound, expressed in grams per mole. It is calculated by summing the atomic masses of all the atoms present in the compound according to their respective stoichiometry in the chemical formula.
How do you determine the molar mass of a compound using its chemical formula?
To determine the molar mass of a compound using its chemical formula, you need to calculate the sum of the atomic masses of all the elements present in the compound. This can be done by looking up the atomic masses of each element on the periodic table and then multiplying each atomic mass by the number of atoms of that element in the compound. Finally, adding all these individual masses together gives you the molar mass of the compound, expressed in grams per mole.
What is the significance of molar mass in chemical calculations?
Molar mass is significant in chemical calculations as it allows us to convert between the mass of a substance and the number of moles of that substance. This enables us to accurately measure and mix substances in reactions, determine reaction yields, and calculate concentrations. Molar mass is crucial for stoichiometry calculations, determining the empirical and molecular formulas of compounds, as well as understanding the properties and behavior of different substances in chemistry.
How does molar mass help in identifying unknown substances?
Molar mass is helpful in identifying unknown substances because it provides information about the mass of one mole of a substance. By comparing the molar mass of an unknown substance to known molar masses of different elements and compounds, scientists can narrow down the possible identities of the unknown substance. This comparison allows them to make educated guesses about the composition of the unknown substance and ultimately identify it based on its molar mass.
Why is molar mass important in stoichiometry calculations?
Molar mass is important in stoichiometry calculations because it is used to convert between the mass of a substance and the number of moles of that substance. By knowing the molar mass of a compound, one can determine the amount of substance needed in a chemical reaction or the amount of product formed. This conversion is essential in balancing chemical equations and determining the quantities of reactants and products involved in a reaction.
How do you convert between grams and moles using molar mass?
To convert between grams and moles using molar mass, you need to know the molar mass of a substance. To convert from grams to moles, divide the given mass by the molar mass. This will give you the number of moles. To convert from moles to grams, multiply the number of moles by the molar mass. This calculation will give you the mass in grams.
What is the relationship between molar mass and Avogadro's number?
The relationship between molar mass and Avogadro's number is that the molar mass of a substance is equal to the mass of one mole of that substance, which contains Avogadro's number (6.022 x 10^23) of particles (atoms, molecules, or ions). This means that the molar mass is directly related to Avogadro's number because it represents the mass of a specific number of particles of a substance.
Have something to share?
Who is Worksheeto?
At Worksheeto, we are committed to delivering an extensive and varied portfolio of superior quality worksheets, designed to address the educational demands of students, educators, and parents.
































Comments