Modeling DNA Replication Worksheet
Are you in search of a comprehensive worksheet that covers the intricate process of DNA replication? Look no further! Our modeling DNA replication worksheet is designed to provide a suitable learning resource for biology students who are interested in understanding the entity and subject of DNA replication in detail.
Table of Images 👆
- The Double Helix DNA Replication Coloring Worksheet
- DNA Replication Worksheet
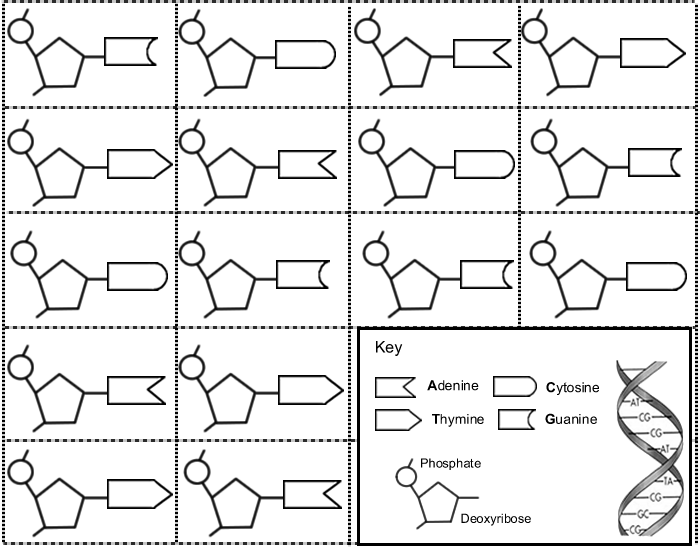
- DNA Paper Model Activity
- DNA Replication Coloring Worksheet
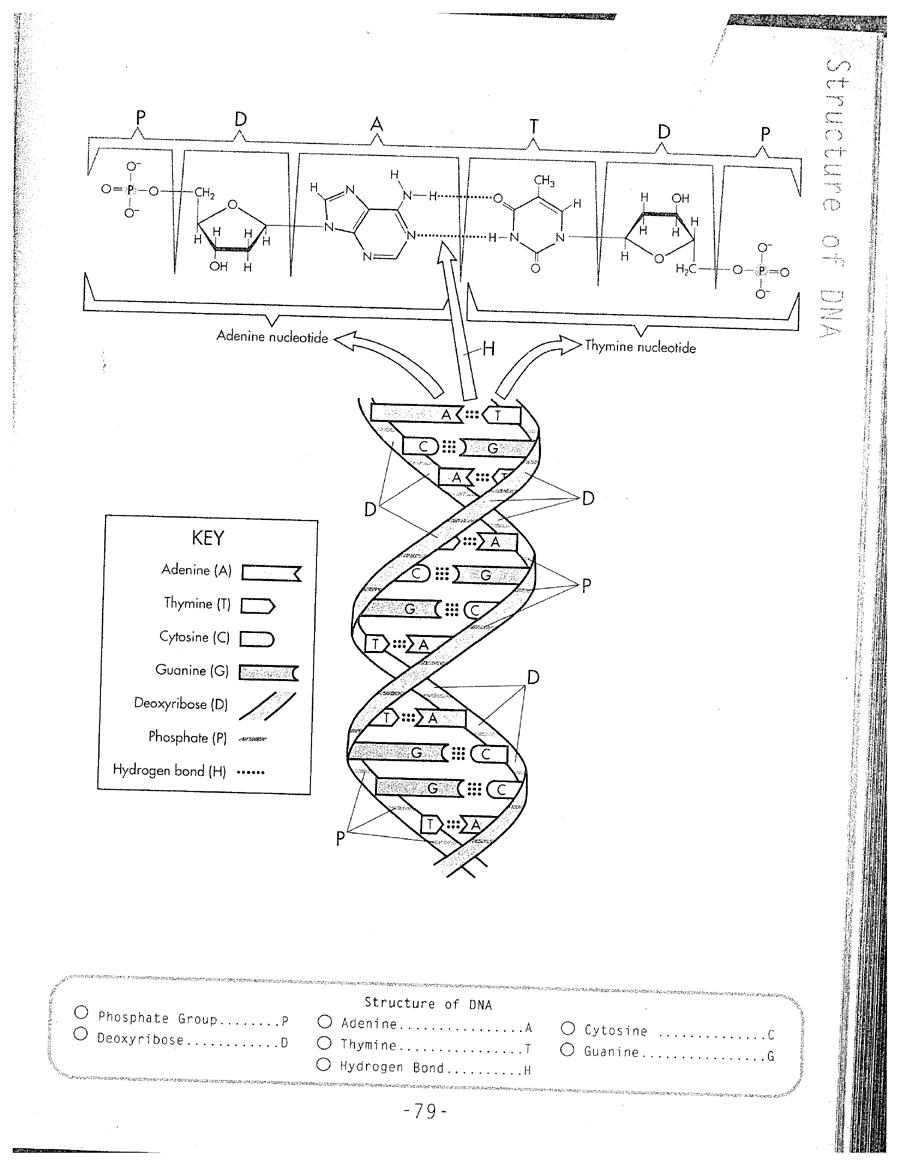
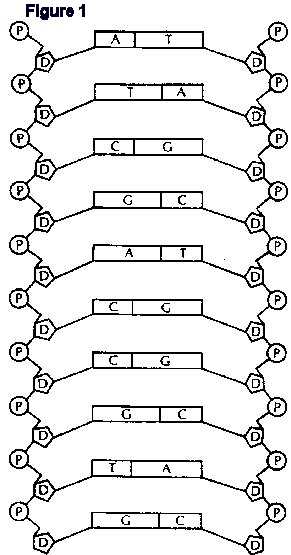
- Labeled DNA Model Worksheet
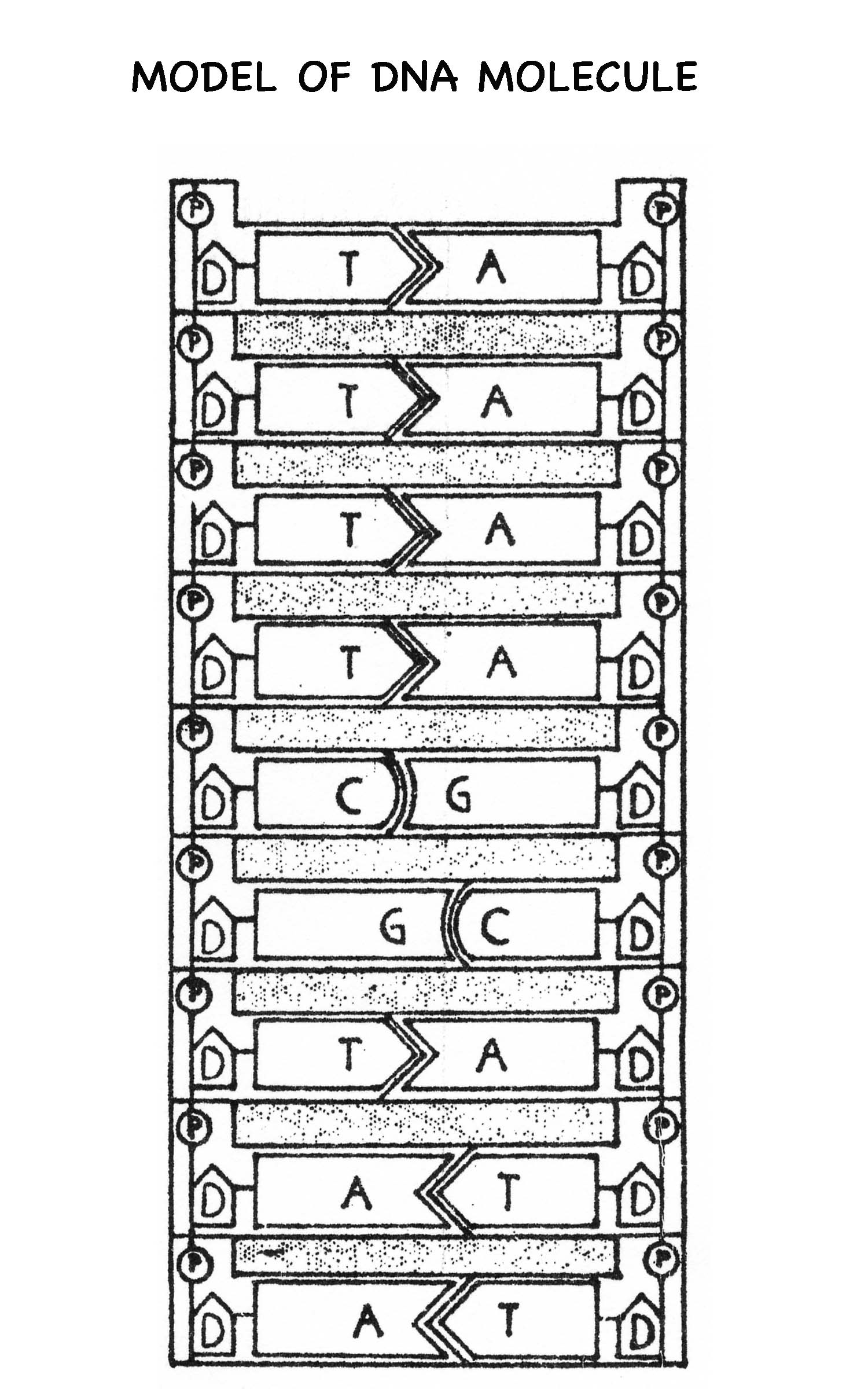
- DNA Model Worksheet
- DNA Model Worksheet
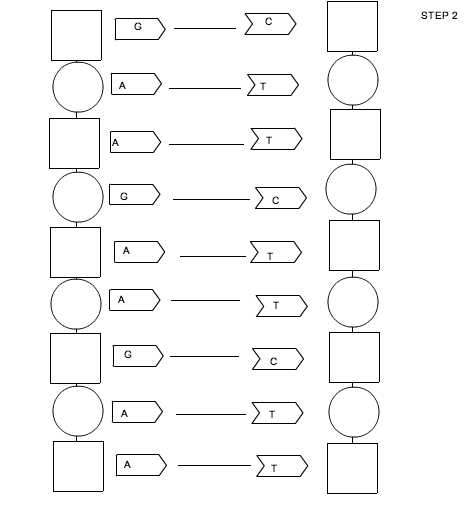
- DNA Replication Structure Worksheet
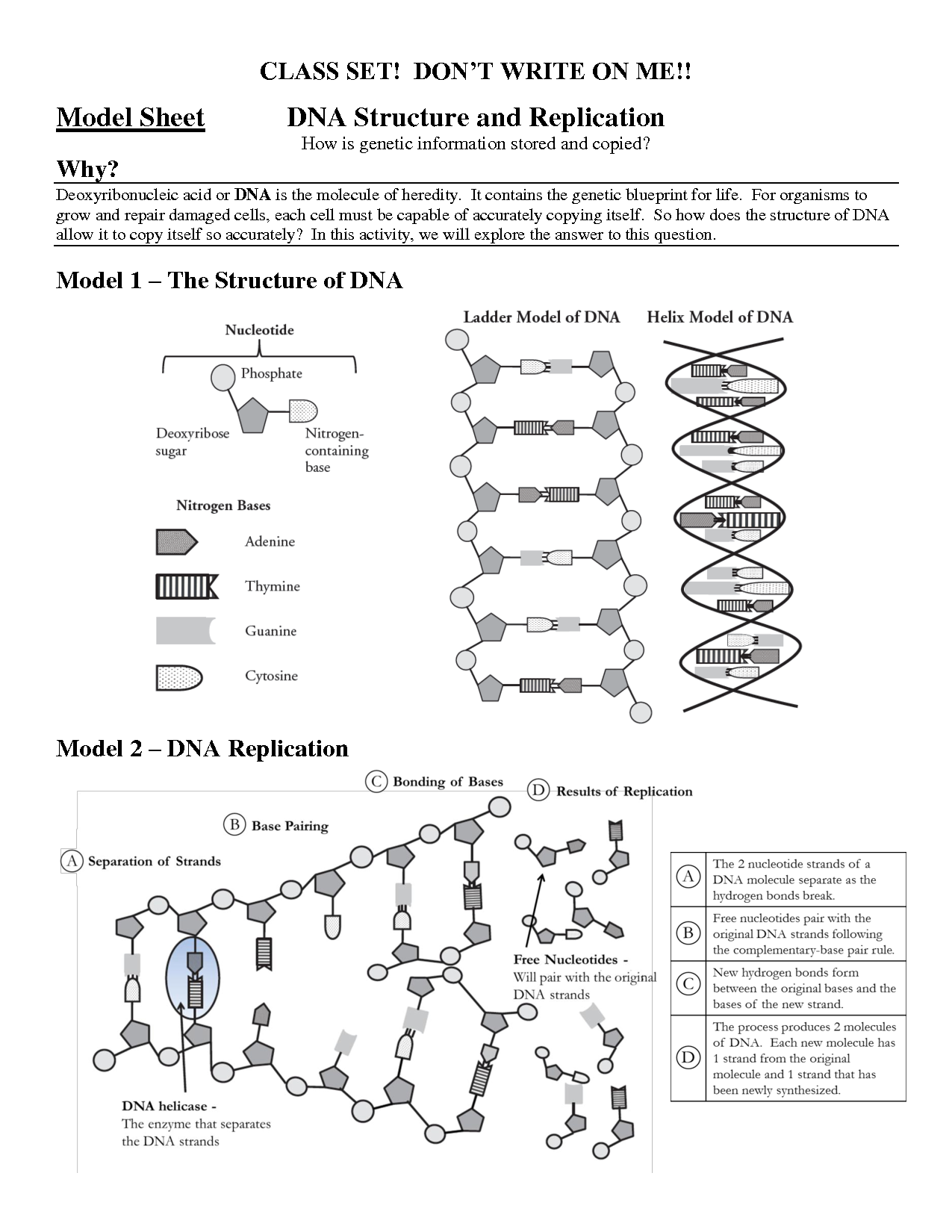
- DNA Structure and Replication Answer Key POGIL
- DNA Paper Model Activity
- Worksheets DNA Coloring Page
- Bacterial DNA Replication
More Other Worksheets
Kindergarten Worksheet My RoomSpanish Verb Worksheets
Healthy Eating Plate Printable Worksheet
Cooking Vocabulary Worksheet
My Shadow Worksheet
Large Printable Blank Pyramid Worksheet
Relationship Circles Worksheet
DNA Code Worksheet
Meiosis Worksheet Answer Key
Rosa Parks Worksheet Grade 1
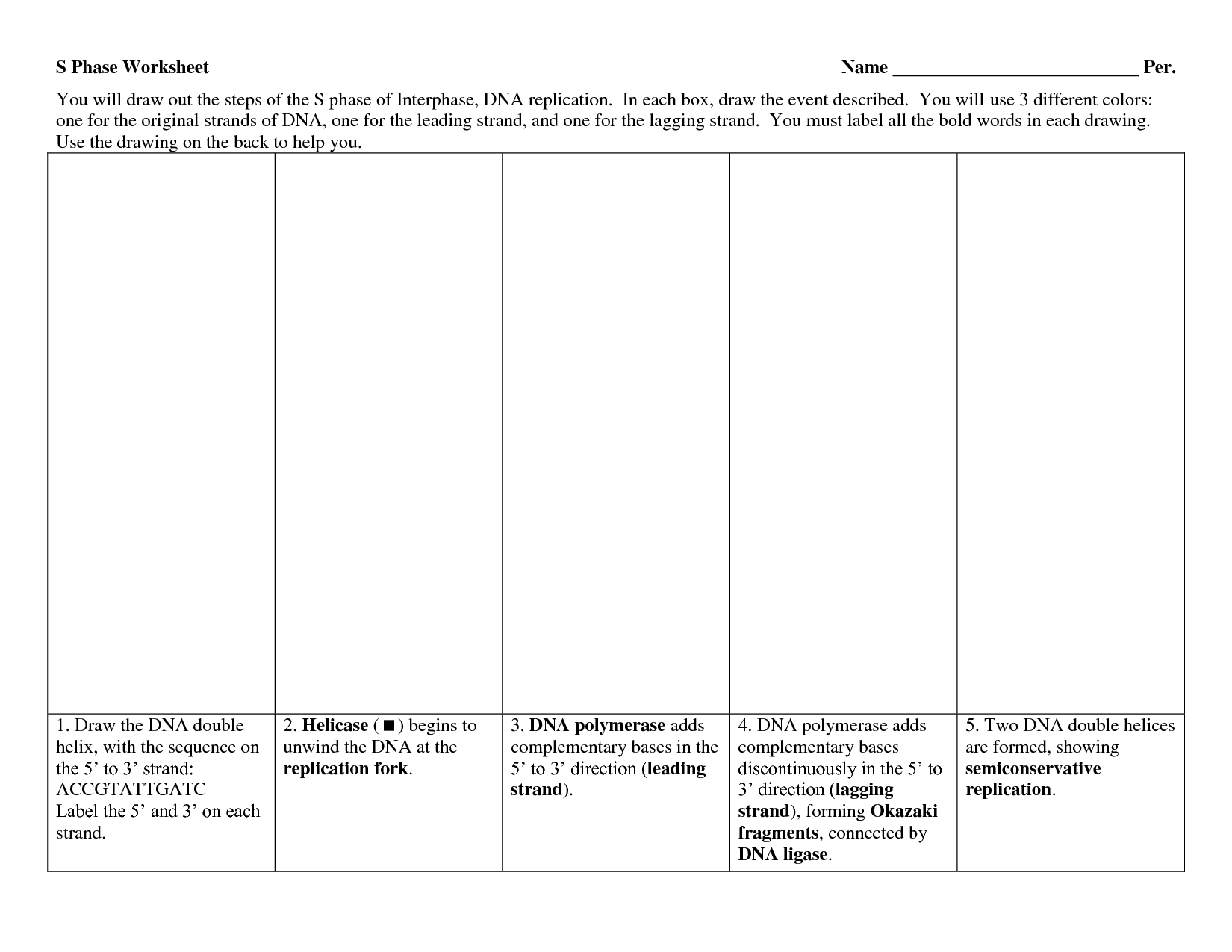
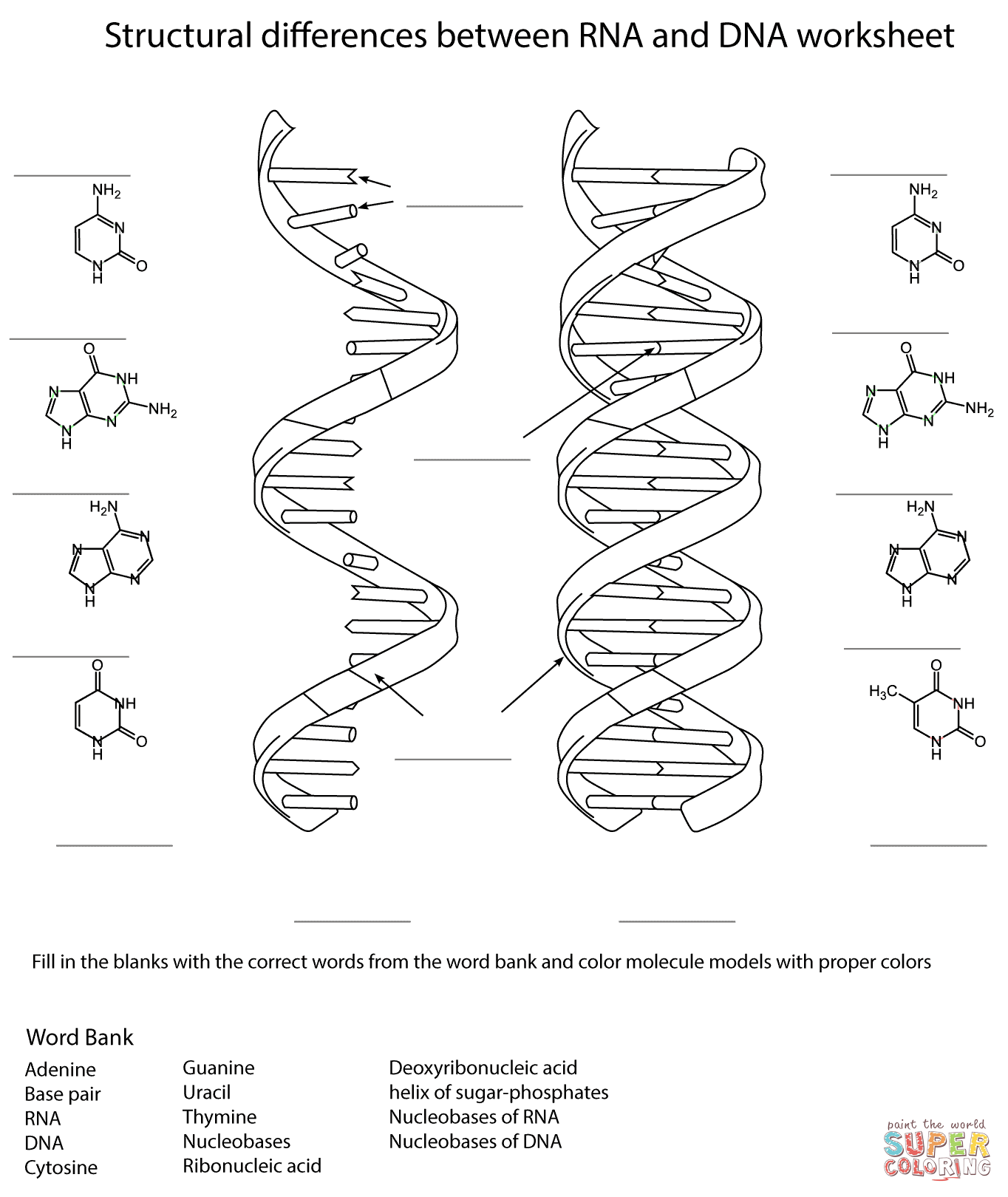
What is DNA replication?
DNA replication is the process by which a cell duplicates its DNA before cell division, ensuring that each new cell receives an identical copy of the genetic information. It involves the synthesis of a new complementary strand of DNA using the existing DNA as a template, resulting in two identical DNA molecules. This process is essential for the growth, development, and repair of organisms.
What is the role of DNA polymerase in DNA replication?
DNA polymerase plays a crucial role in DNA replication by catalyzing the formation of new DNA strands complementary to the original template strands. It accomplishes this by adding nucleotides one by one to the growing DNA chain in the 5' to 3' direction. This enzyme is essential for the accurate and efficient duplication of genetic information during cell division.
What is the function of helicase in DNA replication?
Helicase is an enzyme that plays a crucial role in DNA replication by unwinding the double-stranded DNA helix. It separates the two strands of DNA, creating a replication fork that allows enzymes such as DNA polymerase to access the individual strands and synthesize new complementary strands. This process is essential for the accurate and efficient replication of DNA during cell division.
What is the purpose of primase in DNA replication?
The purpose of primase in DNA replication is to synthesize short RNA primers that provide starting points for DNA polymerase to begin synthesizing new DNA strands. These primers are necessary because DNA polymerase can only add nucleotides to an existing nucleic acid chain, and cannot start a new strand on its own. Primase plays a critical role in initiating the synthesis of new DNA strands during DNA replication.
How does DNA replication ensure accuracy?
DNA replication ensures accuracy through several mechanisms. Firstly, DNA polymerase enzymes have proofreading capabilities to detect and correct errors during replication. Additionally, the DNA template provides a complementary base pairing system that helps ensure the correct nucleotides are added to the growing DNA strand. Lastly, certain proteins help regulate the process of replication to prevent errors and maintain the fidelity of the genetic information being passed on. These mechanisms collectively work to minimize the chances of mutations and maintain the accuracy of DNA replication.
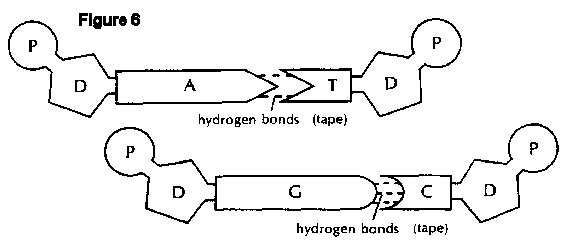
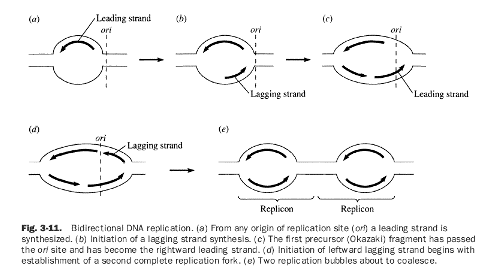
What is the difference between leading and lagging strands in DNA replication?
In DNA replication, the leading strand is synthesized continuously in the 5' to 3' direction by DNA polymerase, while the lagging strand is synthesized discontinuously in the opposite direction in the form of Okazaki fragments, which are later joined together by DNA ligase. The leading strand requires only one primer at the origin of replication, while the lagging strand requires multiple primers for each Okazaki fragment. This difference in synthesis direction and primer requirement is due to the antiparallel nature of DNA strands.
What is the significance of Okazaki fragments in DNA replication?
Okazaki fragments are short fragments of DNA that are formed on the lagging strand during DNA replication. They are significant because DNA replication occurs in a 5' to 3' direction, and the lagging strand is synthesized in short, discontinuous stretches due to its antiparallel orientation. Okazaki fragments are later joined together by DNA ligase to form a continuous strand. These fragments play a crucial role in ensuring accurate and efficient DNA replication.
What role do ligase enzymes play in DNA replication?
Ligase enzymes play a crucial role in DNA replication by sealing the nicks in the phosphodiester backbone of the newly synthesized DNA strands. After the synthesis of Okazaki fragments on the lagging strand, ligase catalyzes the formation of phosphodiester bonds between the fragments, creating a continuous, intact DNA strand. This process helps ensure the accurate and complete replication of the genetic material.
How are the two DNA strands separated during replication?
During DNA replication, the two DNA strands are separated by an enzyme called helicase, which unwinds the double helix by breaking the hydrogen bonds between the nitrogenous bases. This creates a replication fork where the strands are exposed and ready for replication to occur.
What is the overall goal of DNA replication?
The overall goal of DNA replication is to ensure that each new cell receives an identical copy of the genetic material, enabling accurate transmission of genetic information from one generation to the next. This process is essential for cell division, growth, and repair, allowing organisms to maintain genetic stability and pass on hereditary traits.
Have something to share?
Who is Worksheeto?
At Worksheeto, we are committed to delivering an extensive and varied portfolio of superior quality worksheets, designed to address the educational demands of students, educators, and parents.



















Comments