Milky Way Galaxy Worksheets Elementary
Are you in search of engaging and educational resources to teach your elementary students about the Milky Way Galaxy? Look no further! Our Milky Way Galaxy worksheets are perfect for introducing young learners to the fascinating entity that surrounds our planet. These worksheets provide a comprehensive and age-appropriate exploration of the subject, offering an interactive and informative learning experience.
Table of Images 👆
More Other Worksheets
Kindergarten Worksheet My RoomSpanish Verb Worksheets
Cooking Vocabulary Worksheet
My Shadow Worksheet
Large Printable Blank Pyramid Worksheet
Relationship Circles Worksheet
DNA Code Worksheet
Meiosis Worksheet Answer Key
Art Handouts and Worksheets
7 Elements of Art Worksheets
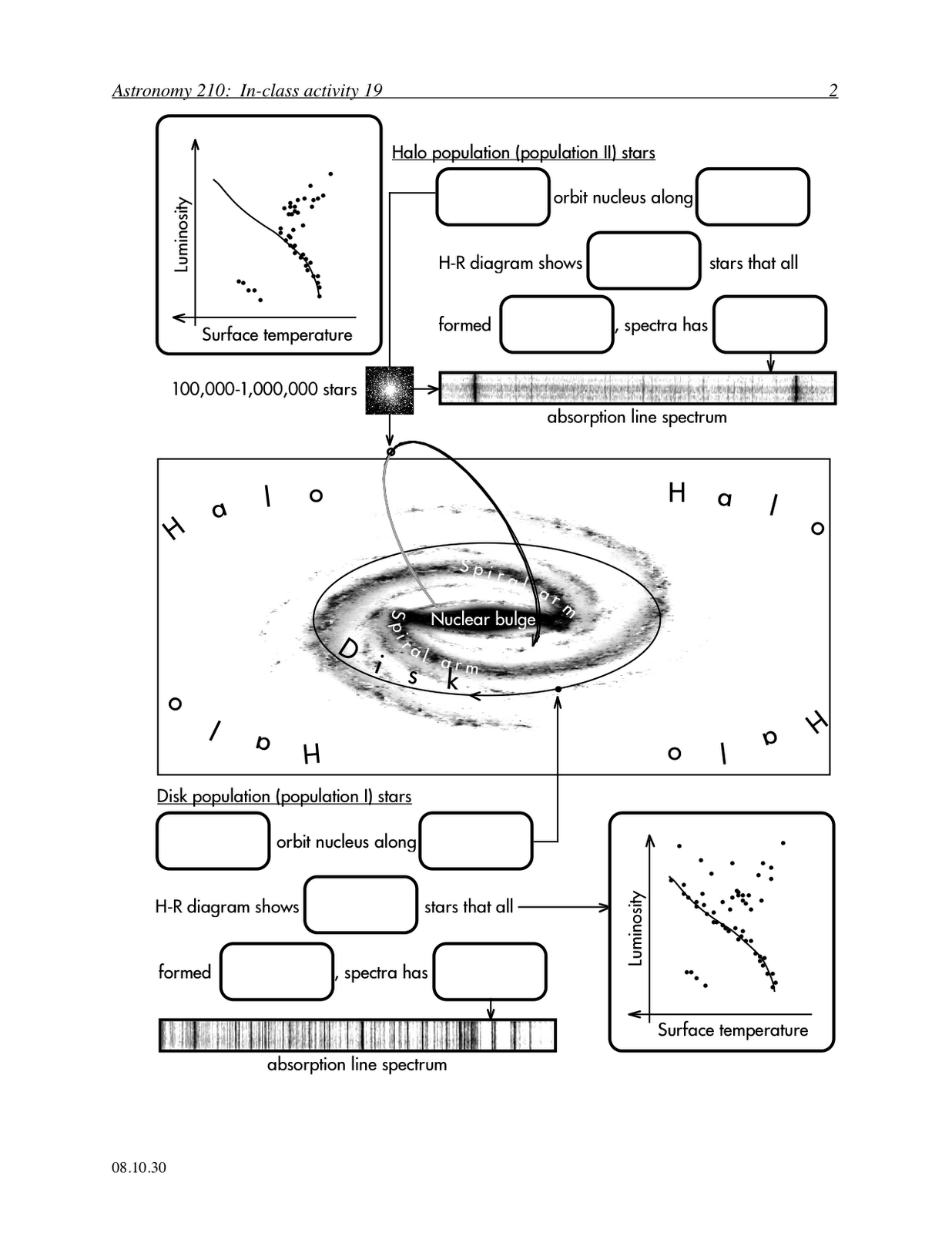
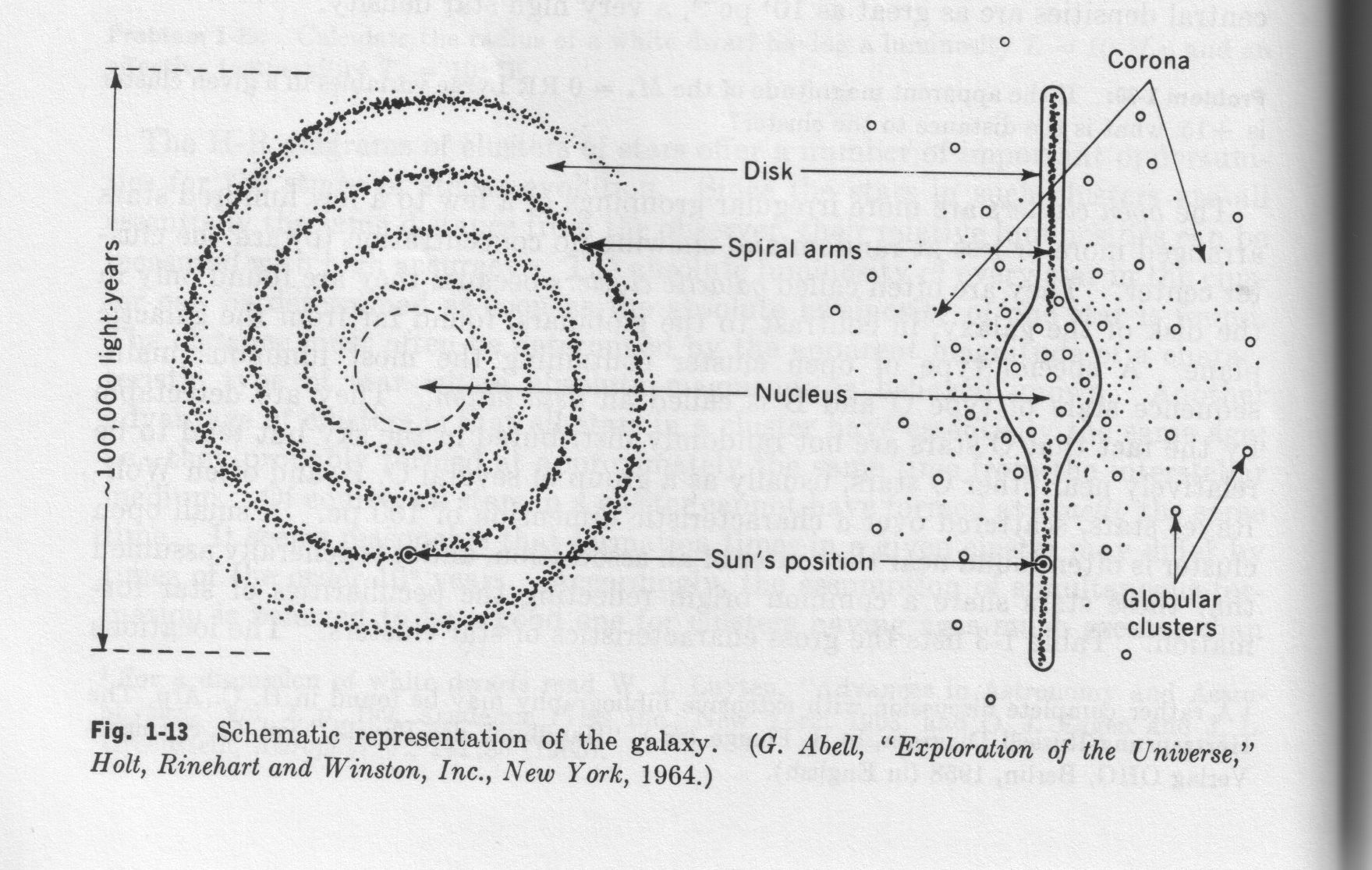
What is the Milky Way galaxy?
The Milky Way galaxy is a massive collection of stars, planets, gas, dust, and other celestial bodies that form a spiral shape in space. It is where our solar system, including Earth, is located. The Milky Way is estimated to contain billions of stars and stretches over 100,000 light-years in diameter.
How many stars are estimated to be in the Milky Way galaxy?
There are estimated to be around 100 to 400 billion stars in the Milky Way galaxy.
How long does it take for our solar system to complete one orbit around the center of the Milky Way galaxy?
It takes approximately 225-250 million years for our solar system to complete one orbit around the center of the Milky Way galaxy.
What are some typical characteristics of stars found in the Milky Way galaxy?
Typical characteristics of stars found in the Milky Way galaxy include being mainly composed of hydrogen and helium, residing in the main sequence stage of their life cycle, having a range of masses and sizes, emitting light and heat due to nuclear fusion reactions in their cores, having varying temperatures and colors (from red dwarfs to blue giants), and being part of multiple star systems or clusters throughout the galaxy.
How is the Milky Way galaxy classified in terms of its shape?
The Milky Way galaxy is classified as a barred spiral galaxy, characterized by a central bar-shaped structure composed of stars surrounded by spiral arms that extend outwards.
What is believed to be located at the center of the Milky Way galaxy?
At the center of the Milky Way galaxy is believed to be a supermassive black hole called Sagittarius A*, which has a mass millions of times greater than that of our sun. This black hole plays a crucial role in shaping the movement of stars and other celestial objects within the galaxy.
Are there any other galaxies in the vicinity of the Milky Way?
Yes, there are several galaxies in the vicinity of the Milky Way. The Milky Way is part of the Local Group, which is a collection of over 54 galaxies, including the Andromeda Galaxy, Triangulum Galaxy, and several dwarf galaxies. These galaxies are gravitationally bound to each other and are relatively close in terms of cosmic distances.
How do astronomers study the Milky Way galaxy?
Astronomers study the Milky Way galaxy using a variety of tools such as telescopes (both ground-based and space-based), radio telescopes, infrared detectors, and computer simulations to gather and analyze data on the structure, composition, movements, and interactions of the stars, gas, dust, and dark matter within our galaxy. By observing different wavelengths of light, measuring the velocities and distances of stars and interstellar matter, and using models to interpret the data, astronomers are able to investigate the formation, evolution, and dynamics of the Milky Way galaxy.
Can humans see the entire Milky Way galaxy from Earth?
No, humans cannot see the entire Milky Way galaxy from Earth as we are inside the galaxy. What we observe from Earth is a portion of the Milky Way that is visible to us based on our location within the galaxy, the presence of dust clouds, and light pollution.
What are some interesting facts about the Milky Way galaxy?
The Milky Way galaxy is estimated to be around 13.6 billion years old, containing between 100 to 400 billion stars. It is part of a galaxy group called the Local Group, which also includes the Andromeda galaxy. The Milky Way is rotating at a speed of about 168 miles per second and is home to a supermassive black hole at its center, which is around 4 million times the mass of our sun. Additionally, the Milky Way is on a collision course with the Andromeda galaxy and is expected to collide in about 4 billion years, merging to form a new galaxy.
Have something to share?
Who is Worksheeto?
At Worksheeto, we are committed to delivering an extensive and varied portfolio of superior quality worksheets, designed to address the educational demands of students, educators, and parents.























Comments