Microscope Magnification Worksheet Answers
This blog post provides the answers to the microscope magnification worksheet. If you are a student or teacher who has been studying the functions and calculations of microscope magnification, then this post is for you.
Table of Images 👆
- Cell Microscope Lab Worksheet
- Microscope Lab Worksheet Answers
- 2nd Grade Reading Comprehension Worksheets
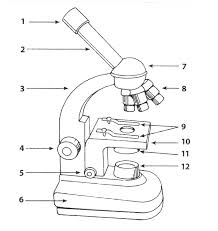
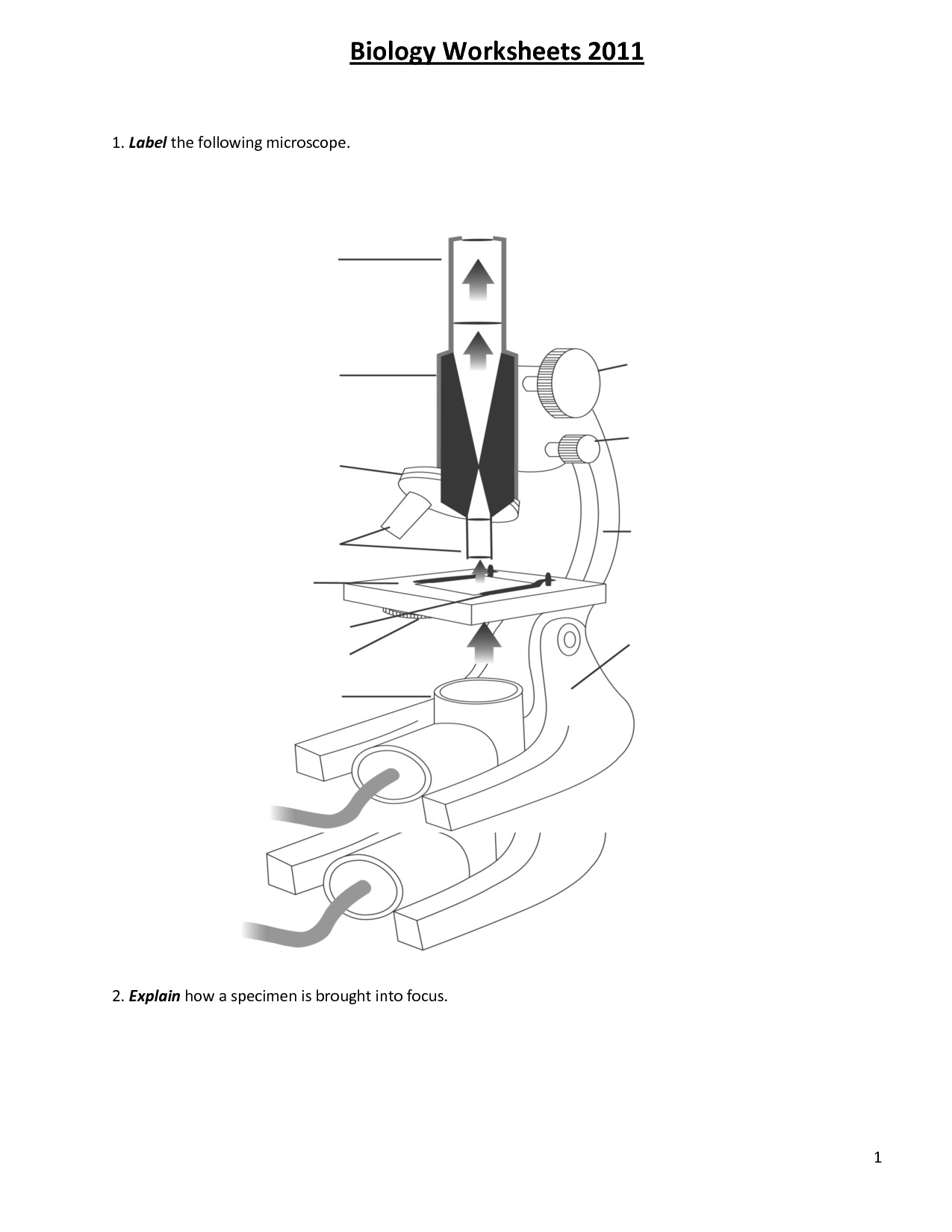
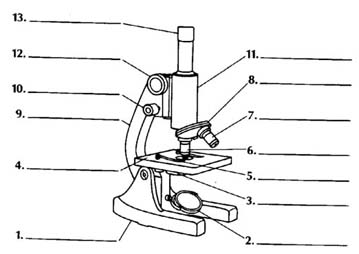
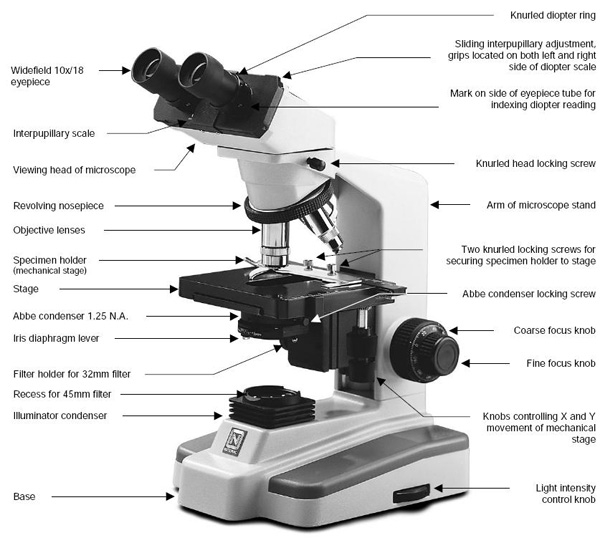
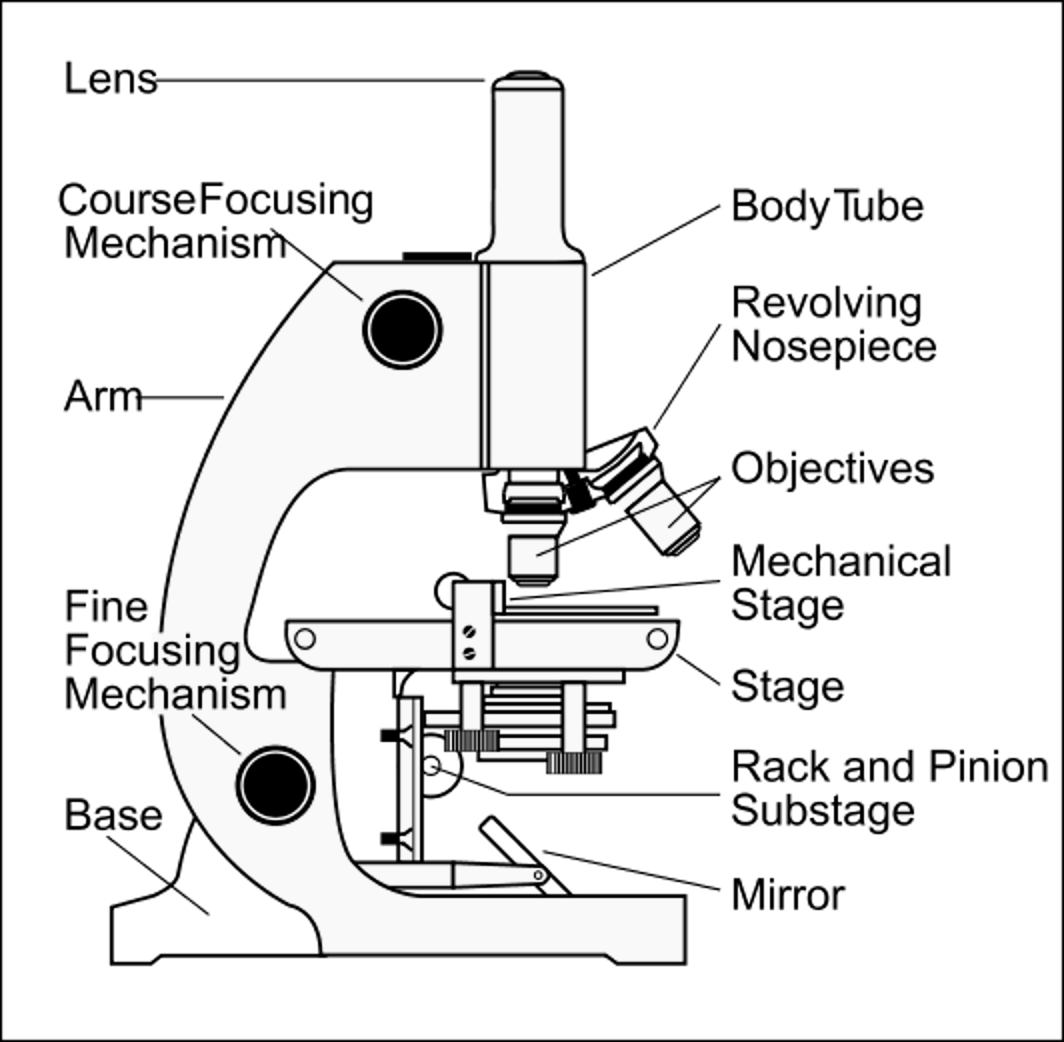
- Microscope Parts and Use Worksheet
- Microscope for Biology Worksheet Answers
- How to Calculate Total Magnification On Microscope
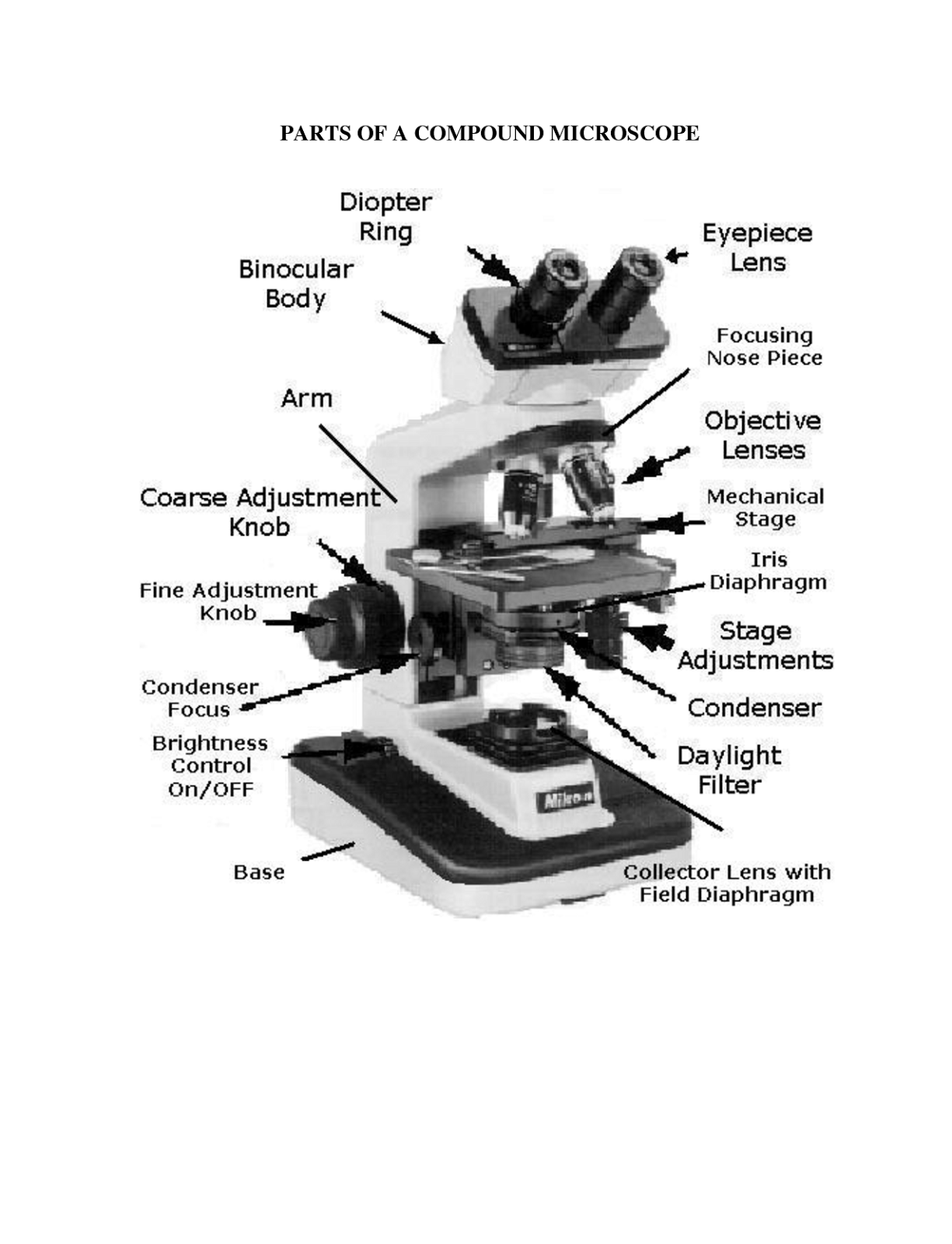
- Compound Light Microscope Parts
- Compound Light Microscope Parts
- Microscope Parts and Their Functions
- Compound Light Microscope Parts
- Labeled Microscope Parts and Functions
- Stereo Microscope Parts and Functions
More Other Worksheets
Kindergarten Worksheet My RoomSpanish Verb Worksheets
Healthy Eating Plate Printable Worksheet
Cooking Vocabulary Worksheet
My Shadow Worksheet
Large Printable Blank Pyramid Worksheet
Relationship Circles Worksheet
DNA Code Worksheet
Meiosis Worksheet Answer Key
Rosa Parks Worksheet Grade 1
What is microscope magnification?
Microscope magnification refers to the degree to which an object appears larger when viewed through a microscope compared to viewing it with the naked eye. This is achieved by lenses in the microscope that focus light rays to produce a highly magnified image of the specimen being observed. Magnification is typically expressed as a ratio or a multiple of how much larger the object appears when viewed through the microscope.
How is microscope magnification measured?
Microscope magnification is typically measured by the total magnification achieved through the combination of the ocular lens (eyepiece) and the objective lens. The magnification of the ocular lens is usually 10x, while the magnification of the objective lens can vary depending on the microscope. To calculate the total magnification, you simply multiply the magnification of the ocular lens by the magnification of the objective lens. For example, if the objective lens has a magnification of 40x and the ocular lens has a magnification of 10x, then the total magnification would be 10x * 40x = 400x.
What is the formula for calculating total magnification?
The formula for calculating total magnification is the product of the magnification of the objective lens and the magnification of the eyepiece. Total magnification = magnification of objective lens x magnification of eyepiece.
What is the purpose of increasing microscope magnification?
The purpose of increasing microscope magnification is to observe and study smaller details and structures with greater clarity and precision. This allows researchers and scientists to analyze and understand specimens at a higher level of detail, enabling advancements in various fields such as biology, medicine, and materials science.
How does increasing magnification affect image clarity?
Increasing magnification typically increases image detail and clarity as it enlarges the image, allowing for a closer view of smaller objects or finer details. However, at very high magnifications, there is a potential for image distortion or reduced depth of field, which can impact the overall clarity of the image. It is important to balance magnification with other factors such as lighting, focus, and resolution to achieve the best image quality.
What are the two types of magnification in a microscope?
The two types of magnification in a microscope are optical magnification, which occurs due to the lenses in the microscope system, and digital magnification, which involves capturing an image of the sample and then zooming in using software or hardware to see details more clearly.
What is the difference between optical and digital magnification?
Optical magnification relies on physical lenses to enlarge an image directly, preserving image quality and details. On the other hand, digital magnification involves electronically enlarging an image by interpolating and extrapolating existing data, leading to a loss of image quality and clarity as the image is essentially being digitally zoomed in.
How does the objective lens contribute to magnification?
The objective lens contributes to magnification by gathering and focusing light from the object being observed. Its larger diameter allows more light to enter the lens, which results in a brighter and more detailed image. The shape and curvature of the lens further bend and magnify the light rays, ultimately increasing the size and resolution of the object being viewed.
How does the eyepiece lens contribute to magnification?
The eyepiece lens contributes to magnification by further enlarging the image created by the objective lens. By bending and focusing the light from the objective lens, the eyepiece lens allows the viewer to see a larger and more detailed image than what is visible through the objective lens alone. This combined magnification effect provides a closer view of the object being observed through the microscope.
Can microscope magnification be increased indefinitely?
Microscope magnification cannot be increased indefinitely. There are limits to how much a microscope can magnify due to the physical properties of light and the design of the lenses. At a certain point, further magnification would result in distortions, reduced resolution, and inability to capture clear images. Scientists and engineers continuously strive to improve microscope technology to achieve higher magnifications and resolution, but there will always be practical limits to how much magnification can be achieved.
Have something to share?
Who is Worksheeto?
At Worksheeto, we are committed to delivering an extensive and varied portfolio of superior quality worksheets, designed to address the educational demands of students, educators, and parents.






















Comments