Macromolecules Concept Map Worksheet
Macromolecules are essential components of all living organisms, playing vital roles in various biological processes. Whether you are a biology student looking to enhance your understanding of these complex molecules or a teacher searching for a valuable resource to engage your students in active learning, the Macromolecules Concept Map Worksheet is designed to help you master this topic.
Table of Images 👆
- Macromolecules Chart Worksheet
- Carbon Cycle Concept Map
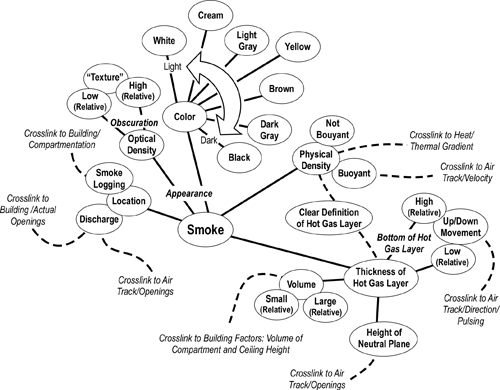
- Blank Concept Map Macromolecules
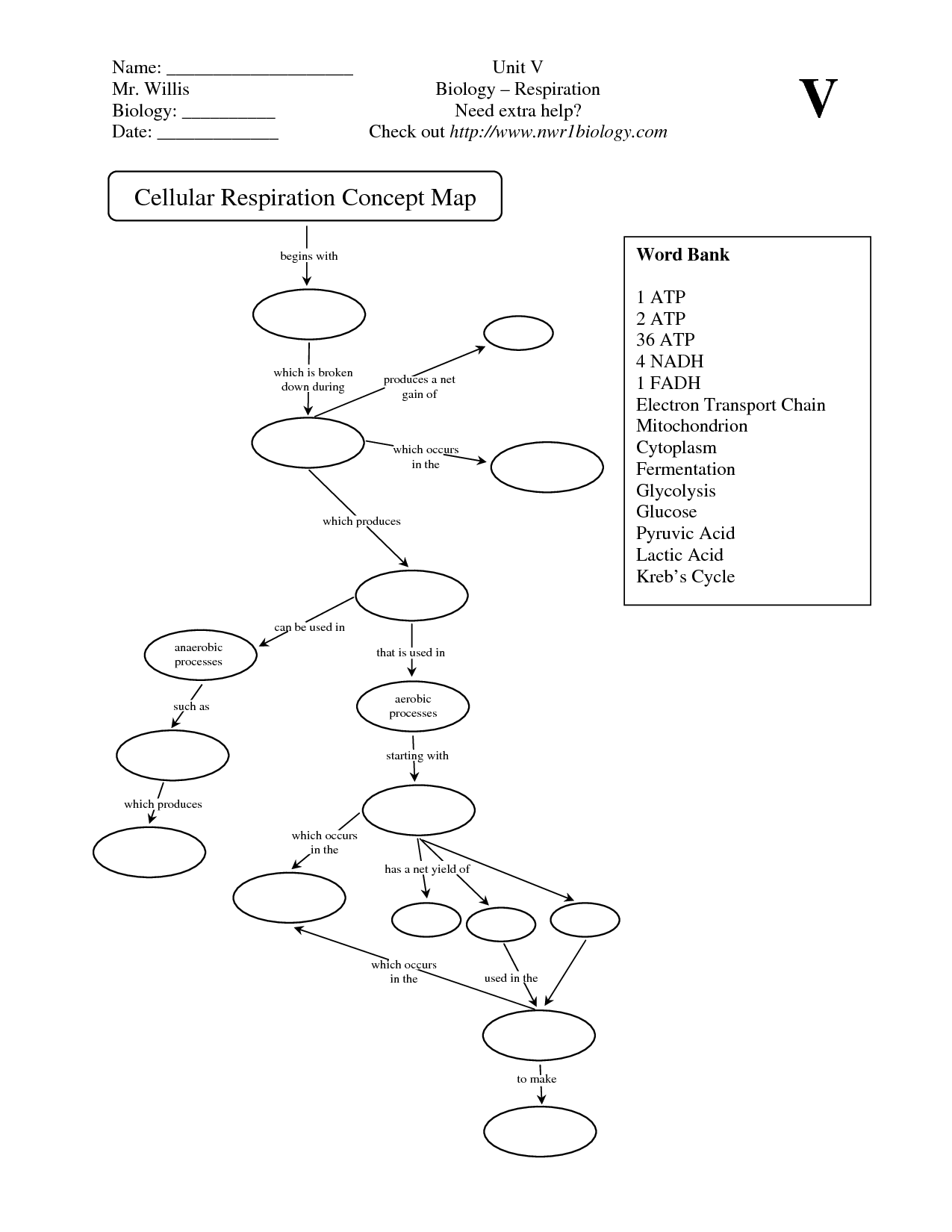
- Cellular Respiration Concept Map Worksheet
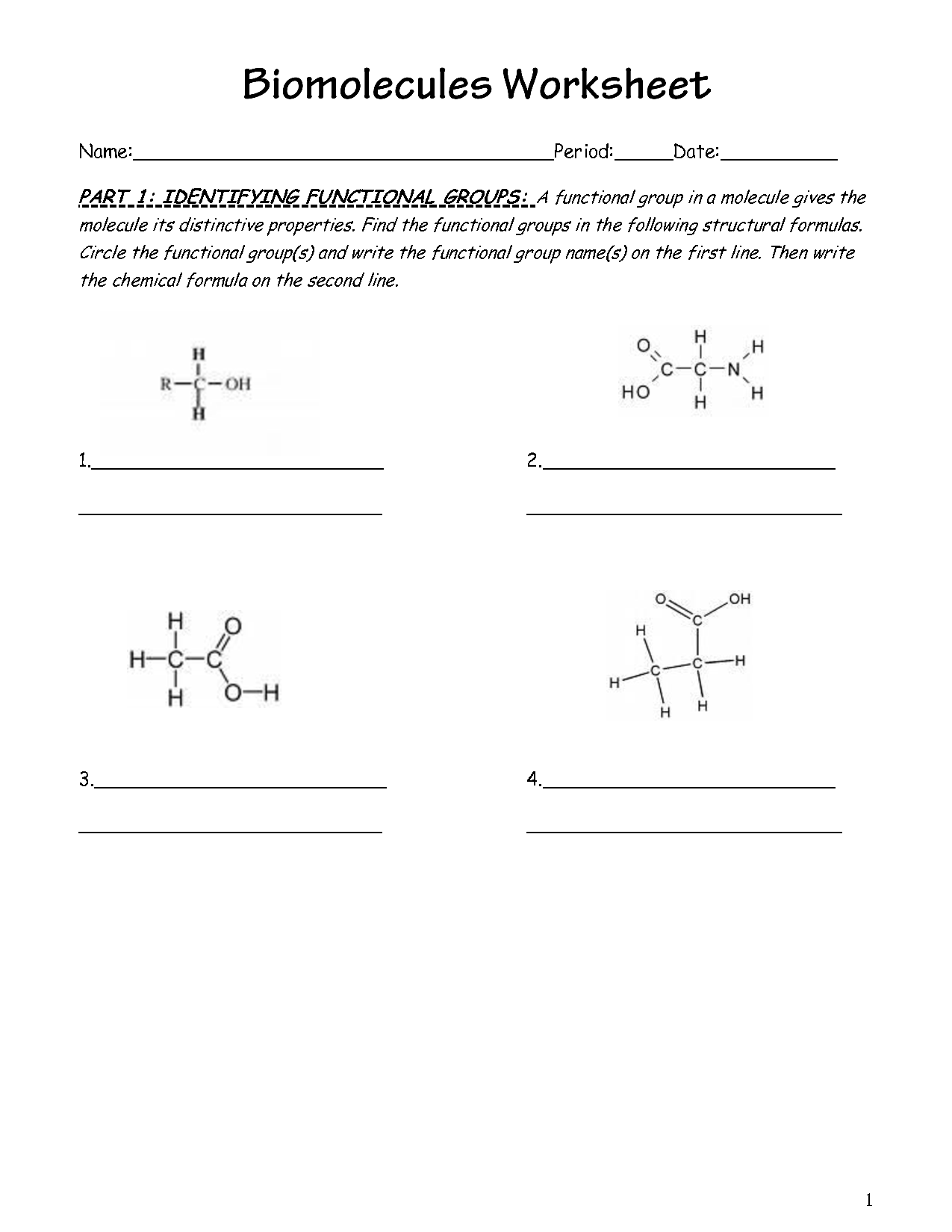
- Identifying Macromolecules Worksheet
- Cell Organelle Concept Map
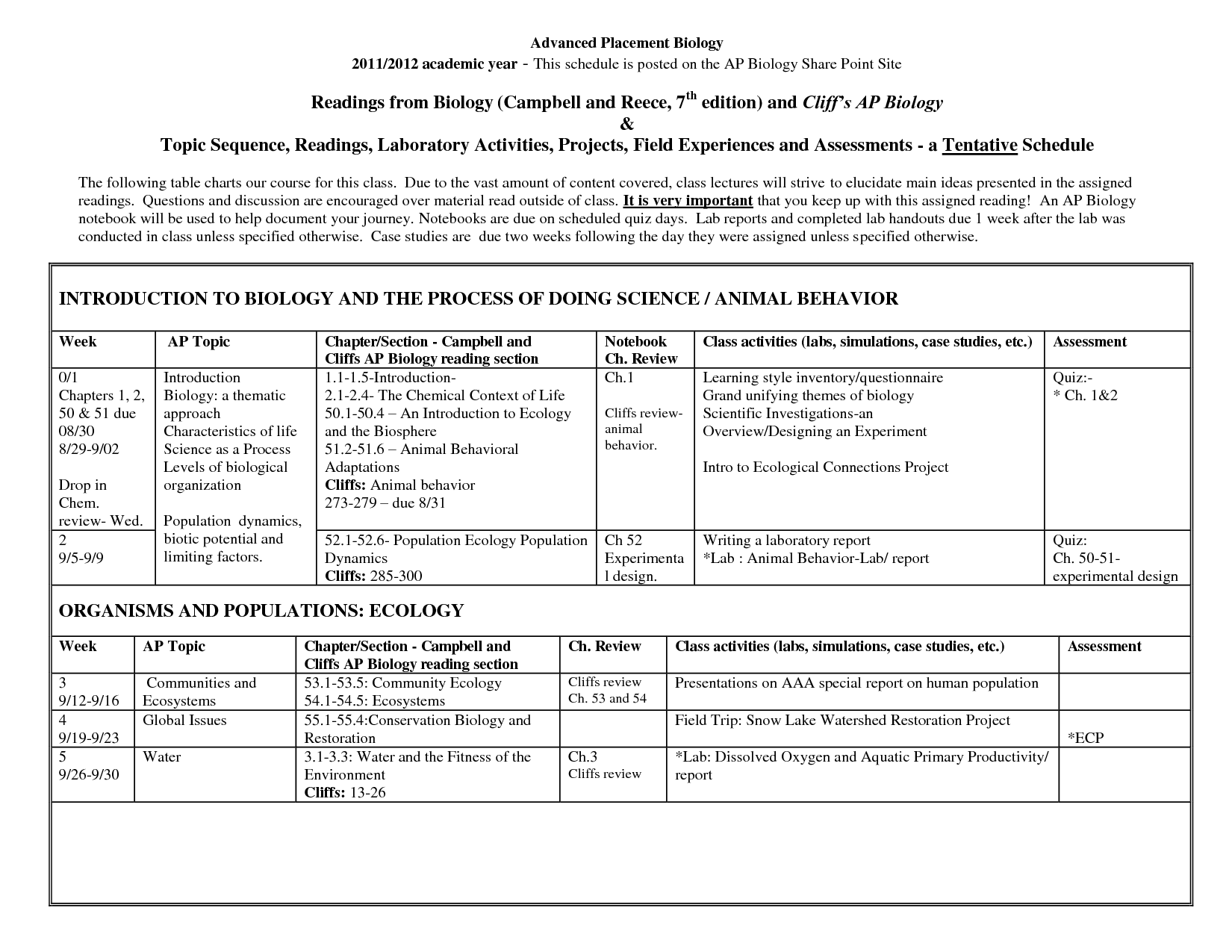
- 9th Biology Macromolecules Chart
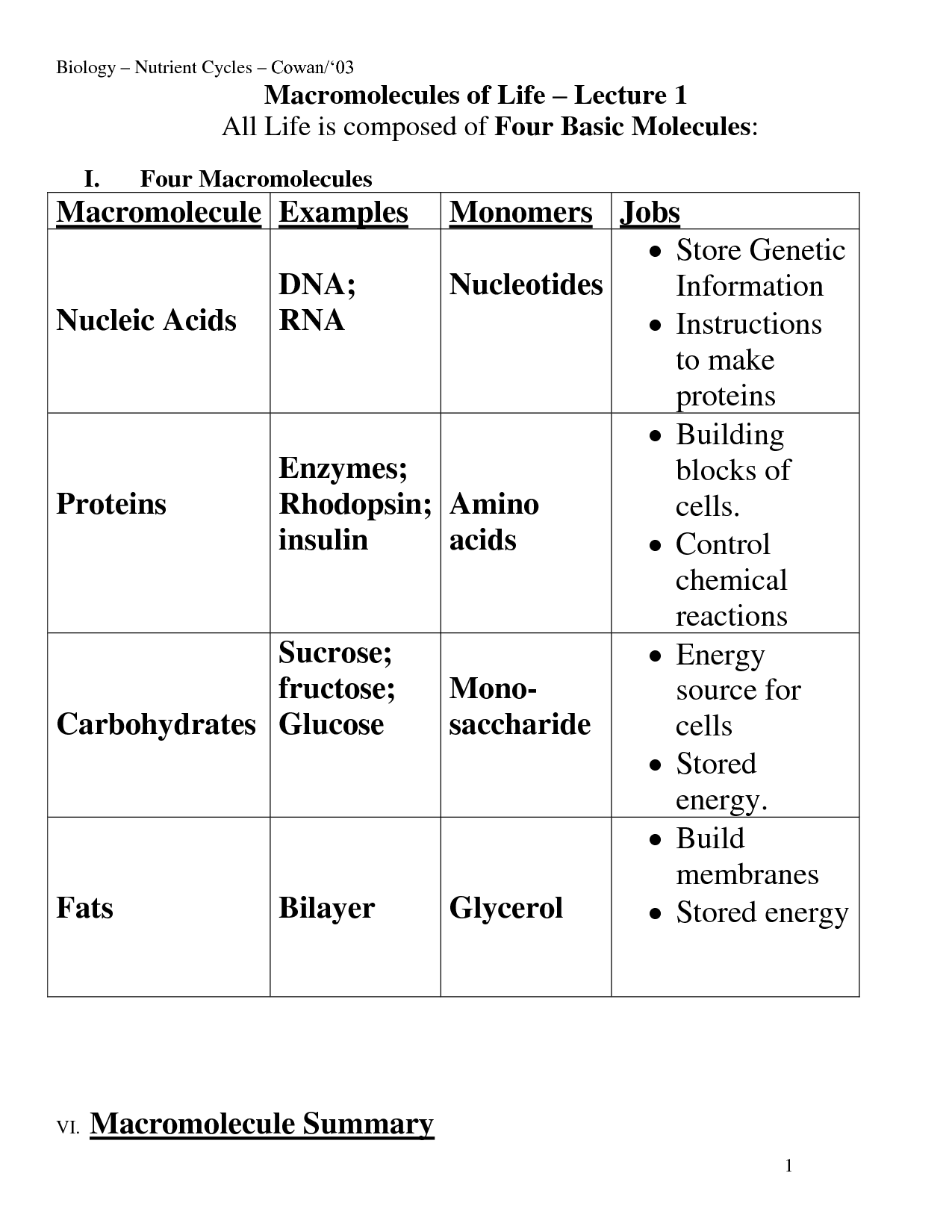
- 4 Macromolecules and Their Functions
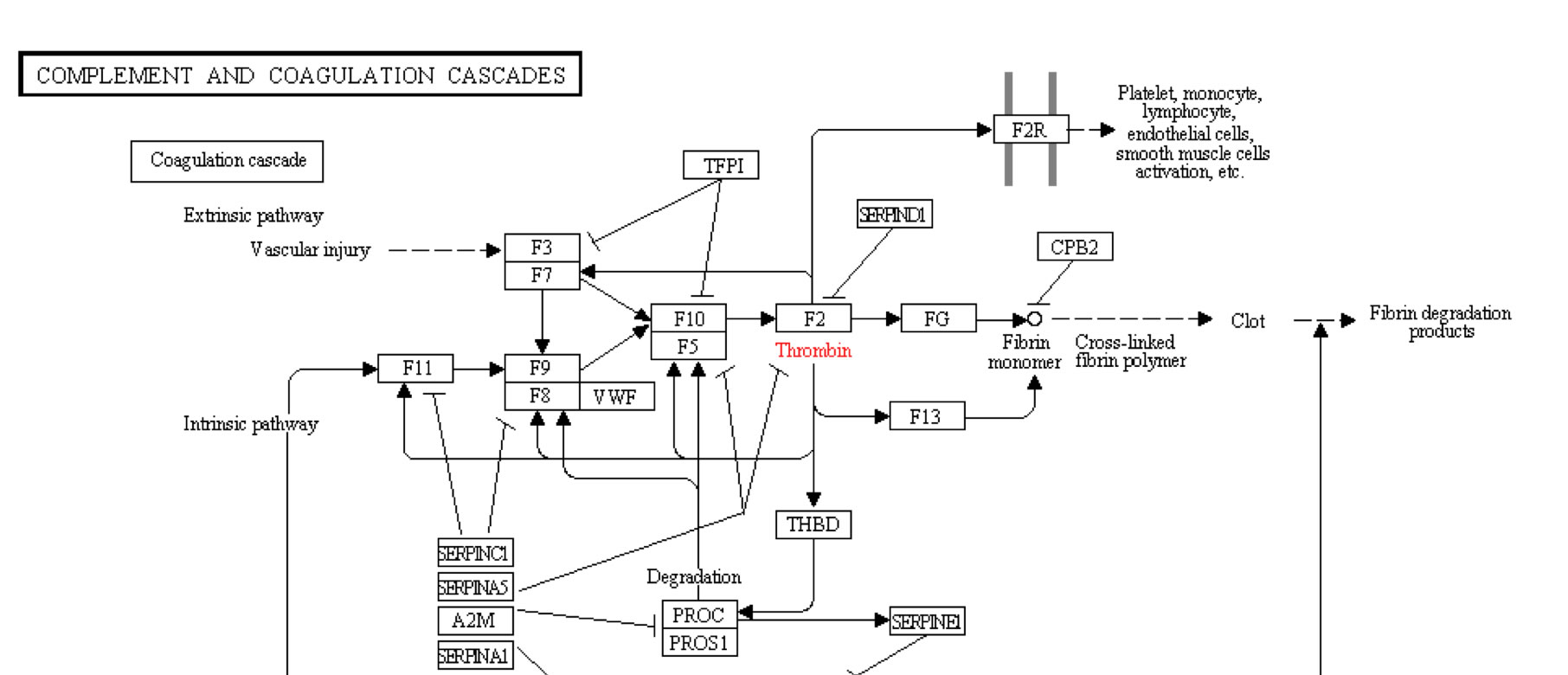
- Blood Clotting Cascade Diagram
- Macromolecule Worksheet Answer Key
- Macromolecule Concept Map Activity
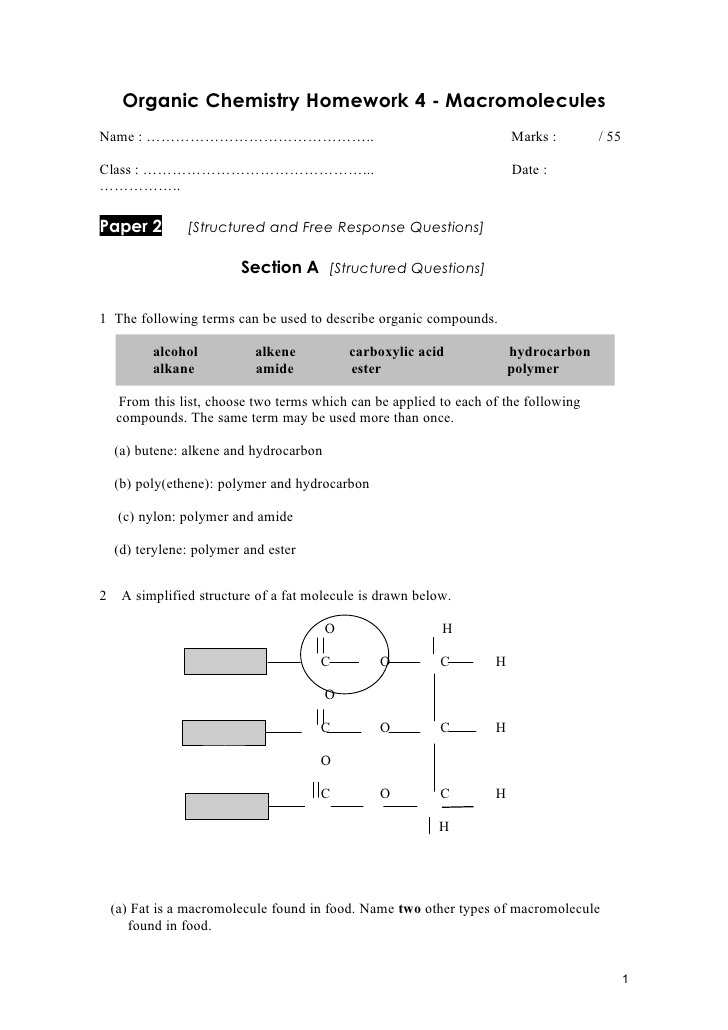
- Organic Macromolecules Worksheet Answers
- Macromolecules Chart Answers
- Organic Macromolecules Worksheet
- Macromolecules Graphic Organizer Answer Key
More Other Worksheets
Kindergarten Worksheet My RoomSpanish Verb Worksheets
Healthy Eating Plate Printable Worksheet
Cooking Vocabulary Worksheet
My Shadow Worksheet
Large Printable Blank Pyramid Worksheet
Relationship Circles Worksheet
DNA Code Worksheet
Meiosis Worksheet Answer Key
Rosa Parks Worksheet Grade 1
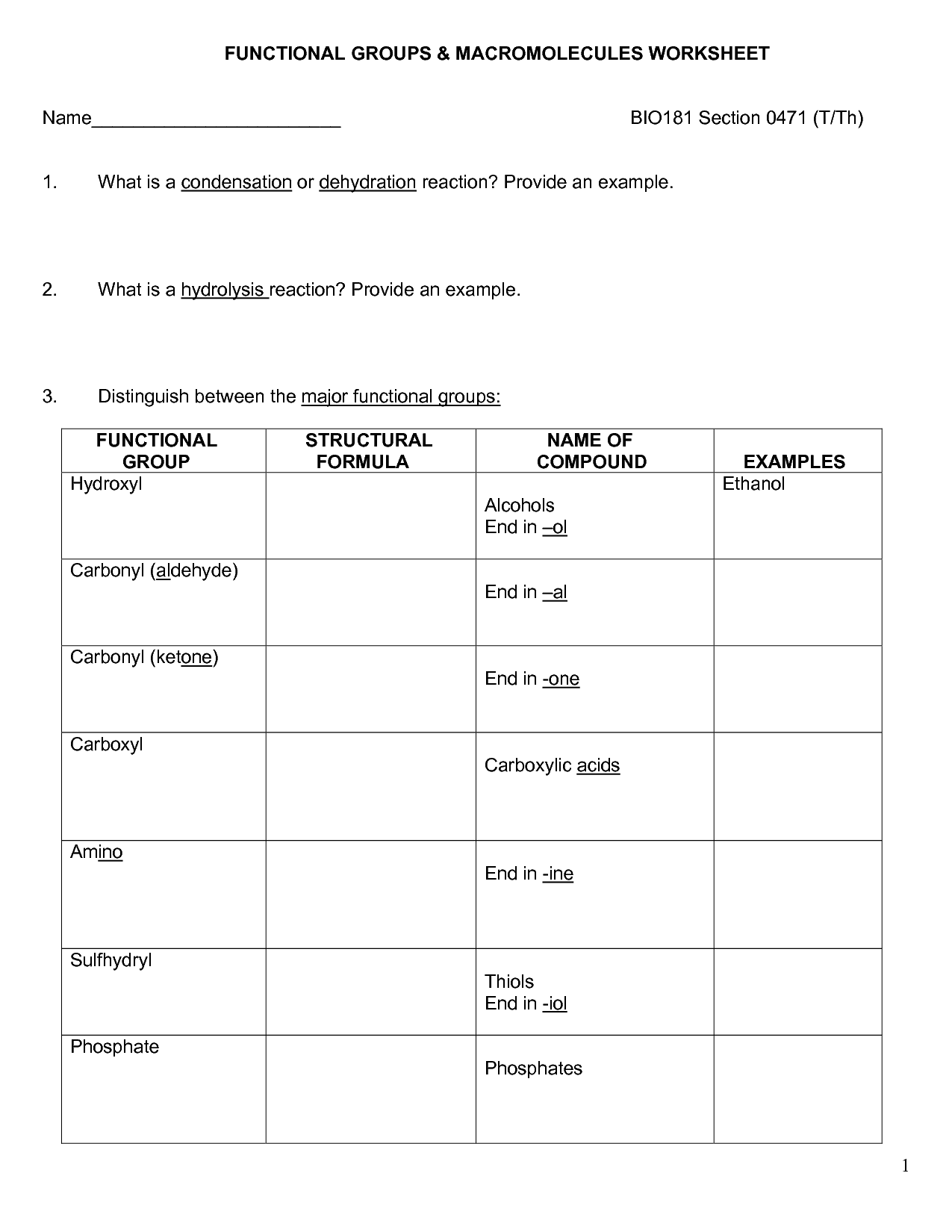
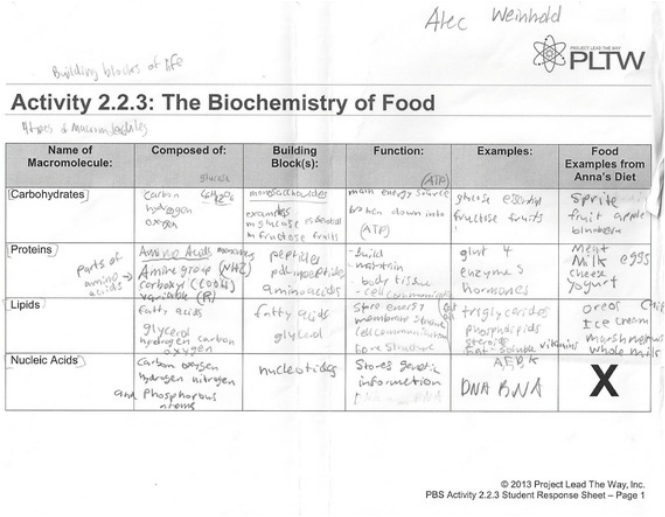
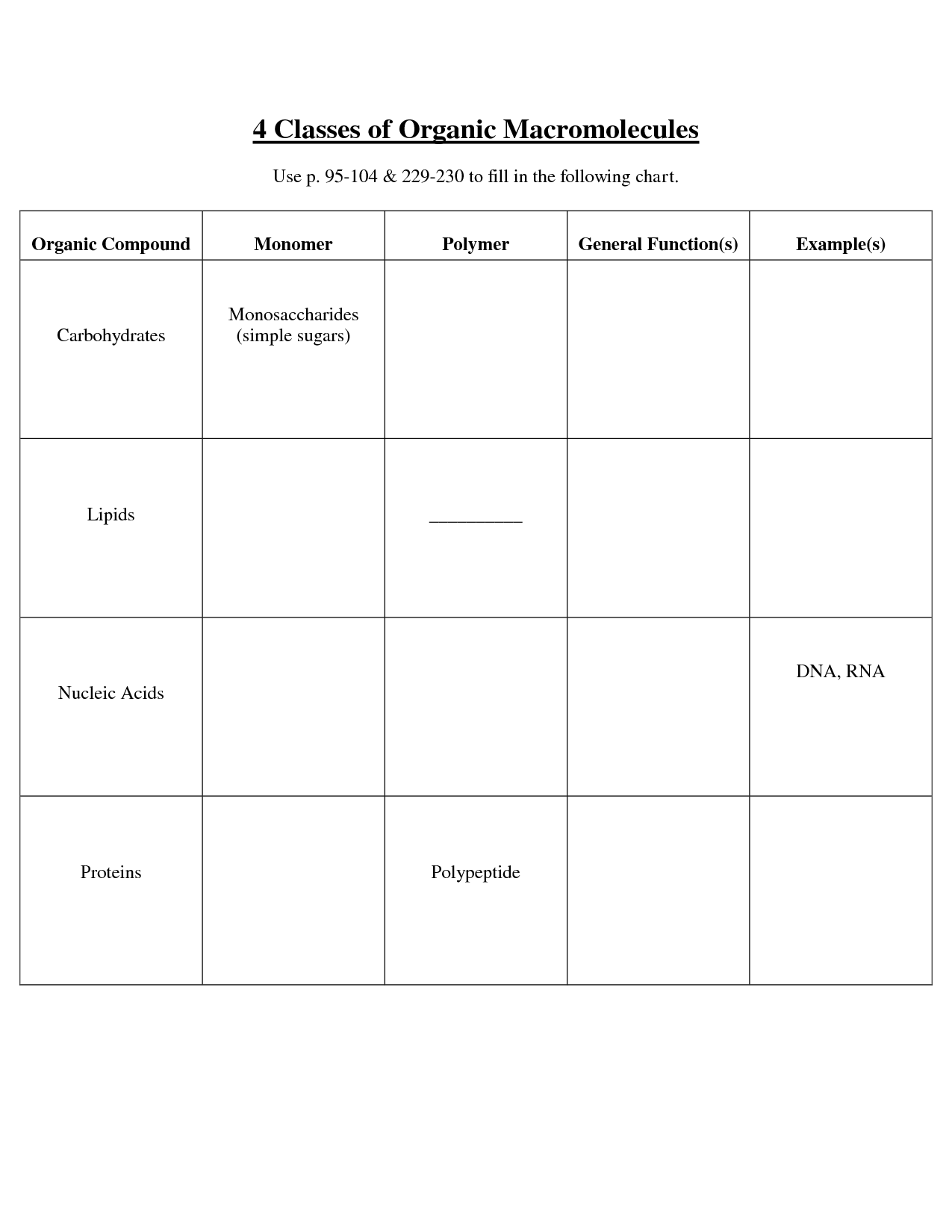
What are the four main types of macromolecules?
The four main types of macromolecules are carbohydrates, lipids, proteins, and nucleic acids. Carbohydrates provide energy and structural support, lipids serve as energy storage molecules and building blocks for cell membranes, proteins function in various biological processes and provide structure, and nucleic acids carry genetic information and aid in protein synthesis.
Describe the structure and function of carbohydrates.
Carbohydrates are organic molecules made up of carbon, hydrogen, and oxygen. They exist in various forms, such as simple sugars (monosaccharides), double sugars (disaccharides), and complex carbohydrates (polysaccharides). Carbohydrates serve as a primary source of energy for the body, particularly glucose, which is the main fuel for cellular functions. They also play a crucial role in providing structural support and maintaining cell integrity. Additionally, carbohydrates contribute to various biological processes, including cell signaling and immune response.
What are the building blocks of proteins, and how are they connected?
Proteins are made up of building blocks called amino acids. There are 20 different types of amino acids that can be combined in various sequences to form proteins. Amino acids are connected together through peptide bonds, which form between the carboxyl group of one amino acid and the amino group of another amino acid. This chain of amino acids, linked by peptide bonds, forms the primary structure of a protein.
Explain the structure and function of lipids.
Lipids are diverse molecules that share the common feature of being hydrophobic, meaning they do not mix well with water. They are essential components of cell membranes, providing a barrier that controls the flow of substances in and out of cells. Lipids also serve as energy storage molecules, with triglycerides storing energy in the form of fatty acids. Additionally, lipids play a crucial role in cell signaling and are involved in processes such as hormone production and nerve signaling. The main types of lipids include fats, phospholipids, and steroids, each with specific structures and functions in the body.
How are nucleic acids involved in the storage and transmission of genetic information?
Nucleic acids, such as DNA and RNA, are involved in the storage and transmission of genetic information through their structure and function. DNA carries the genetic code in the form of nucleotide sequences, which encode instructions for making proteins and governing cell functions. This genetic information is passed from parent to offspring during reproduction. RNA plays a critical role in decoding and translating this genetic code into proteins through the process of transcription and translation. Overall, nucleic acids serve as the fundamental molecules responsible for storing and transmitting genetic information in living organisms.
Describe the process of dehydration synthesis and its role in the formation of macromolecules.
Dehydration synthesis is a chemical reaction in which two molecules covalently bond together with the removal of a water molecule. It plays a crucial role in the formation of macromolecules such as proteins, carbohydrates, and lipids by linking smaller subunits to form larger chain-like molecules. During dehydration synthesis, the OH group from one molecule and an H atom from another molecule combine to form water, while the remaining oxygen and hydrogen atoms combine to form a covalent bond between the two molecules. This process is essential for building complex biological structures and facilitating the synthesis of various macromolecules in living organisms.
What are enzymes, and how do they facilitate chemical reactions in living organisms?
Enzymes are biological molecules that act as catalysts to facilitate chemical reactions in living organisms. They speed up reactions by lowering the activation energy required for a reaction to occur, making the process more efficient and faster. Enzymes achieve this by binding to reactant molecules and bringing them together in a precise orientation to promote the formation of products. This allows cells to carry out essential processes such as metabolism, growth, and repair at a much quicker rate than would be possible without enzymes.
Explain the importance of DNA and RNA in protein synthesis.
DNA is crucial in protein synthesis as it contains the genetic instructions necessary for building proteins. RNA plays a key intermediary role by transcribing these instructions from DNA and translating them into protein sequences. DNA serves as the blueprint for synthesizing specific proteins, while RNA helps facilitate the translation process, ensuring that the correct amino acids are assembled to form the desired proteins. Overall, DNA and RNA are essential components in the intricate process of protein synthesis, playing critical roles in ensuring accuracy and efficiency in gene expression.
Describe the role of carbohydrates in providing energy to living organisms.
Carbohydrates are a primary source of energy for living organisms. When consumed, carbohydrates are broken down into glucose, which is then used by cells as fuel to carry out various biological processes, including growth, reproduction, and movement. Glucose can be immediately used for energy or stored in the form of glycogen in the liver and muscles for later use. In this way, carbohydrates play a crucial role in providing the necessary energy for the survival and functioning of living organisms.
How do macromolecules contribute to the structure and function of cell membranes?
Macromolecules, such as phospholipids, cholesterol, proteins, and carbohydrates, contribute to the structure and function of cell membranes by forming a dynamic barrier that controls the passage of substances in and out of the cell. Phospholipids create a bilayer structure that is selectively permeable, allowing certain molecules to pass through while blocking others. Cholesterol helps maintain membrane fluidity and stability. Proteins embedded in the membrane play key roles in cell signaling, transport of molecules, and structural support. Carbohydrates on the outer surface of the membrane are involved in cell recognition and cell-cell interactions. Together, these macromolecules help regulate the transport of nutrients and waste, maintain cell shape, and facilitate cell communication.
Have something to share?
Who is Worksheeto?
At Worksheeto, we are committed to delivering an extensive and varied portfolio of superior quality worksheets, designed to address the educational demands of students, educators, and parents.




















Comments