Macromolecules Coloring Worksheet
Are you an educator or a biology enthusiast in search of a useful tool to engage your students or enhance your understanding of macromolecules? Look no further than the Macromolecules Coloring Worksheet. This worksheet is designed to help you explore the different types of macromolecules, their functions, and their structural characteristics in a fun and interactive way.
Table of Images 👆
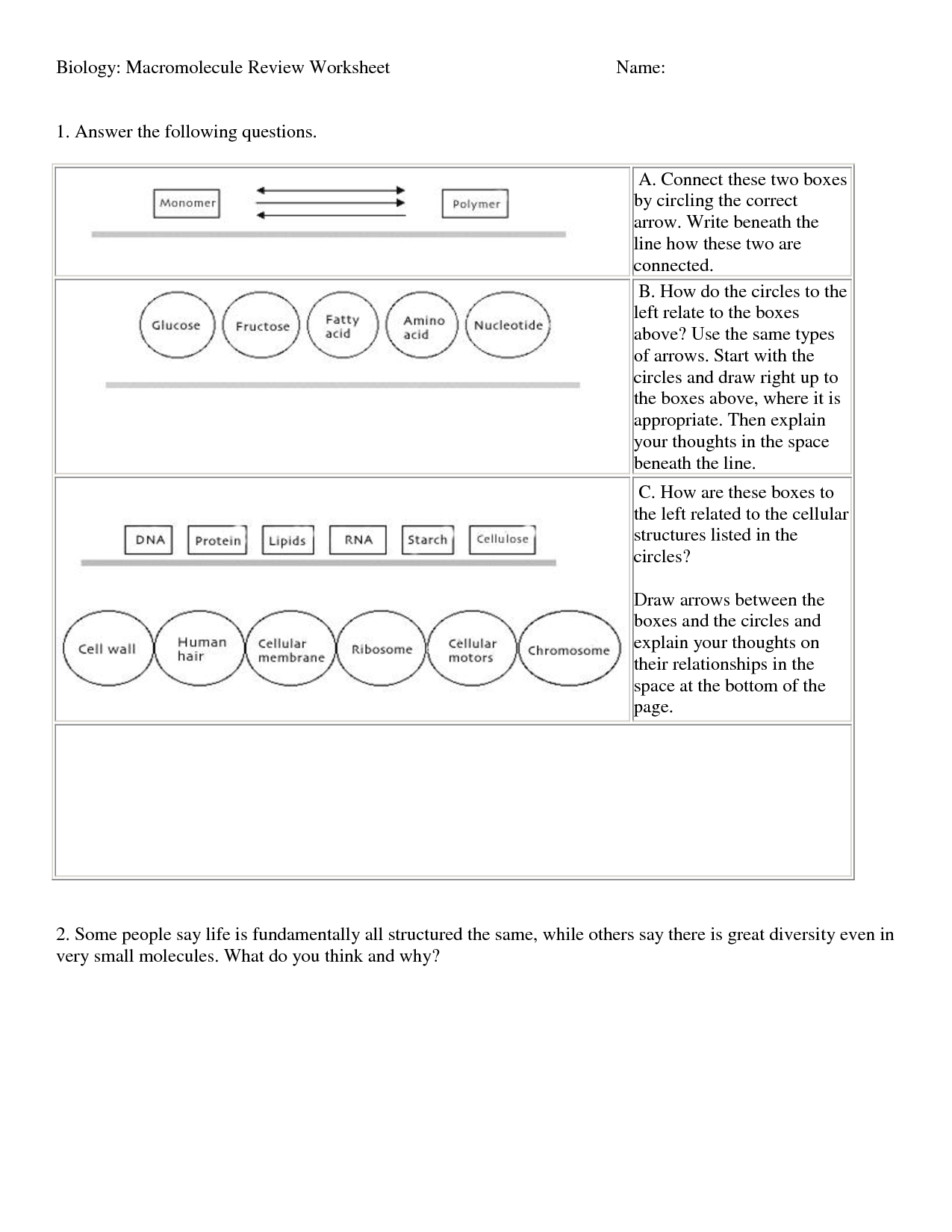
- Macromolecule Worksheet Answer Key
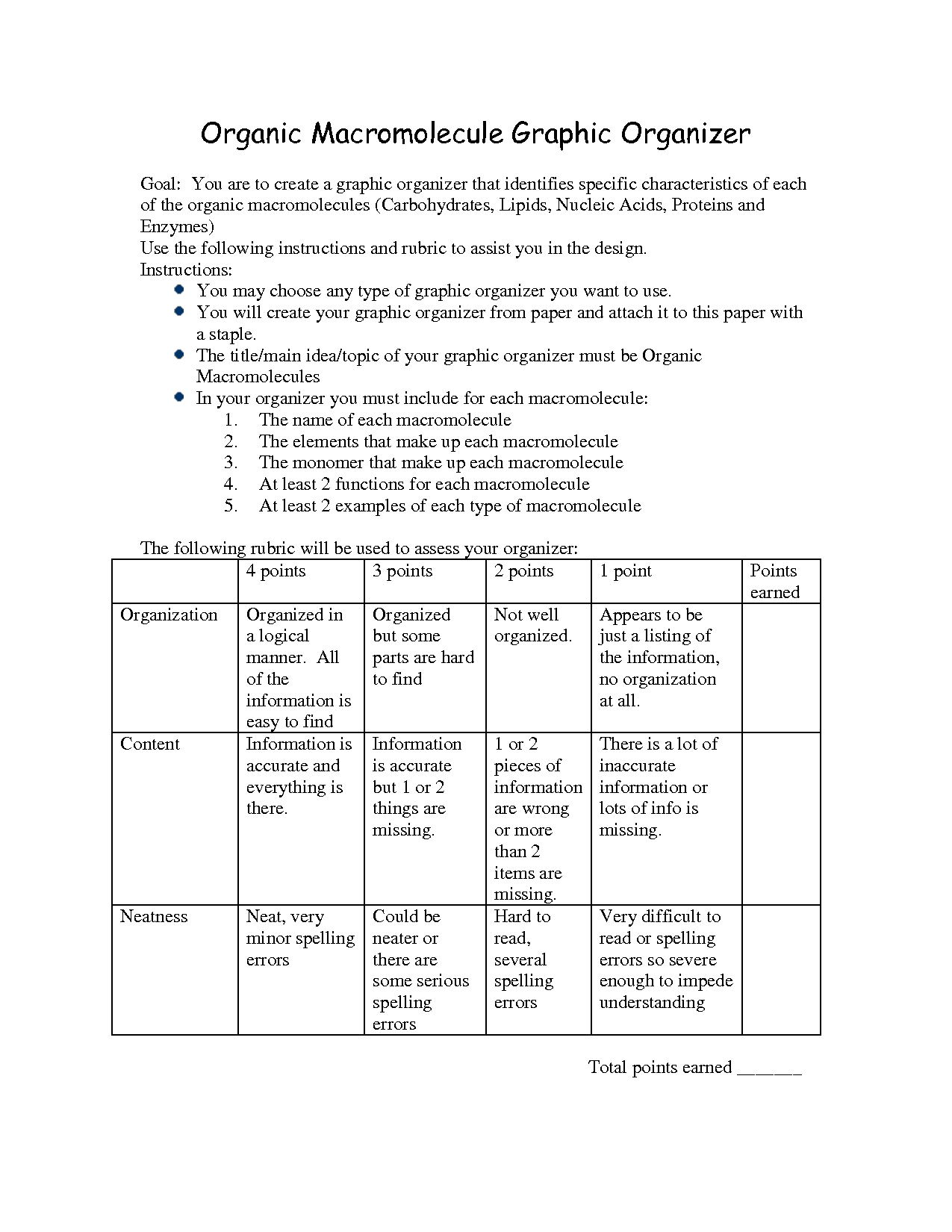
- Organic Macromolecules Graphic Organizer
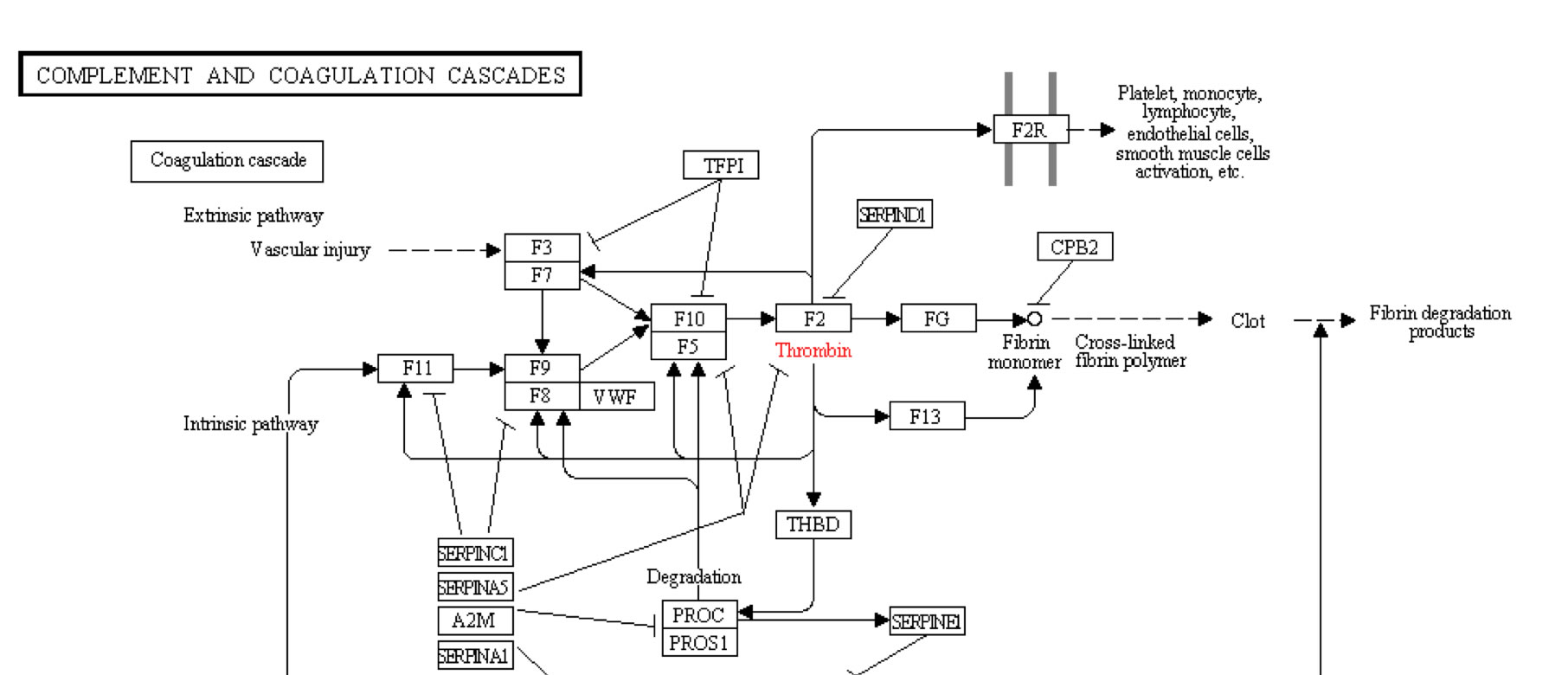
- Blood Clotting Cascade Diagram
- Nucleic Acids Worksheet Answer Key
- Halloween Coloring Pages Comic
- Elements and Macromolecules in Organisms Answer Key
- Macromolecules Graphic Organizer Answer Key
- Macromolecule Monomers and Polymers Chart
- Carbon Cycle Concept Map
- Plant Cell Coloring Diagram
- Macromolecule Worksheet with Answers
- DNA Double Helix Coloring Worksheet
- Moon Phases Cut and Paste Activity
- Evolution Worksheet Answer Key
- Carbohydrates Food Coloring Page
More Other Worksheets
Kindergarten Worksheet My RoomSpanish Verb Worksheets
Cooking Vocabulary Worksheet
My Shadow Worksheet
Large Printable Blank Pyramid Worksheet
Relationship Circles Worksheet
DNA Code Worksheet
Meiosis Worksheet Answer Key
Art Handouts and Worksheets
7 Elements of Art Worksheets
What is the purpose of the Macromolecules Coloring Worksheet?
The purpose of the Macromolecules Coloring Worksheet is to help students understand and visually differentiate between the various types of macromolecules (carbohydrates, lipids, proteins, and nucleic acids) by coloring and labeling different structures, which can aid in their comprehension of these important biomolecules and their functions in living organisms.
How many main types of macromolecules are included in the worksheet?
There are four main types of macromolecules included in the worksheet: carbohydrates, lipids, proteins, and nucleic acids.
Can you name the four main types of macromolecules included in the worksheet?
The four main types of macromolecules included in the worksheet are carbohydrates, lipids, proteins, and nucleic acids.
What are the primary functions of carbohydrates in living organisms?
Carbohydrates primarily serve as a source of energy for living organisms by being broken down into glucose, which is used in cellular respiration to produce ATP. Additionally, carbohydrates play a role in providing structural support in cells, tissues, and organisms through the formation of compounds like cellulose in plants and chitin in arthropods. Carbohydrates also act as a storage form of energy, such as glycogen in animals and starch in plants.
Which macromolecule is responsible for storing and transmitting genetic information?
The macromolecule responsible for storing and transmitting genetic information is deoxyribonucleic acid (DNA).
How do proteins contribute to the structure and function of living organisms?
Proteins play a critical role in the structure and function of living organisms. They serve as building blocks for tissues, organs, and cells, providing structural support and helping with movements. Proteins also act as enzymes, catalyzing chemical reactions necessary for various metabolic processes. Additionally, proteins help transport molecules, regulate gene expression, and contribute to the immune system's defense mechanism. In essence, proteins are essential for the maintenance of life and the functioning of biological systems.
What are the building blocks or monomers of nucleic acids?
The building blocks or monomers of nucleic acids are nucleotides. Each nucleotide consists of a nitrogenous base (adenine, thymine, cytosine, or guanine), a sugar molecule (ribose in RNA or deoxyribose in DNA), and a phosphate group. These nucleotides are joined together through phosphodiester bonds to form the long chains of DNA or RNA molecules.
How are lipids different from other macromolecules in terms of their structure and function?
Lipids are distinct from other macromolecules due to their hydrophobic nature, consisting of long hydrocarbon chains that are not soluble in water. This unique structure enables lipids to serve as important components of cell membranes, acting as a barrier that separates the cell from its environment. Unlike proteins, nucleic acids, and carbohydrates which are mainly involved in structural support, energy storage, and genetic information transfer, lipids primarily function in energy storage, insulation, and signaling, playing crucial roles in maintaining cell structure, regulating metabolism, and serving as precursors for important molecules such as hormones and vitamins.
How do enzymes relate to macromolecules and their role in living organisms?
Enzymes are macromolecules that play a crucial role in living organisms by facilitating and speeding up biochemical reactions. They act as biological catalysts and help in breaking down or building up macromolecules such as proteins, carbohydrates, lipids, and nucleic acids. Enzymes do so by lowering the activation energy required for a reaction to occur, making the process more efficient. Ultimately, enzymes play a vital role in various physiological processes within living organisms, contributing to their survival and function.
What are some real-life examples of macromolecules found in our daily diet?
Some real-life examples of macromolecules found in our daily diet include carbohydrates such as starch in grains, proteins in meat or legumes, and fats in oils or dairy products. These macromolecules provide the essential nutrients and energy needed for our bodies to function properly. Additionally, nucleic acids found in foods like fruits and vegetables play a role in genetic information and cell function. Consuming a balanced diet rich in these macromolecules is important for overall health and well-being.
Have something to share?
Who is Worksheeto?
At Worksheeto, we are committed to delivering an extensive and varied portfolio of superior quality worksheets, designed to address the educational demands of students, educators, and parents.






















Comments