Macromolecule Worksheet Practice
Are you in need of additional practice with macromolecules? Look no further! This macromolecule worksheet is perfect for students who are studying biology or chemistry and want to reinforce their understanding of these important molecules. Whether you're a high school student preparing for an exam or a college student reviewing for a test, this worksheet provides a variety of questions that cover the different types of macromolecules, their structure, and their functions. Get ready to dive into the world of macromolecules with this comprehensive worksheet.
Table of Images 👆
- Nomenclature Worksheet 2 Answer Key
- Identifying Macromolecules Worksheet
- Macromolecule Worksheet Answer Key
- Organic Molecules Worksheet Review Answers
- Macromolecule Worksheet with Answers
- Rabbit Population By Season Gizmo Answer Key
- Identifying Macromolecules Worksheet
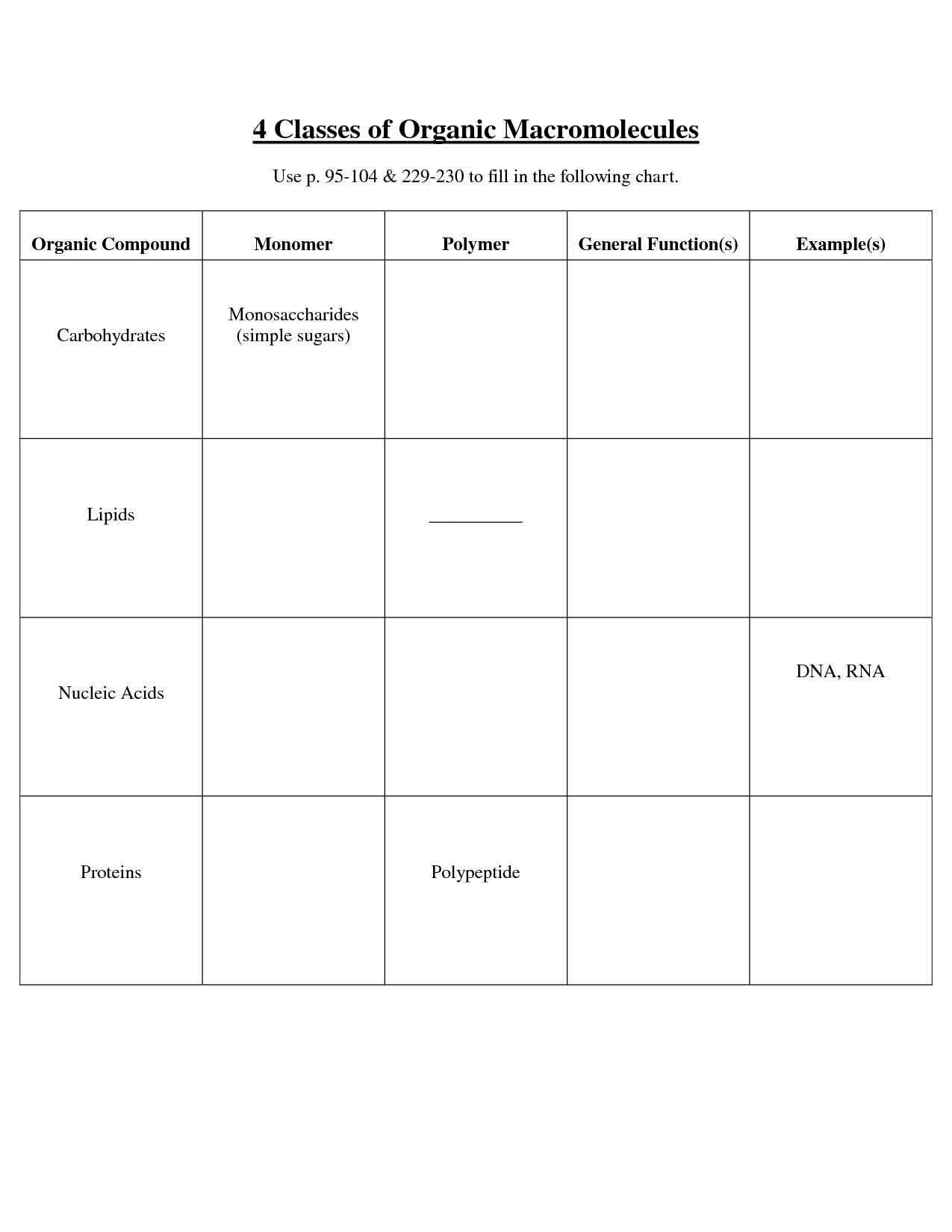
- Organic Macromolecules Worksheet
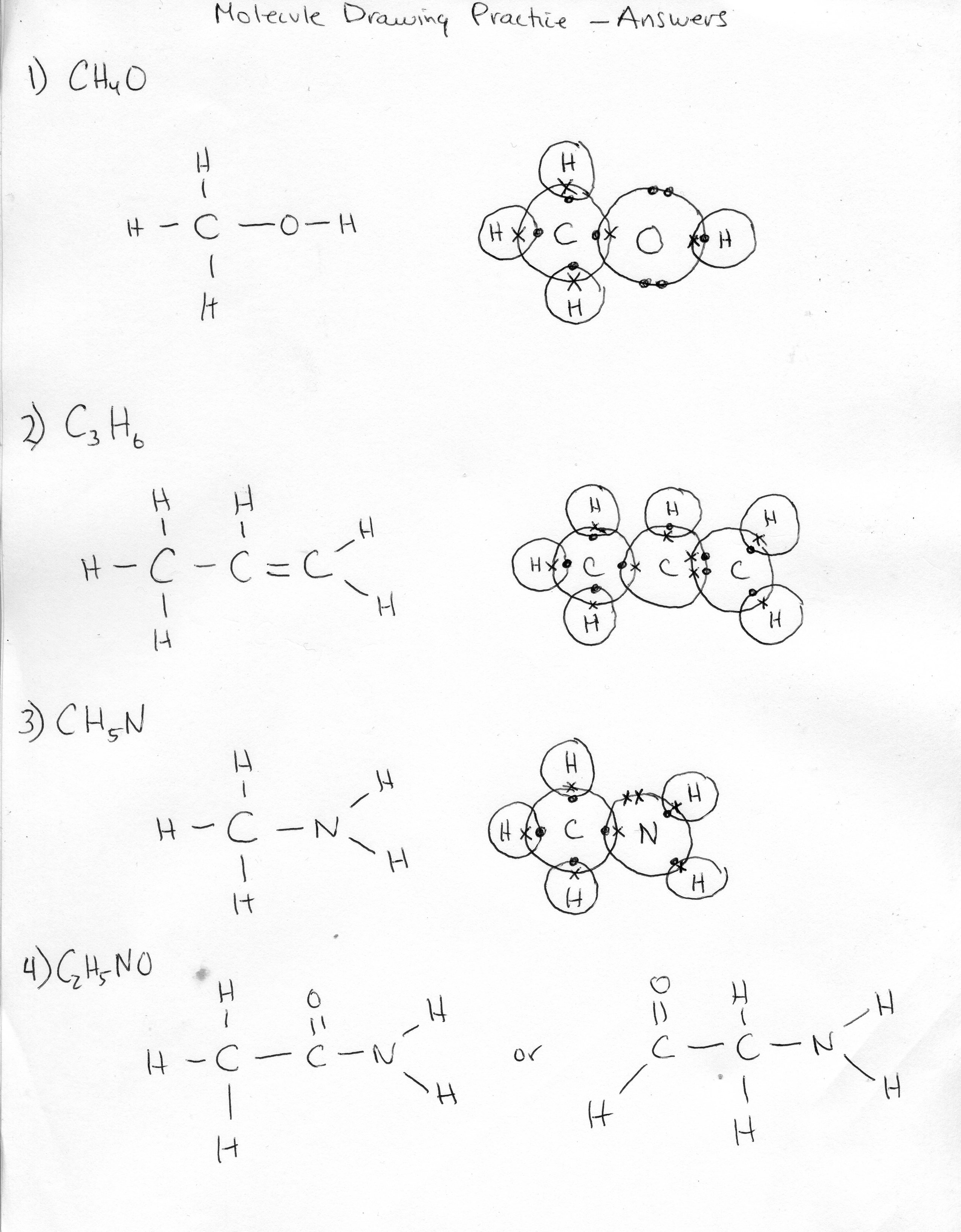
- Drawing Atoms Worksheet Answers
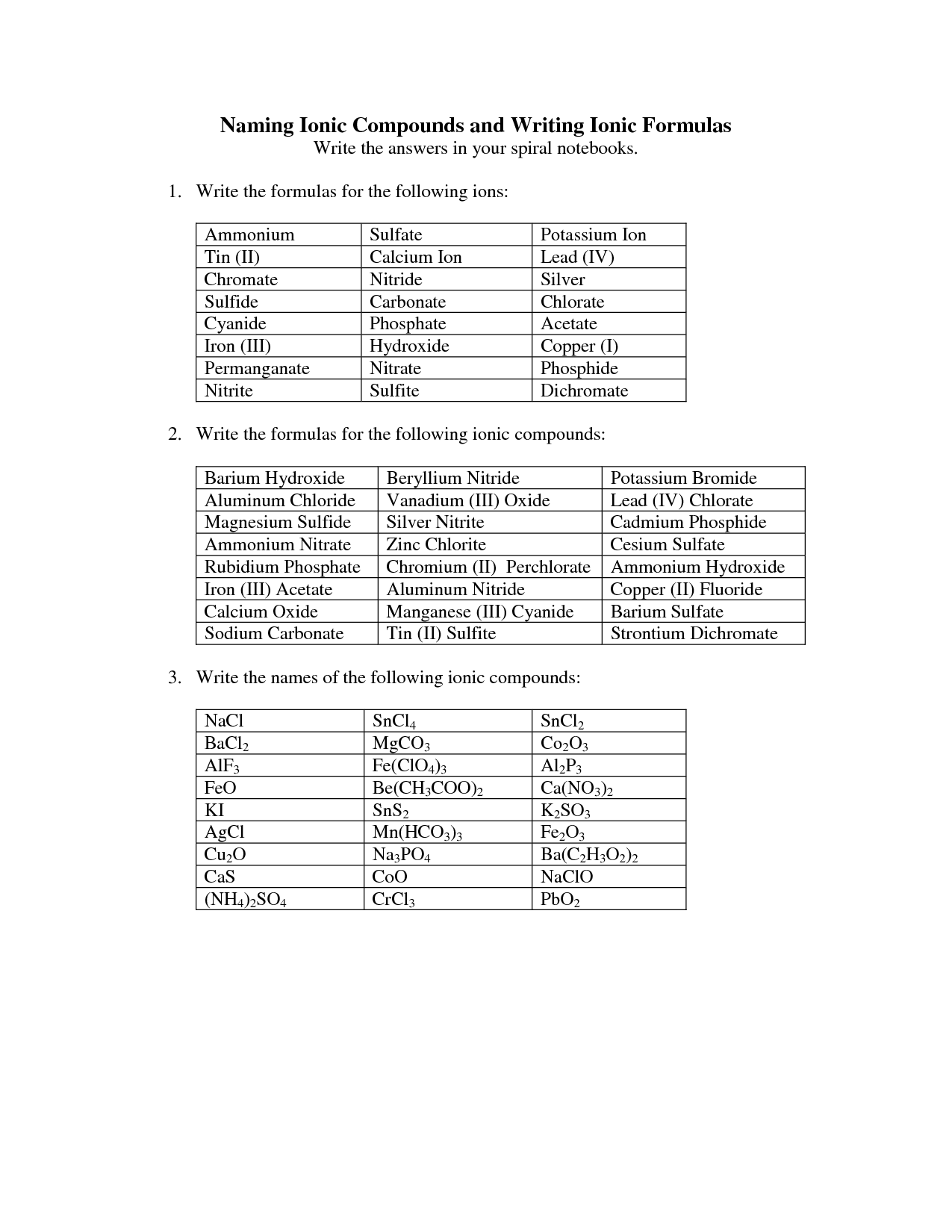
- Writing Ionic Compound Formula Worksheet Answers
- Molecules and Atoms Worksheet Answer Key
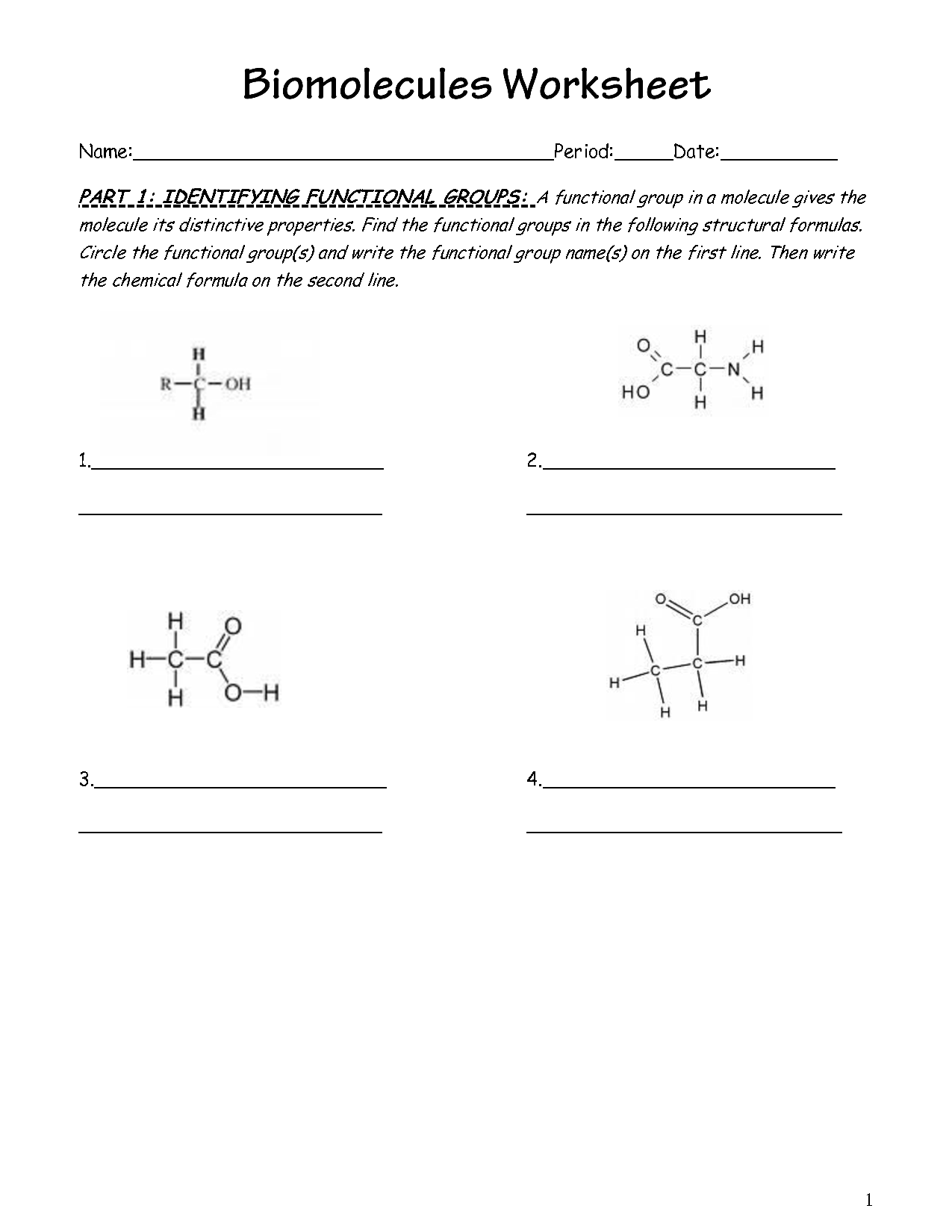
- Organic Molecules Functional Groups Worksheet
- Cinco De Mayo Worksheets Answer Key
More Other Worksheets
Kindergarten Worksheet My RoomSpanish Verb Worksheets
Cooking Vocabulary Worksheet
My Shadow Worksheet
Large Printable Blank Pyramid Worksheet
Relationship Circles Worksheet
DNA Code Worksheet
Meiosis Worksheet Answer Key
Art Handouts and Worksheets
7 Elements of Art Worksheets
What are the monomers of proteins?
The monomers of proteins are amino acids.
What is the primary function of carbohydrates?
The primary function of carbohydrates is to provide energy for the body, specifically in the form of glucose. Carbohydrates are broken down during digestion into glucose, which is used by cells as their main source of fuel to carry out various functions in the body.
How are lipids different from other macromolecules?
Lipids are different from other macromolecules such as proteins, carbohydrates, and nucleic acids because they are hydrophobic, meaning they are insoluble in water. This property allows lipids to form structures such as cell membranes and energy storage molecules that are crucial for the functioning of cells. Additionally, lipids have a higher energy content per gram compared to carbohydrates and proteins, making them an efficient way for organisms to store and utilize energy.
What is the structure of a nucleotide?
A nucleotide is composed of three components: a pentose sugar (either ribose or deoxyribose), a phosphate group, and a nitrogenous base. The nitrogenous base can be adenine (A), cytosine (C), guanine (G), or thymine (T) in DNA, or uracil (U) in RNA. These components are bonded together to form the basic building blocks of nucleic acids like DNA and RNA.
Why are enzymes important in biological processes?
Enzymes are important in biological processes because they act as catalysts, speeding up chemical reactions that are essential for sustaining life. They lower the energy barrier needed for reactions to occur, allowing them to happen at a much faster rate than they would without enzymes. Enzymes are specific in their function, matching with particular substrates to carry out precise biochemical reactions in cells, such as digestion, energy production, and DNA replication. Without enzymes, these essential processes would occur too slowly to sustain life.
What role do nucleic acids play in storing and transmitting genetic information?
Nucleic acids, such as DNA and RNA, play a crucial role in storing and transmitting genetic information. DNA holds the genetic blueprint of an organism, encoding the instructions for protein synthesis and ultimately determining an individual's traits. Through processes like transcription and translation, genetic information is transmitted from DNA to RNA and then to proteins, allowing for the expression of specific genes and the production of necessary molecules for cellular functions. As a result, nucleic acids are essential for genetic inheritance and the passing on of traits from one generation to the next.
What are the three components of a nucleotide?
A nucleotide consists of three components: a phosphate group, a sugar molecule (deoxyribose in DNA and ribose in RNA), and a nitrogenous base (adenine, thymine, cytosine, guanine in DNA; adenine, uracil, cytosine, guanine in RNA).
What is the primary function of a protein?
The primary function of a protein is to serve as a building block for cells, tissues, and organs in the body. Proteins are essential for various biological processes such as growth, repair, and maintenance of the body. They also play a crucial role in regulating enzymes, hormones, and immune responses, as well as providing structural support and transportation of molecules within the body.
How do carbohydrates provide energy to living organisms?
Carbohydrates are broken down into glucose during digestion, which is then used by cells to produce energy through a process called cellular respiration. Glucose enters cells where it is converted into ATP (adenosine triphosphate), the energy currency of cells, through a series of chemical reactions. This ATP is used by cells for various biological processes, such as muscle contraction, cell division, and the synthesis of molecules essential for life.
What is the primary function of lipids in cells?
Lipids in cells primarily serve as components of cell membranes, providing structure and regulating permeability. They also act as energy storage molecules, serving as a long-term energy reserve. Additionally, lipids play a crucial role in cell signaling, serving as precursors for various signaling molecules that regulate important cellular processes.
Have something to share?
Who is Worksheeto?
At Worksheeto, we are committed to delivering an extensive and varied portfolio of superior quality worksheets, designed to address the educational demands of students, educators, and parents.

























Comments