Looking Inside Cells Worksheet Answers
Worksheet activities are a valuable tool for individuals seeking a deeper understanding of the intricate workings of cells. Designed to engage and challenge learners, these worksheets provide detailed explanations and answers to help unravel the complex subject matter. Whether you're a student seeking to expand your knowledge or an educator looking for educational resources, these worksheets offer a comprehensive and reliable source to explore the fascinating world inside cells.
Table of Images 👆
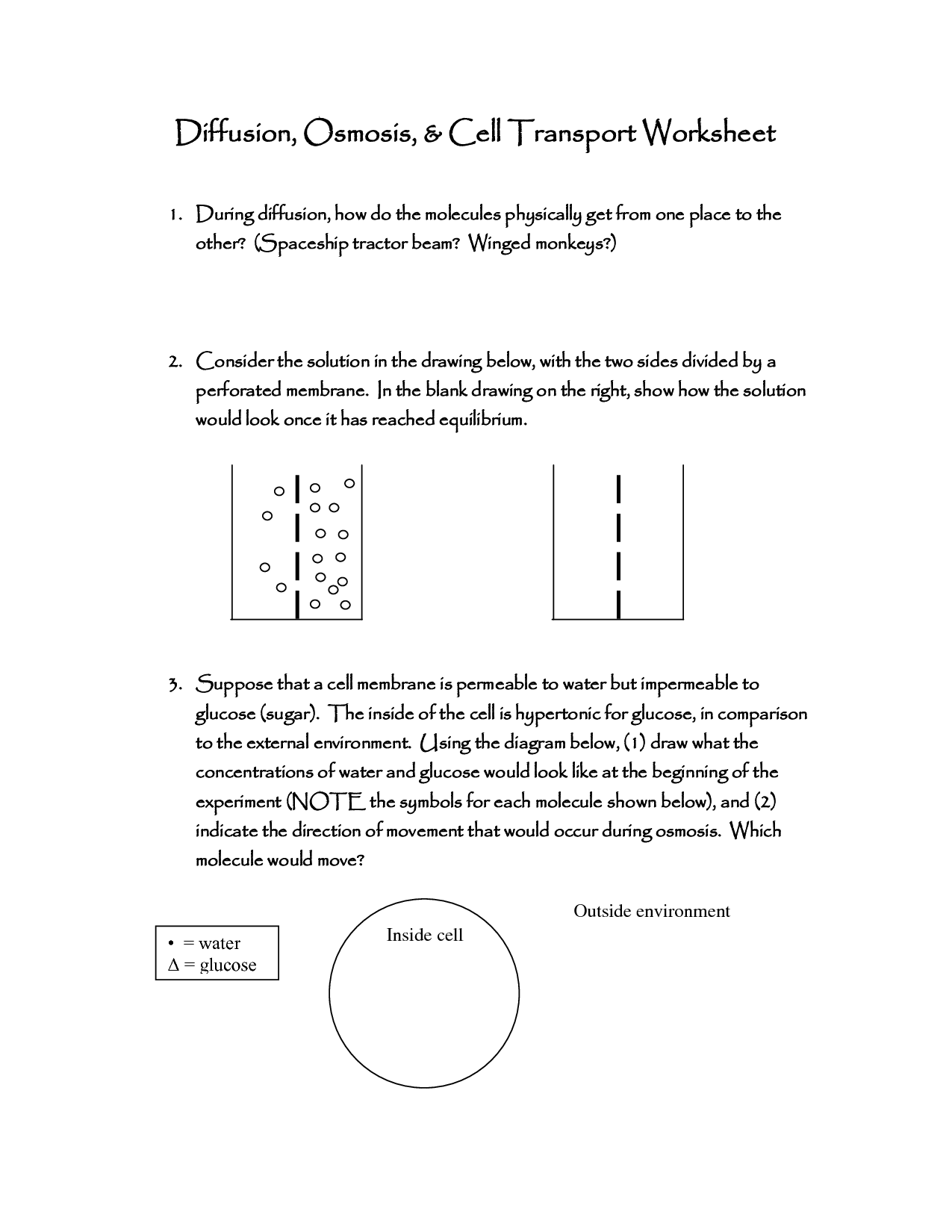
- Cell Transport Diffusion and Osmosis Worksheet
- Plant Cell Coloring Key Labeled
- Cell Division Worksheet Answers
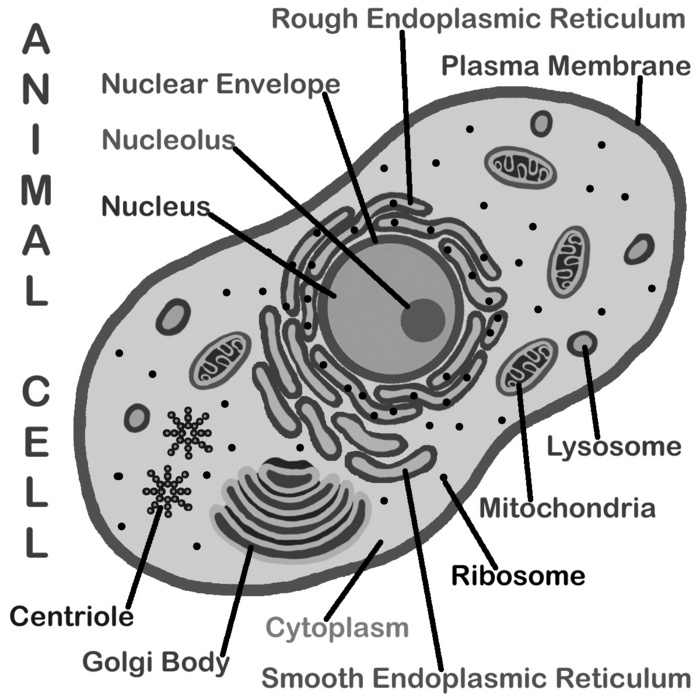
- Cell Organelles Worksheet Answer Key
- Cell Organelle Riddles Worksheet Answer Key
- Cell Cycle Worksheet Answer Key
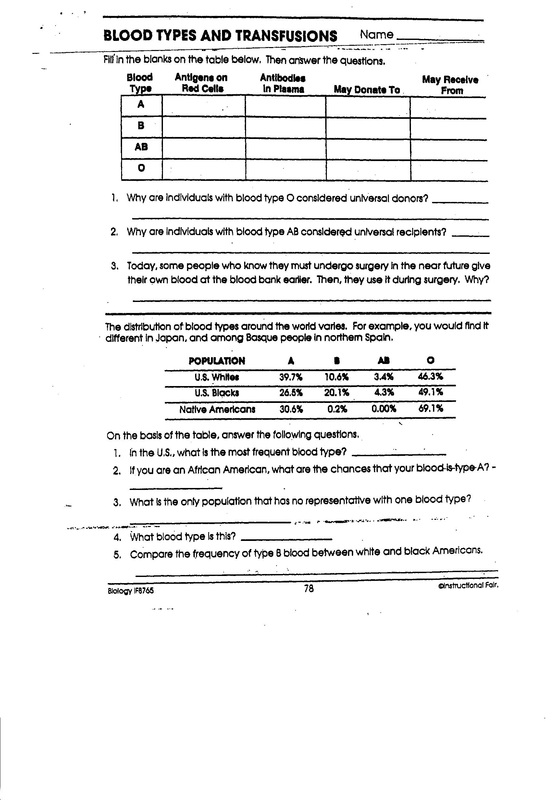
- Circulatory System Worksheet Answer Key
- Brianna Name Coloring Pages
- Cell Membrane Structure Worksheet
- Nervous System Worksheet Answers
More Other Worksheets
Kindergarten Worksheet My RoomSpanish Verb Worksheets
Healthy Eating Plate Printable Worksheet
Cooking Vocabulary Worksheet
My Shadow Worksheet
Large Printable Blank Pyramid Worksheet
Relationship Circles Worksheet
DNA Code Worksheet
Meiosis Worksheet Answer Key
Rosa Parks Worksheet Grade 1
What are the main components of a cell?
The main components of a cell are the cell membrane, cytoplasm, nucleus, and organelles such as mitochondria, endoplasmic reticulum, Golgi apparatus, and ribosomes. These components work together to carry out essential functions in maintaining the cell's structure, metabolism, and genetic information.
What is the function of the cell membrane?
The cell membrane functions as a protective barrier that surrounds the cell, controlling the movement of molecules in and out of the cell. It helps maintain cell shape and structure, and is responsible for communication between cells and their environment. Additionally, the cell membrane plays a crucial role in recognizing and interacting with other cells and substances in its surroundings.
Describe the structure and function of the nucleus.
The nucleus is a membrane-bound organelle found in eukaryotic cells that contains the genetic material, DNA, organized into chromosomes. It serves as the control center of the cell, regulating gene expression and coordinating cellular activities. The nucleus also contains the nucleolus, which is responsible for the production of ribosomes. The nuclear envelope surrounds the nucleus, separating its contents from the cytoplasm and regulating the movement of molecules in and out of the nucleus through nuclear pores. Overall, the nucleus plays a crucial role in the storage, protection, and expression of genetic information in the cell.
What are mitochondria and what is their role in the cell?
Mitochondria are organelles found in eukaryotic cells that are responsible for producing energy in the form of adenosine triphosphate (ATP) through the process of aerobic respiration. They are often referred to as the powerhouse of the cell because of this vital role. Mitochondria utilize nutrients and oxygen to generate ATP, which fuels various cellular activities and processes. Additionally, mitochondria also have a role in regulating cellular metabolism, signaling, and cell death pathways.
Explain the function of the endoplasmic reticulum.
The endoplasmic reticulum (ER) serves as a network of membranes in eukaryotic cells that plays a crucial role in protein and lipid synthesis, folding, and transport. It is responsible for the production of proteins and lipids, as well as the detoxification of drugs and other harmful substances. The ER also acts as a transportation system within the cell, allowing molecules to move between different parts of the cell or be secreted outside the cell. Additionally, the ER is involved in calcium storage and release, which is important for cellular processes such as muscle contraction and nerve signaling.
Describe the function of ribosomes in protein synthesis.
Ribosomes are the cellular structure responsible for protein synthesis. They read the genetic information from messenger RNA and use transfer RNA to assemble amino acids in the correct order to form a protein chain. This process occurs during translation, where ribosomes catalyze the formation of peptide bonds between amino acids, resulting in the creation of a functional protein that carries out specific functions in the cell.
What is the purpose of Golgi apparatus in the cell?
The Golgi apparatus in a cell serves as a key organelle responsible for processing, packaging, and sorting proteins and lipids into vesicles for transportation to various destinations within and outside the cell. It modifies proteins and lipids synthesized in the endoplasmic reticulum, ensuring they are appropriately tagged and directed to their correct locations, such as other organelles, the plasma membrane, or outside the cell, playing a crucial role in intracellular trafficking and secretion processes.
Explain the function of lysosomes in cell waste disposal.
Lysosomes are membrane-bound organelles within cells that contain digestive enzymes. Their main function is to break down waste materials, old cell parts, and foreign substances through a process called autophagy. This allows the cell to recycle useful components and eliminate harmful materials, maintaining cellular homeostasis. Additionally, lysosomes are involved in cellular processes such as nutrient recycling, defense against pathogens, and cell signaling.
Describe the structure and function of chloroplasts in plant cells.
Chloroplasts are organelles found in plant cells responsible for photosynthesis, the process by which plants convert sunlight into energy. They contain chlorophyll, a green pigment that absorbs light energy and uses it to produce glucose from carbon dioxide and water. The structure of a chloroplast includes a double membrane, thylakoid membranes where light absorption occurs, and stroma where the Calvin cycle takes place to produce glucose. Overall, chloroplasts play a crucial role in providing energy for plants and are essential for their growth and survival.
What are vacuoles and what is their role in the cell?
Vacuoles are membrane-bound organelles found in plant and fungal cells that store various substances such as water, nutrients, and waste products. Their main role in the cell is to maintain turgor pressure, store essential molecules, help in waste disposal, and provide structural support to the cell. Vacuoles also play a crucial role in maintaining the pH balance of the cell and are involved in various cellular processes such as growth, development, and defense.
Have something to share?
Who is Worksheeto?
At Worksheeto, we are committed to delivering an extensive and varied portfolio of superior quality worksheets, designed to address the educational demands of students, educators, and parents.























Comments