Light Worksheets for Middle School
Middle school students often require engaging and interactive resources to enhance their understanding of various concepts. When it comes to learning about light, worksheets can play a crucial role in reinforcing key ideas and allowing students to practice their knowledge. With a focus on the principles of light and its behavior, these worksheets provide an excellent platform for middle schoolers to explore this fascinating subject in an accessible and enjoyable manner.
Table of Images 👆
- Waves and Electromagnetic Spectrum Worksheet Answers
- Sound Wave Worksheet Answer
- Middle School Science Word Search
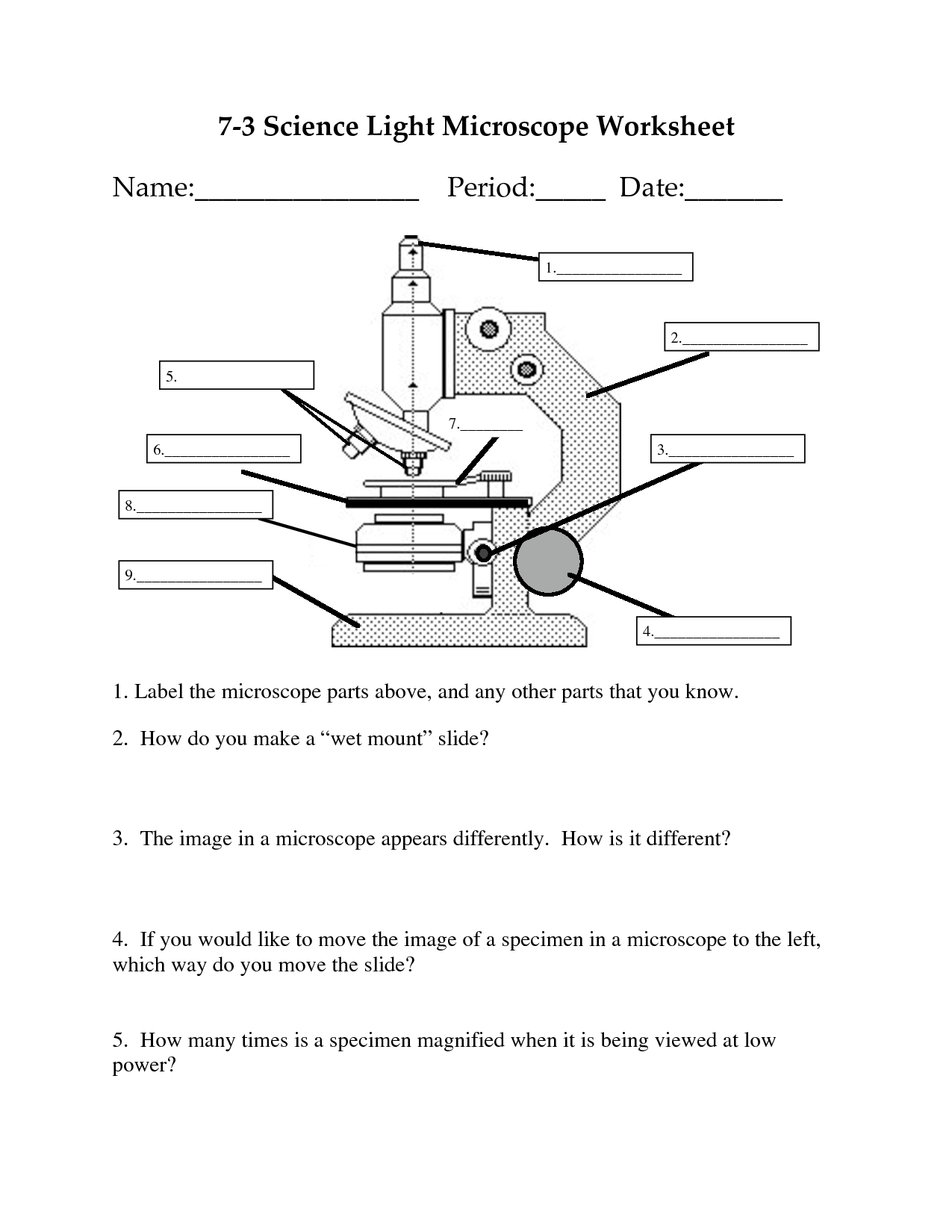
- Label Microscope Parts Worksheet
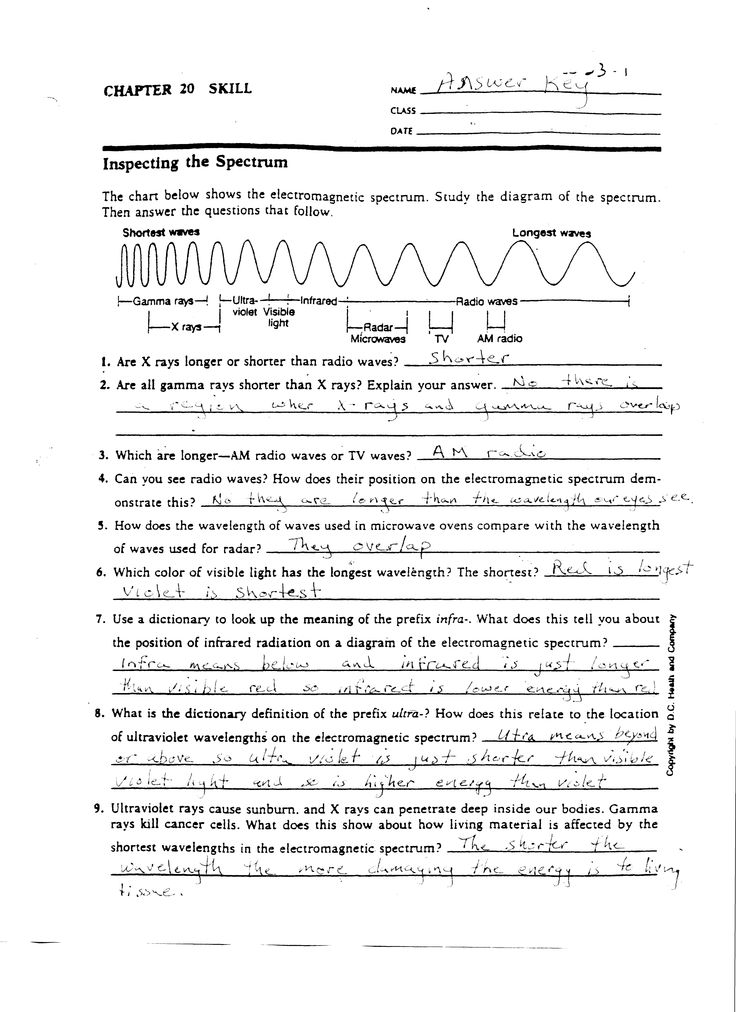
- Waves and Electromagnetic Spectrum Worksheet
- Electromagnetic Spectrum Worksheet
- 4th Grade Moon Phases Worksheet
- Energy Worksheets Middle School
- Speed Wavelength Frequency Energy Worksheet Answers
- Electromagnetic Spectrum Worksheet Answers
- Electromagnetic Spectrum Worksheet Answers
- Electromagnetic Spectrum Worksheet Answers
- Waves and Electromagnetic Spectrum Worksheet Answers
- Electromagnetic Spectrum Worksheet Middle School
More Other Worksheets
Kindergarten Worksheet My RoomSpanish Verb Worksheets
Cooking Vocabulary Worksheet
My Shadow Worksheet
Large Printable Blank Pyramid Worksheet
Relationship Circles Worksheet
DNA Code Worksheet
Meiosis Worksheet Answer Key
Art Handouts and Worksheets
7 Elements of Art Worksheets
What is light?
Light is a form of electromagnetic radiation that is visible to the human eye. It consists of particles called photons that have both wave-like and particle-like properties. Light travels in a straight line at a constant speed of about 186,282 miles per second in a vacuum. It plays a crucial role in our daily lives, allowing us to see the world around us and is essential for various biological and physical processes.
How does light travel?
Light travels in the form of electromagnetic waves, which are waves of energy that do not require a medium to propagate. When light is emitted, it moves at the speed of light in a straight line until it interacts with an object or medium that causes it to reflect, refract, or absorb. This interaction can change the direction, speed, or wavelength of the light, allowing it to be perceived by our eyes as different colors or intensities.
What is the speed of light?
The speed of light in a vacuum is approximately 299,792,458 meters per second, or about 186,282 miles per second.
What are the primary sources of light?
The primary sources of light are natural sources, such as the Sun, stars, and other celestial bodies, as well as artificial sources like light bulbs and LED lights. These sources emit light energy that is essential for illuminating our surroundings and enabling us to see objects around us.
How does light interact with objects?
Light interacts with objects through a process called absorption, reflection, and transmission. When light hits an object, it can be absorbed, where the object absorbs some or all of the light energy, reflecting it by bouncing off the object's surface, or transmitting through the object by passing through it. The color of an object is determined by the wavelengths of light it reflects or transmits, and the material properties of the object, such as transparency or opacity, affect how light interacts with it.
What is reflection?
Reflection is the act of thinking about or reviewing something in a thoughtful or deep way. It involves contemplation, introspection, and consideration of one's thoughts, actions, or experiences to gain insight, understanding, or learn and grow from them. It is a process of self-examination and self-evaluation that can lead to personal development and improvement.
What is refraction?
Refraction is the bending of light as it passes from one medium to another, such as air to water. This bending occurs because the speed of light changes when it moves from one medium to another, causing the light rays to change direction. Refraction is responsible for phenomena such as the apparent bending of a stick when placed in water and the formation of rainbows in the sky.
How does light pass through different materials?
Light passes through different materials by either being transmitted, absorbed, or reflected. The interaction of light with a material depends on its optical properties, such as transparency, opacity, and refractive index. In transparent materials, such as glass, light can pass through with minimal absorption or scattering. In opaque materials, like metal, light is mostly absorbed or reflected, resulting in little transmission. For translucent materials, like frosted glass, light is scattered in various directions. The amount of light passing through a material is influenced by its thickness, composition, and the wavelength of the light.
What is the electromagnetic spectrum?
The electromagnetic spectrum is the range of all possible frequencies of electromagnetic radiation, from the lowest to the highest frequencies. It includes various types of radiation such as radio waves, microwaves, infrared, visible light, ultraviolet, X-rays, and gamma rays. Each type of radiation has its own unique properties and uses, ranging from communication and entertainment with radio waves to medical imaging with X-rays and gamma rays.
How do we perceive different colors of light?
We perceive different colors of light through the wavelengths of the light that are absorbed by the cones in our eyes. Cones are photoreceptor cells that are sensitive to different wavelengths, allowing us to see a range of colors. When a specific wavelength of light enters our eye and stimulates a particular cone type, it sends a signal to our brain which interprets it as a particular color. This process enables us to perceive the diverse spectrum of colors that make up our visible world.
Have something to share?
Who is Worksheeto?
At Worksheeto, we are committed to delivering an extensive and varied portfolio of superior quality worksheets, designed to address the educational demands of students, educators, and parents.






























Comments