Light Refraction Worksheets 3rd Grade
Light refraction worksheets can be an effective learning tool for 3rd-grade students. These worksheets provide engaging activities that focus on the concept of light refraction, offering a structured approach to help young learners understand this scientific phenomenon. By utilizing these worksheets, students can enhance their understanding of the subject and explore the various aspects of light refraction in a fun and interactive way.
Table of Images 👆
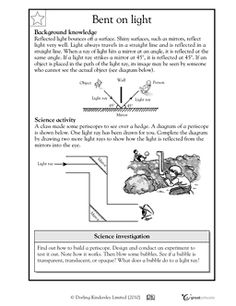
- Light Reflection and Refraction Worksheet
- Physics Refraction Worksheet
- Reflection Refraction Worksheet
- Absorption Reflection and Refraction for Kids
- Science Worksheets Light
- 4th Grade Light Worksheets
- 3rd Grade Science True or False
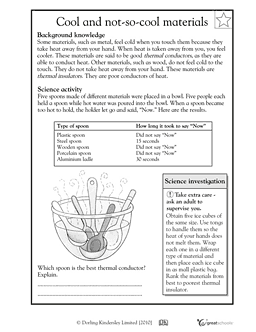
- Heat Conductor and Insulator Worksheets 3rd Grade
- 5th Grade Science Worksheets Light
- Light Reflection Refraction Worksheets
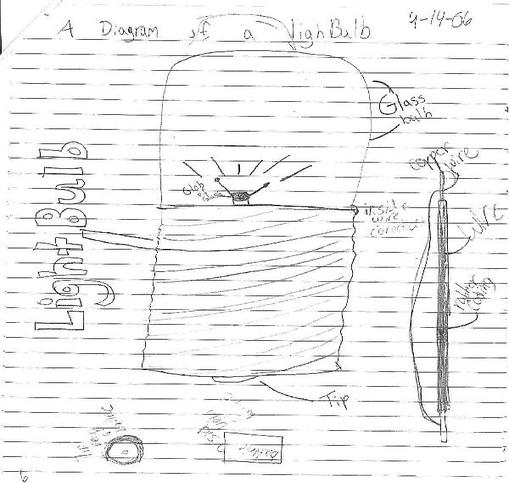
- 4th Grade Science Light Bulb Diagram
- Light Reflection Refraction Worksheets
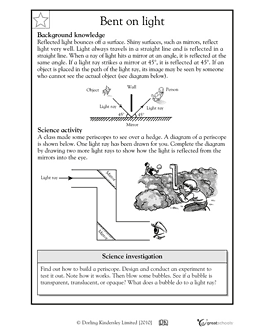
- Light Reflection Worksheet
- Third Grade Science Worksheets
More 3rd Grade Worksheets
3rd Grade Math WorksheetsTelling Time Worksheets 3rd Grade
Time Worksheets for 3rd Grade
3rd Grade Reading Comprehension Worksheets
Energy Worksheets 3rd Grade Science
Multiplication Worksheets for 3rd Grade
3rd Grade Math Division Worksheets Printable
Short Reading Comprehension Worksheets 3rd Grade
Soil Worksheets for 3rd Grade
Cursive Writing Worksheets for 3rd Grade
What is refraction?
Refraction is the bending of light as it passes through different mediums with varying densities. This bending occurs due to a change in the speed of light, causing the light rays to change direction. The amount of bending depends on the angle at which the light enters the new medium, with the light bending towards the normal (perpendicular line) when entering a more dense medium, and away from the normal when entering a less dense medium.
How does light travel?
Light travels in straight lines known as rays or beams, propagating as electromagnetic waves that do not require a medium for transmission. This means that light can travel through a vacuum as well as through transparent materials like air, water, and glass. The speed of light in a vacuum is approximately 299,792 kilometers per second, making it the fastest-known phenomenon in the universe.
What happens to light when it passes through a different medium?
When light passes through a different medium, such as air to glass, its speed and direction can be altered due to the change in the medium's optical density. This change in speed and direction causes the light to bend or refract. Additionally, some of the light may be absorbed by the new medium, converted to other forms of energy, or scattered in different directions, depending on the properties of the medium and the wavelength of the light.
How does the speed of light change when it passes through different materials?
The speed of light changes when it passes through different materials due to their differing refractive indices. When light enters a material with a higher refractive index, such as glass or water, it bends and slows down. This phenomenon is known as refraction. The speed of light in a vacuum is around 299,792 kilometers per second, but it can decrease to varying degrees when passing through materials with different refractive indices, ultimately affecting the overall speed of light.
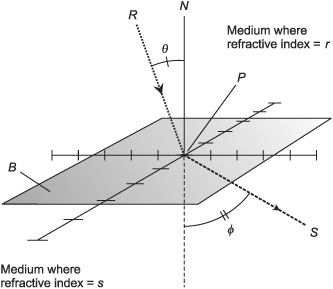
What is the angle of incidence?
The angle of incidence is the angle between an incident ray and the normal (a line perpendicular to the surface) at the point of incidence on a surface.
What is the angle of refraction?
The angle of refraction is the angle between the refracted ray and the normal to the interface between two different media through which a light ray passes. It is determined by Snell's Law, which states that the ratio of the sines of the angles of incidence and refraction is equal to the ratio of the velocities of light in the two media.
What is the relationship between the angle of incidence and the angle of refraction?
The relationship between the angle of incidence and the angle of refraction is described by Snell's Law, which states that the ratio of the sine of the angle of incidence to the sine of the angle of refraction is equal to the ratio of the speed of light in the two different mediums. This relationship dictates how light rays bend when they pass through boundaries between different mediums with varying refractive indices.
How does refraction affect the shape of objects?
Refraction can distort the appearance of objects by bending light as it passes from one medium to another. This bending of light can make objects appear shifted, elongated, shortened, or even inverted depending on the angles and properties of the mediums involved. Essentially, refraction alters the path of light rays, leading to changes in the way objects are perceived by an observer.
Why does a pencil look broken when placed in a glass of water?
When a pencil is placed in a glass of water, it appears broken due to refraction. Refraction occurs because light travels at different speeds through air and water. The light rays passing through the water are bent, causing the pencil to appear disjointed at the water's surface. This bending of light makes the pencil seem broken or displaced from its actual position.
How does refraction help us see objects?
Refraction is the bending of light as it passes through different mediums, such as air and water. This bending of light allows our eyes to perceive objects by redirecting the light rays towards our eyes, helping us to see the object in a different location than where it actually is. Refraction plays a key role in focusing light onto the retina in our eyes, enabling us to form clear images and see objects around us.
Have something to share?
Who is Worksheeto?
At Worksheeto, we are committed to delivering an extensive and varied portfolio of superior quality worksheets, designed to address the educational demands of students, educators, and parents.






















Comments