Light Energy Worksheets
Light energy worksheets are a valuable educational resource designed to engage students in learning about the fascinating entity that is light. These worksheets offer a variety of activities and exercises that allow students to explore and understand the properties, behavior, and uses of light. Whether you are a teacher searching for classroom materials or a parent looking to supplement your child's learning, these worksheets provide the perfect opportunity to delve into the subject of light energy in an interactive and informative way.
Table of Images 👆
- Light Energy Wavelength and Frequency Worksheet
- Photosynthesis Making Energy Worksheet
- Light Energy Sources Worksheet
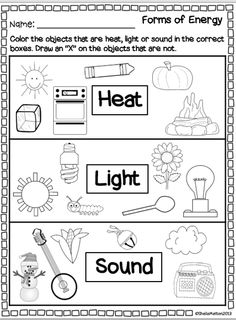
- Kindergarten Energy Worksheets
- Light Energy Wavelength and Frequency Worksheet Answers
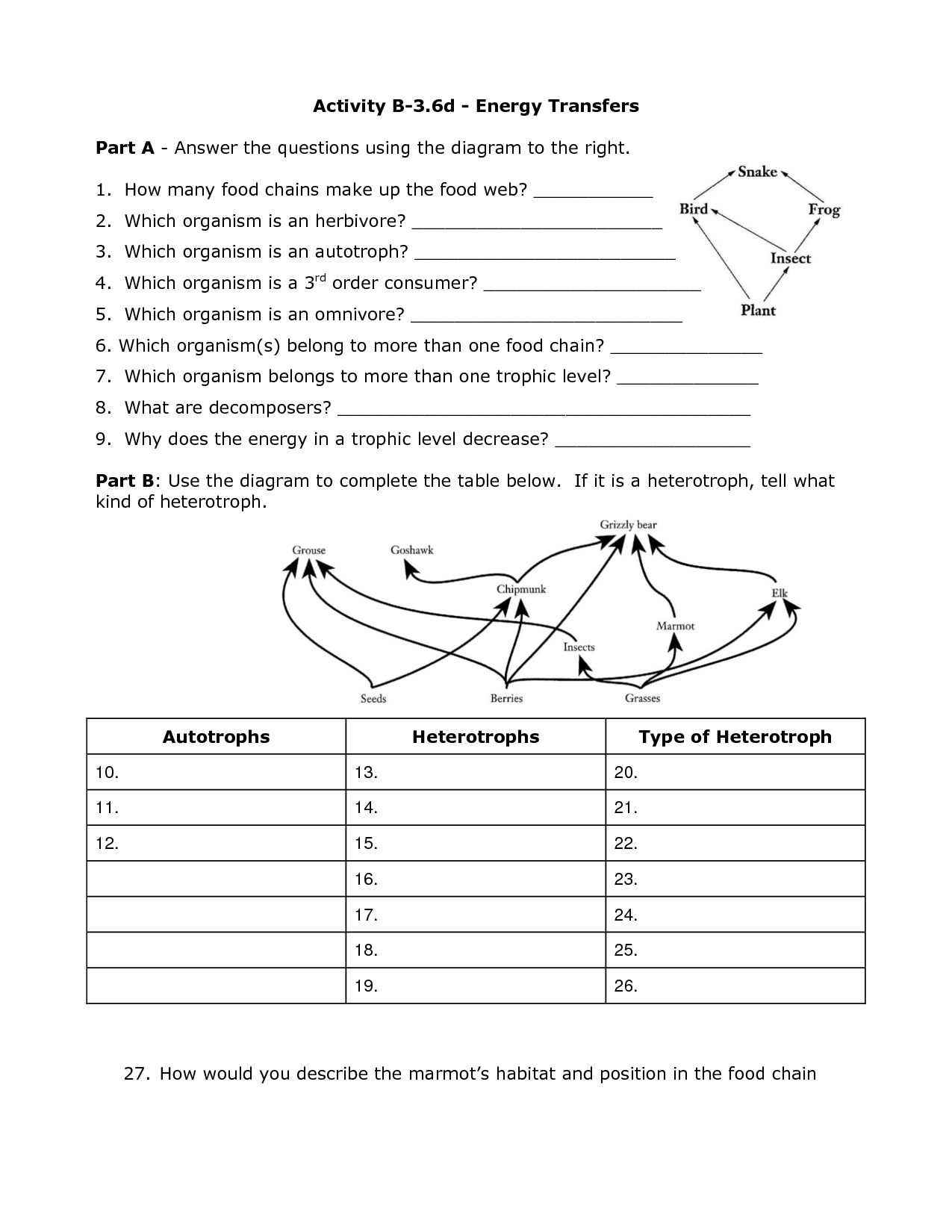
- Energy Transfer Worksheets
- Light Reflection Worksheet
- Heat Energy Worksheets Kindergarten
- Light Sources Worksheets
- Potential and Kinetic Energy Worksheets for Kids
- Light Energy Wavelength and Frequency Worksheet
- Sound Energy Worksheet Kindergarten
More Energy Worksheets
Light and Heat Energy WorksheetsTypes of Energy Transfer Worksheet
Energy Light Heat Sound Worksheets
3 Forms of Energy Worksheets
Types of Energy Worksheet PDF
Energy Worksheets for Third Grade
What is light energy?
Light energy is a type of electromagnetic radiation that is visible to the human eye. It is a form of energy that moves in waves and can be seen as colors ranging from red to violet in the visible spectrum. Light energy is essential for various processes on Earth, including photosynthesis in plants, vision in animals, and powering technologies such as solar panels.
How is light energy produced?
Light energy is produced through a variety of processes, one of the most common being when an atom's electrons are excited to higher energy levels and then fall back down to lower levels, releasing photons in the form of light. This can occur through mechanisms like heat, electrical currents, chemical reactions, or even nuclear reactions in stars. The specific process of light generation can vary depending on the source and the conditions in which it occurs.
What are the different sources of light energy?
The different sources of light energy include natural sources such as the sun, stars, and bioluminescent organisms, as well as artificial sources such as incandescent and fluorescent light bulbs, LEDs, lasers, and fire. Light energy can also be generated through chemical reactions, nuclear reactions, and electrical circuits.
How does light travel?
Light travels in the form of electromagnetic waves, which are waves of energy that do not require a medium to propagate through. These waves consist of perpendicular electric and magnetic fields that oscillate in sync as they move through space at a constant speed of approximately 299,792 kilometers per second in a vacuum. The dual nature of light allows it to exhibit properties of both particles and waves, enabling it to travel in straight lines unless it interacts with matter and undergoes scattering, reflection, refraction, or absorption.
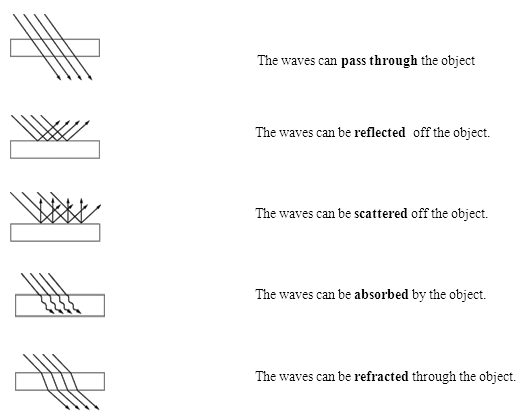
How does light interact with objects?
When light interacts with objects, it can be absorbed, reflected, transmitted, or refracted. The absorption of light causes the object to heat up, while reflection results in the bouncing of light off the surface. Transmitted light passes through the object, while refraction occurs when light changes direction as it passes through the object. The color of an object is determined by the wavelengths of light that are reflected or transmitted, while the texture and shape of the object can influence how light interacts with it.
What are the properties of light energy?
Light energy is a form of electromagnetic radiation that travels in waves and does not require a medium to propagate. It travels in straight lines, and its speed in a vacuum is constant at approximately 3.00 x 10^8 meters per second. Light energy can be reflected, refracted, absorbed, or transmitted when it interacts with different materials, and it can be described by its wavelength, frequency, and amplitude. It exhibits both particle-like and wave-like properties, known as the wave-particle duality of light, and can be described by the electromagnetic spectrum which includes visible light, infrared, ultraviolet, microwaves, and radio waves.
How is light energy converted into other forms of energy?
Light energy can be converted into other forms of energy through several processes, such as photosynthesis in plants where light energy is transformed into chemical energy, or in solar panels where light energy is converted into electrical energy through the photovoltaic effect. Additionally, light energy can also be converted into heat energy when absorbed by surfaces, or into kinetic energy when it causes molecules to vibrate. Ultimately, the conversion of light energy into other forms is governed by the specific properties of the materials involved and the physical and chemical reactions taking place.
What are the practical applications of light energy?
Light energy has numerous practical applications, including in lighting systems for homes, buildings, and streets; in lasers for surgery, cutting, and welding; in solar panels for producing electricity; in fiber optics for telecommunications; in photography and cinematography for capturing images; in light therapy for treating certain medical conditions; and in optical sensors for detecting and measuring various parameters in scientific and industrial settings.
How does light energy affect the environment?
Light energy affects the environment through various ways such as light pollution, disruption of wildlife behavior, and impact on ecosystems. Excessive artificial lighting can disrupt the natural cycles of nocturnal animals, affecting their ability to forage, navigate, and reproduce. Light pollution also wastes energy, contributes to carbon emissions, and disrupts human sleep patterns. Additionally, excessive exposure to artificial light can negatively affect plants' growth and reproduction cycles. Overall, careful management of light energy is crucial to minimize its impact on the environment.
How can we harness and utilize light energy efficiently?
To harness and utilize light energy efficiently, we can use technologies such as solar panels to convert sunlight into electricity, daylight harvesting systems to make use of natural light in buildings, and fiber optics to transmit light over long distances with minimal loss. Additionally, optimizing the design of buildings and devices to maximize exposure to sunlight, as well as incorporating energy-efficient lighting solutions like LEDs, can further enhance the efficient use of light energy. By combining these approaches and continuing to innovate in the field of light energy technology, we can effectively harness and utilize light energy in a sustainable and environmentally-friendly manner.
Have something to share?
Who is Worksheeto?
At Worksheeto, we are committed to delivering an extensive and varied portfolio of superior quality worksheets, designed to address the educational demands of students, educators, and parents.


























Comments