Identifying Organic Compounds Worksheet
Organic compounds are the building blocks of life, and understanding their properties and characteristics is essential for students studying chemistry. To help students improve their knowledge in this area, an identifying organic compounds worksheet is a valuable resource. This worksheet provides a variety of examples and exercises that focus on the identification and classification of organic compounds, making it an ideal tool for high school and college-level chemistry students seeking to deepen their understanding of this subject.
Table of Images 👆
- Organic Chemistry Functional Groups
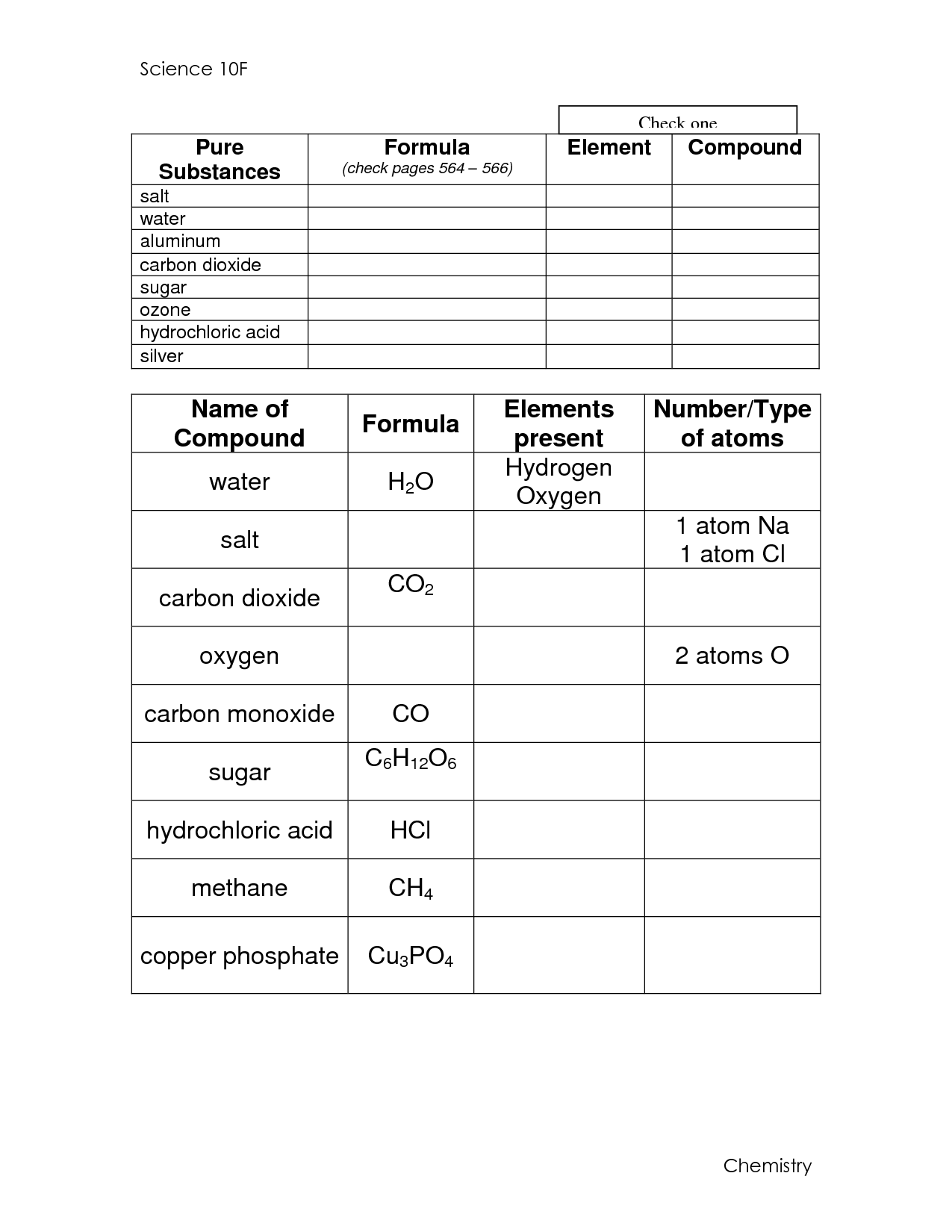
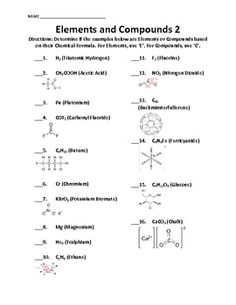
- Atoms Elements and Compounds Worksheets
- Carbon Compounds Worksheet
- Chemistry Naming Compounds Worksheet Answers
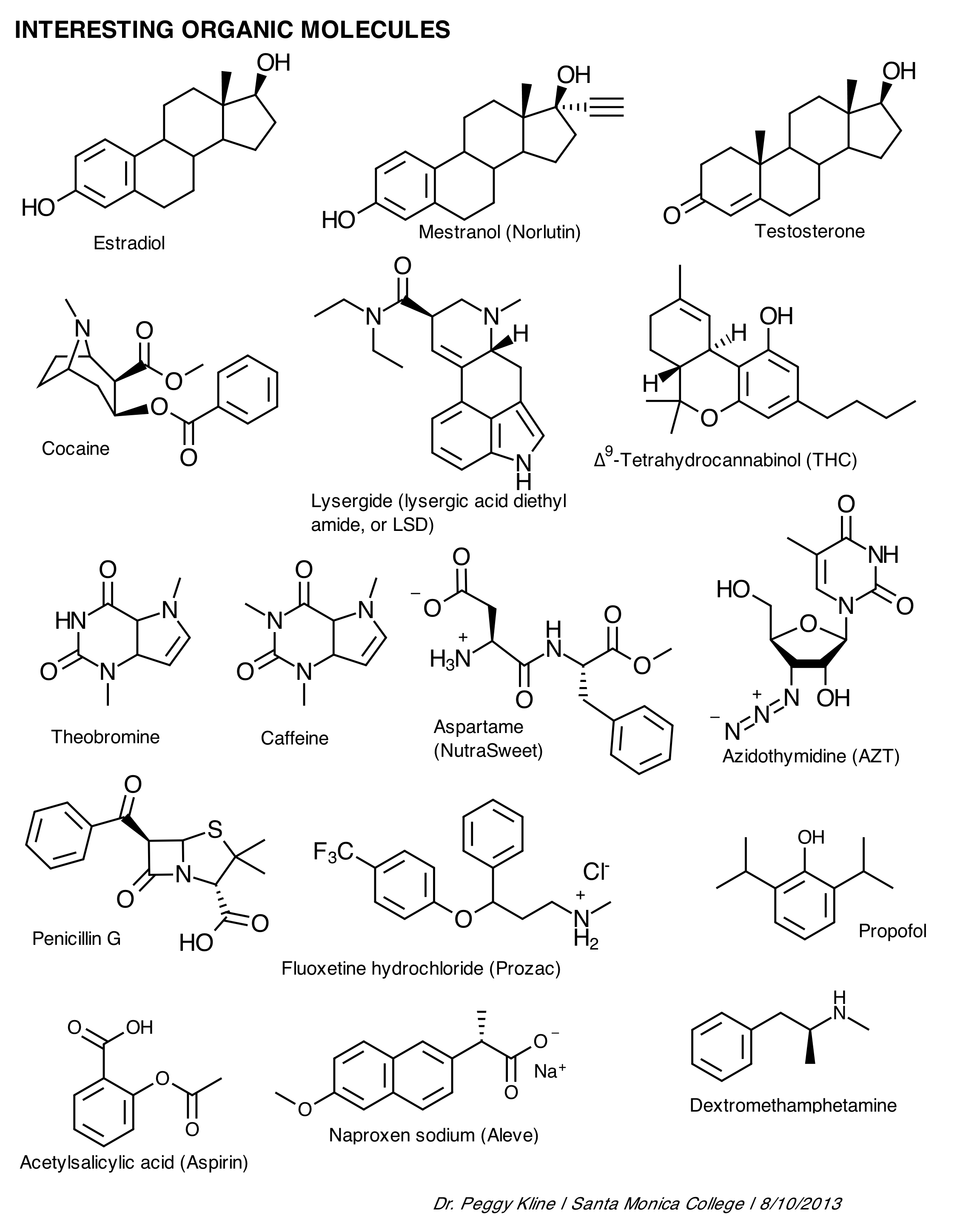
- Biology Organic Molecules Worksheet Review
- Identifying Chemical Reaction Types Worksheet
- Elements and Compounds Worksheet 6th Grade
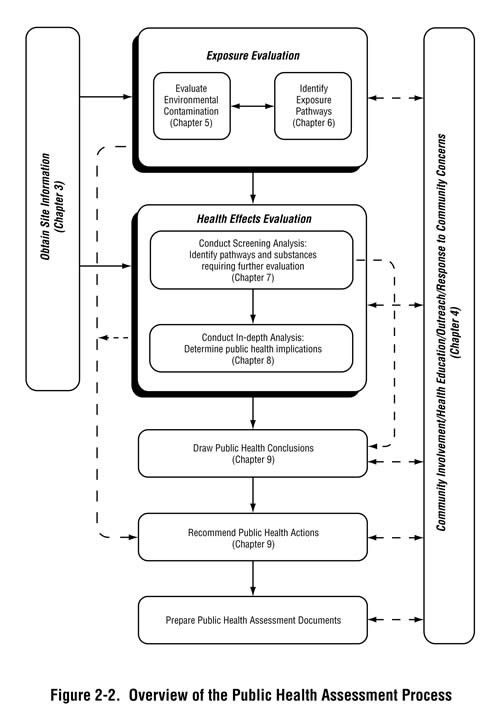
- Community Health Needs Assessment Process
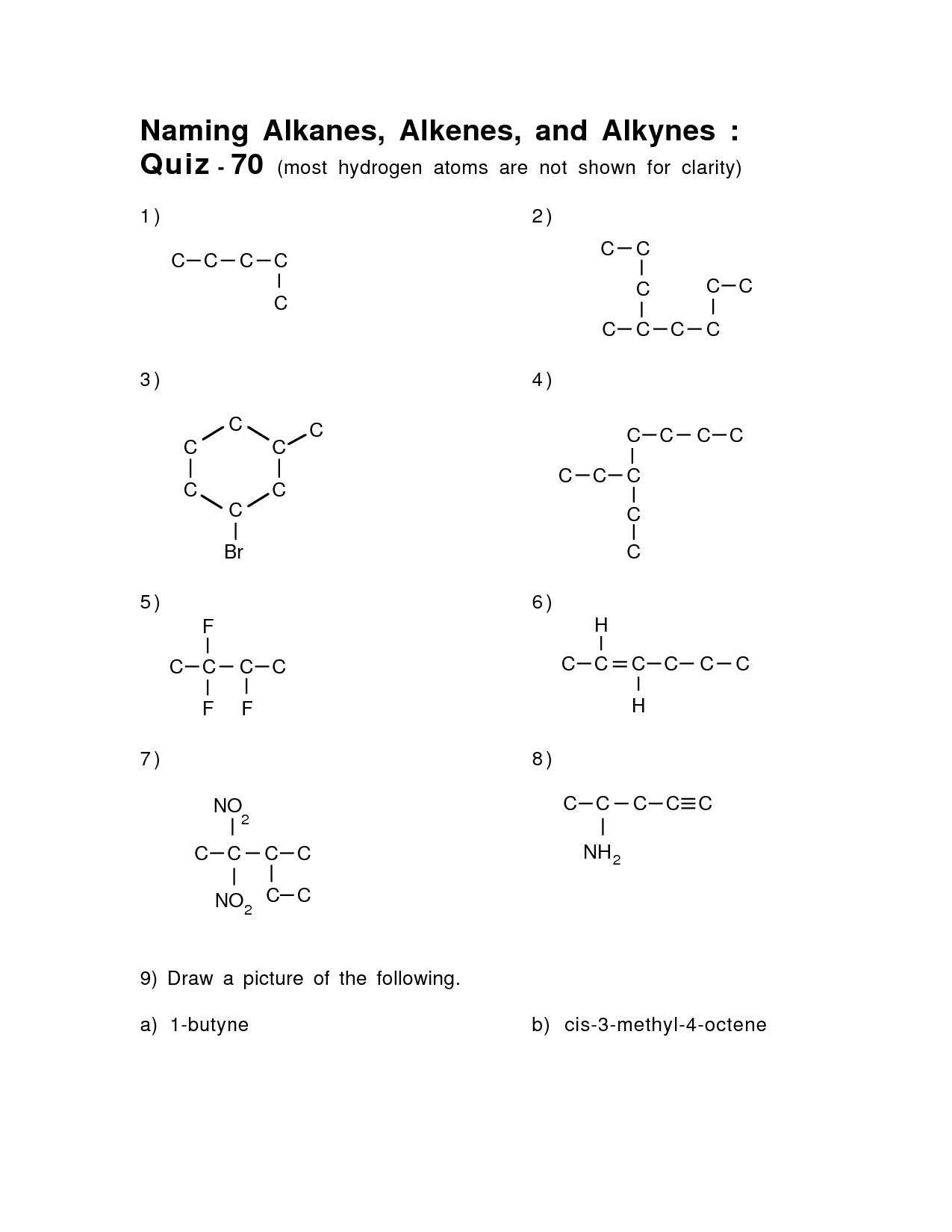
- Naming Alkanes Alkenes and Alkynes
More Other Worksheets
Kindergarten Worksheet My RoomSpanish Verb Worksheets
Cooking Vocabulary Worksheet
My Shadow Worksheet
Large Printable Blank Pyramid Worksheet
Relationship Circles Worksheet
DNA Code Worksheet
Meiosis Worksheet Answer Key
Art Handouts and Worksheets
7 Elements of Art Worksheets
What is the basic definition of an organic compound?
An organic compound is a type of chemical compound that contains carbon atoms bonded to other elements, typically hydrogen, oxygen, nitrogen, and other atoms. These compounds are found in living organisms and are characterized by their complex structures and unique properties.
How are organic compounds different from inorganic compounds?
Organic compounds contain carbon-hydrogen bonds and are typically derived from living organisms, such as proteins, carbohydrates, lipids, and nucleic acids. Inorganic compounds, on the other hand, do not contain carbon-hydrogen bonds and are often simpler molecules like salts, metals, and minerals. This distinction is based on the presence or absence of carbon-hydrogen bonds, with organic compounds being more complex and diverse in their structures and properties compared to inorganic compounds.
What are the main elements found in organic compounds?
The main elements found in organic compounds are carbon, hydrogen, oxygen, nitrogen, sulfur, and phosphorus. These elements form the building blocks of organic molecules and are essential for the diverse range of chemical structures and functions found in living organisms.
How are organic compounds named?
Organic compounds are named using a systematic naming system called IUPAC nomenclature. This system involves identifying the longest carbon chain in the molecule, determining the functional groups present, assigning appropriate prefixes and suffixes based on the functional groups, and placing numbers to indicate the positions of substituent groups. The goal is to provide a unique and standardized way to name organic compounds, ensuring clarity and consistency in chemical communication and understanding.
What is the role of functional groups in organic compounds?
Functional groups in organic compounds are key components that determine the chemical reactivity and physical properties of molecules. These groups consist of specific arrangements of atoms that confer characteristic behaviors and functions to the compounds they are part of. Functional groups can influence how the compound interacts with other molecules, undergoes chemical reactions, and ultimately determines its overall structure and properties. By identifying and understanding the role of functional groups in organic compounds, chemists can predict and manipulate their behavior and properties for a variety of applications in fields such as medicine, agriculture, and materials science.
How is the boiling point of an organic compound related to its molecular structure?
The boiling point of an organic compound is related to its molecular structure because it depends on the strength and nature of intermolecular forces within the molecules. Compounds with stronger intermolecular forces, such as hydrogen bonding or dipole-dipole interactions, will have higher boiling points as more energy is required to break these forces and change the compound from a liquid to a gas. Conversely, compounds with weaker intermolecular forces, such as London dispersion forces, will have lower boiling points. Additionally, the size and shape of the molecules can also influence the boiling point, as larger molecules typically have stronger intermolecular forces and higher boiling points compared to smaller ones.
How can we distinguish between saturated and unsaturated organic compounds?
One way to distinguish between saturated and unsaturated organic compounds is by looking at their chemical structure. Saturated compounds contain only single bonds between carbon atoms, while unsaturated compounds contain at least one double or triple bond between carbon atoms. Additionally, saturated compounds tend to have higher melting and boiling points compared to unsaturated compounds due to the stronger intermolecular forces in saturated molecules. Lastly, unsaturated compounds are more reactive than saturated compounds due to the presence of double or triple bonds that are capable of undergoing addition reactions.
What are isomers in organic chemistry?
Isomers in organic chemistry are compounds with the same molecular formula but different structural arrangements or connectivity of atoms. This results in different chemical and physical properties despite having the same number and types of atoms. Isomers can be classified into different categories such as structural isomers, stereoisomers, and geometric isomers based on the differences in their arrangements.
How do we test for the presence of alcohols in organic compounds?
One common way to test for the presence of alcohols in organic compounds is by performing a reaction called Lucas test. In this test, the organic compound is mixed with Lucas reagent (concentrated hydrochloric acid and zinc chloride). The appearance of a cloudy or milky solution or the formation of a white precipitate indicates the presence of an alcohol. This test is particularly useful for distinguishing between primary, secondary, and tertiary alcohols based on the rate at which they react with the Lucas reagent.
How can we identify the presence of a carboxylic acid in an organic compound?
One way to identify the presence of a carboxylic acid in an organic compound is by performing a chemical test known as the “ferric chloride test.” When a carboxylic acid reacts with ferric chloride, it forms a colored complex that can be observed visually. The presence of a carboxylic acid can also be confirmed using other tests such as the reaction with sodium bicarbonate to produce effervescence due to the release of carbon dioxide gas. Additionally, infrared spectroscopy can be employed to detect the characteristic peaks associated with the carboxylic acid functional group.
Have something to share?
Who is Worksheeto?
At Worksheeto, we are committed to delivering an extensive and varied portfolio of superior quality worksheets, designed to address the educational demands of students, educators, and parents.





















Comments