Human Brain Worksheet
Worksheets are a valuable learning tool designed to engage and challenge learners in various educational subjects. Whether you are a teacher looking for interactive activities to enhance your lesson plans or a student seeking to reinforce and apply knowledge, worksheets provide a structured format to stimulate the brain and foster understanding.
Table of Images 👆
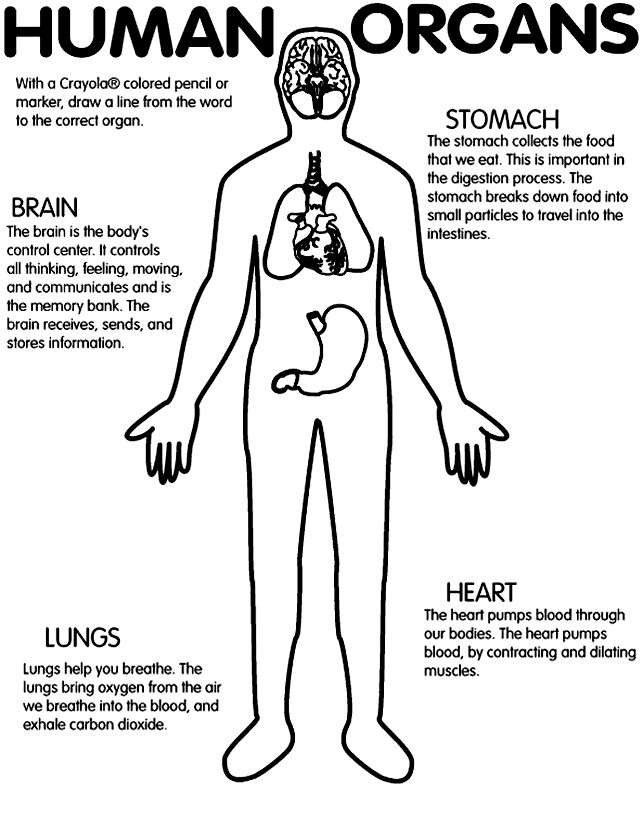
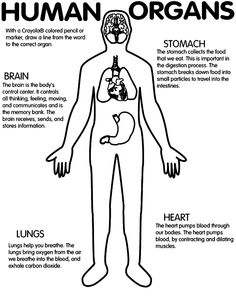
- Human Organs Coloring Page
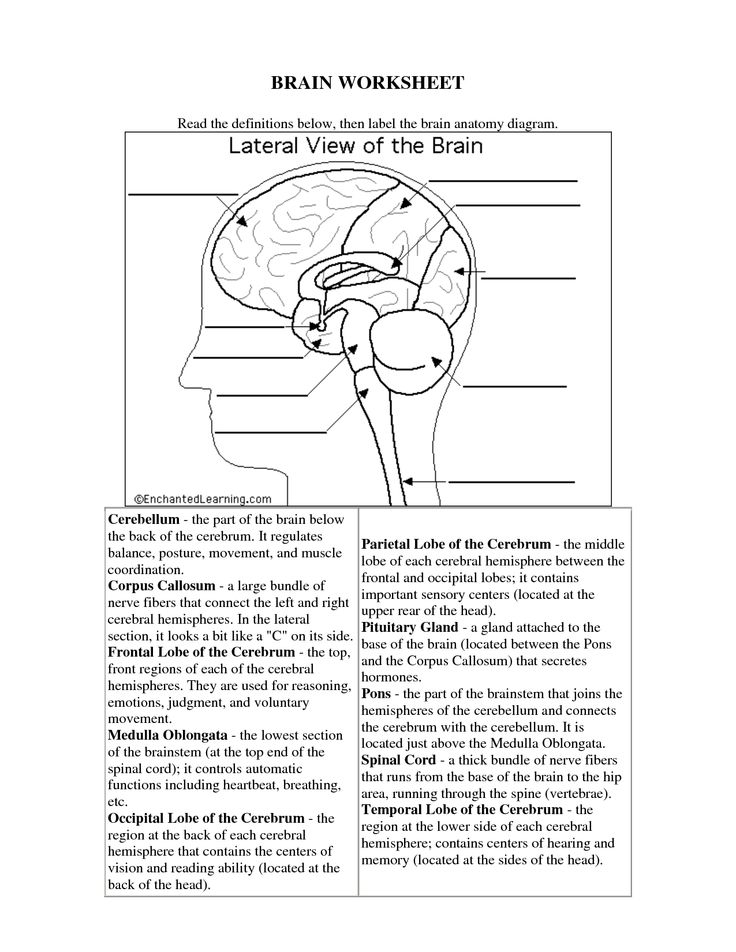
- Brain Diagram Worksheet for Kids
- Human Organs Coloring Page
- Human Brain Worksheets for Kids
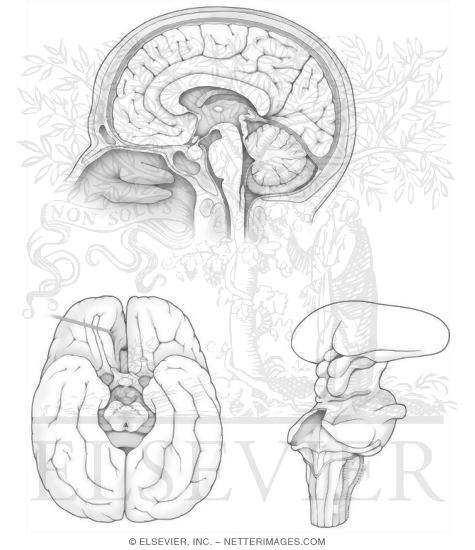
- Brain Anatomy Coloring Book
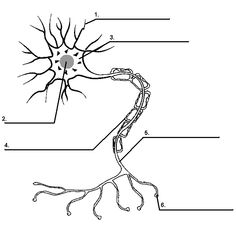
- Blank Neuron Cell Diagram
- Blank Brain Diagram
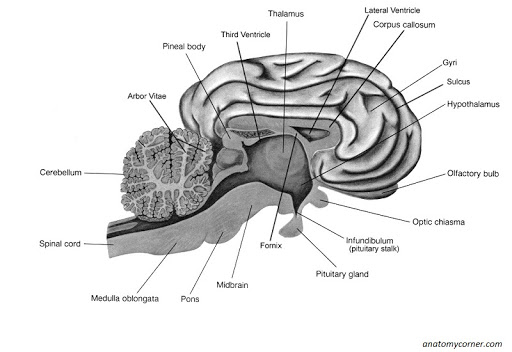
- Labeled Sheep Brain Worksheet
- Chalkboard Illustration Lung
- Human Brain Printable Worksheet
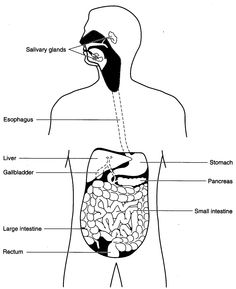
- Human Digestive System Worksheet
- Fetal Pig Heart Diagram
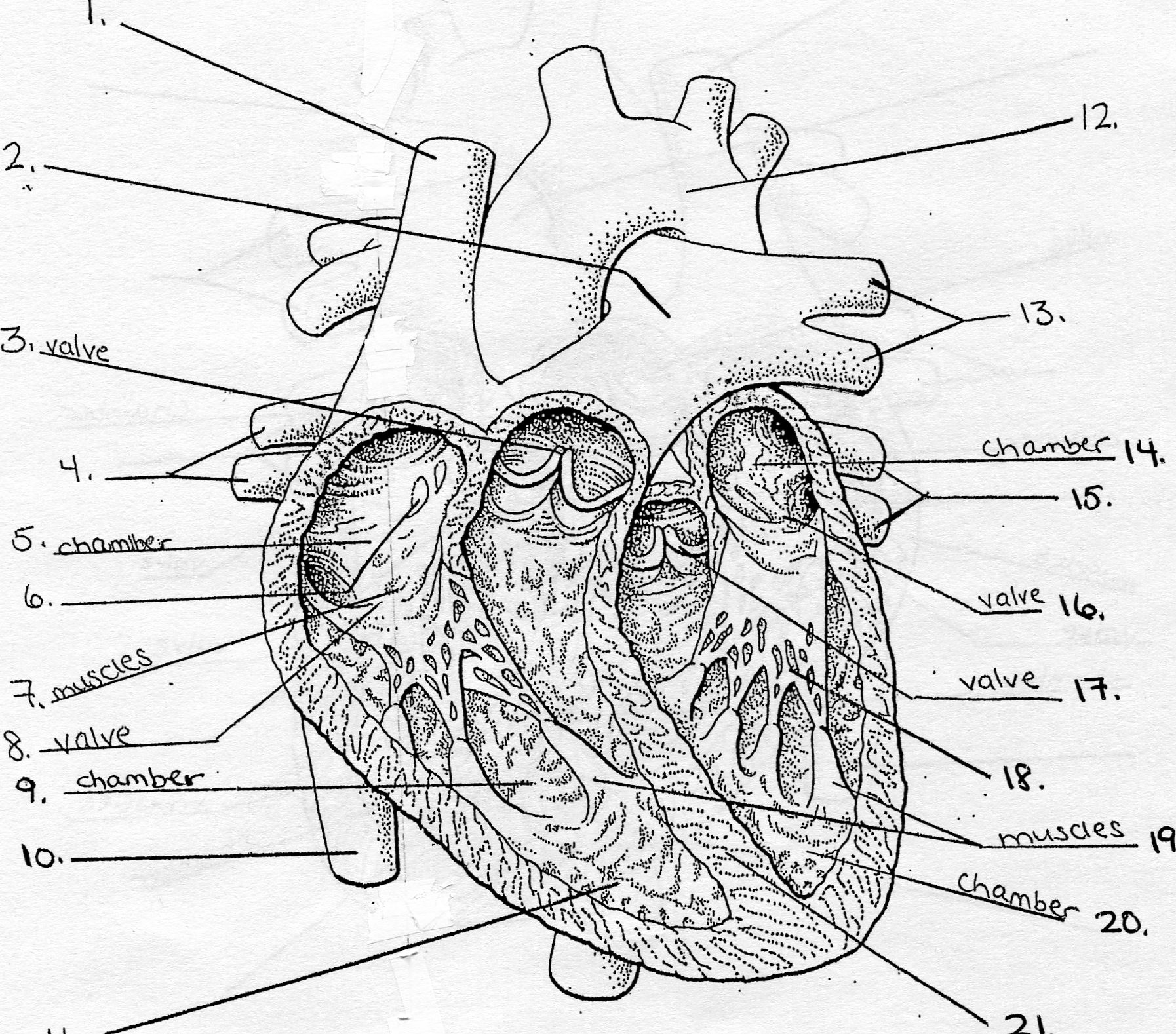
- Heart Label Worksheet
- Types of Human Body Worksheet Joint
- Kidney Dissection Lab Worksheet Answers
- Eye Diagram Worksheet
More Other Worksheets
Kindergarten Worksheet My RoomSpanish Verb Worksheets
Cooking Vocabulary Worksheet
My Shadow Worksheet
Large Printable Blank Pyramid Worksheet
Relationship Circles Worksheet
DNA Code Worksheet
Meiosis Worksheet Answer Key
Art Handouts and Worksheets
7 Elements of Art Worksheets
What are the main functions of the human brain?
The main functions of the human brain include controlling bodily functions, processing sensory information, regulating emotions, forming memories, solving problems, making decisions, and coordinating movement and actions. Additionally, the brain is responsible for higher cognitive functions such as language processing, creativity, and reasoning.
How is the brain divided into different regions and what are their respective functions?
The brain is divided into different regions known as lobes, each with its own specific functions. The frontal lobe is responsible for decision-making and personality. The parietal lobe processes sensory information such as taste and touch. The occipital lobe interprets visual information. The temporal lobe is important for memory and hearing. Additionally, the brainstem controls basic life functions like breathing and heart rate, while the cerebellum coordinates movement and balance. Finally, the limbic system plays a key role in emotions and memory.
What is the role of neurons in the brain?
Neurons are the building blocks of the nervous system and play a crucial role in transmitting and processing information in the brain. They receive signals from sensory organs or other neurons, process these signals, and then transmit them to other neurons, muscles, or glands. This communication between neurons is essential for various brain functions such as thinking, memory, emotion, and movement.
How does the brain facilitate communication within itself and with the rest of the body?
The brain facilitates communication within itself and with the rest of the body through a complex network of neurons and neurotransmitters. Neurons transmit information through electrical signals within the brain and release chemical messengers called neurotransmitters to communicate with other neurons and cells throughout the body. This intricate system allows for the coordination of bodily functions, sensory processing, and the control of movements, emotions, and cognitive processes. Additionally, the brain communicates with the rest of the body through the central nervous system, which includes the spinal cord and peripheral nerves, enabling the brain to receive sensory input and send motor commands to different parts of the body.
What is the concept of plasticity in the brain and how does it allow for learning and adaptation?
Plasticity in the brain refers to its ability to reorganize itself by forming new connections between neurons. This process allows the brain to adapt, learn new information, and change in response to experiences. Through plasticity, the brain can strengthen existing neural connections or create new ones, enabling us to acquire new skills, modify behavior, and recover from injuries. This adaptability is crucial for cognitive development and learning throughout our lives.
How do chemicals called neurotransmitters play a role in brain functioning?
Neurotransmitters are essential chemicals that transmit messages between neurons in the brain, influencing a variety of functions such as mood, memory, movement, and more. These chemicals help regulate brain activity by either exciting or inhibiting neurons, affecting the speed and strength of signals sent between brain cells. Imbalances in neurotransmitter levels are linked to various neurological and psychiatric disorders, highlighting the crucial role they play in brain functioning and overall mental health.
What are some common disorders that can affect the brain, such as Alzheimer's disease or stroke?
Some common disorders that can affect the brain include Alzheimer's disease, which is a progressive neurodegenerative disorder leading to memory loss and cognitive decline, stroke, a sudden interruption in blood supply to the brain causing brain damage, traumatic brain injury (TBI) caused by an external force impacting the brain and disrupting its normal function, and Parkinson's disease, a degenerative disorder of the central nervous system affecting movement and coordination. Other disorders include epilepsy, multiple sclerosis, and brain tumors, each with their own set of symptoms and complications affecting brain function.
How does the brain process and interpret sensory information, such as sight, sound, and touch?
The brain processes and interprets sensory information through a complex network of neural pathways that transmit signals from sensory receptors to the brain. Upon receiving these signals, different areas of the brain, such as the visual cortex for sight, the auditory cortex for sound, and the somatosensory cortex for touch, analyze and interpret the incoming information. This information is then integrated with past experiences, emotions, and memories to create a coherent perception of the world around us. The brain uses this processed sensory information to guide behavior, make decisions, and interact with the environment.
What is the role of the limbic system in regulating emotions and behavior?
The limbic system plays a crucial role in regulating emotions and behavior by processing and interpreting emotional stimuli. It includes structures such as the amygdala, hippocampus, and hypothalamus, which are involved in emotional responses, memory formation, and the release of hormones involved in stress and arousal. The limbic system helps to process and attach emotional significance to experiences, enabling us to react and adapt to our environment appropriately.
What are some ongoing areas of research and study in the field of neuroscience and brain function?
Some ongoing areas of research and study in the field of neuroscience and brain function include neuroplasticity, which explores how the brain can reorganize itself by forming new neural connections; brain-machine interfaces, that seek to develop technologies enabling direct communication between the brain and external devices; and the study of neurodegenerative diseases such as Alzheimer's and Parkinson's, aiming to better understand their mechanisms and develop new treatment strategies. Additionally, research is also focusing on the role of neurotransmitters, hormones, and genetics in brain function to further advance our understanding of how the brain works.
Have something to share?
Who is Worksheeto?
At Worksheeto, we are committed to delivering an extensive and varied portfolio of superior quality worksheets, designed to address the educational demands of students, educators, and parents.























Comments