How Enzymes Work Worksheet
Enzymes play a crucial role in various biological processes. This worksheet is designed to help students understand the incredible workings of enzymes, their structure, and function. By providing clear explanations and engaging activities, this worksheet aims to enhance the students' understanding of this fascinating subject. Whether you are a high school student studying biology or a college student pursuing a degree in biochemistry, this worksheet will provide you with a comprehensive introduction to the world of enzymes.
Table of Images 👆
- Biology Enzyme Worksheet High School
- Enzyme Activity Worksheet
- Enzymes Worksheet Answer Key
- Gel Electrophoresis Worksheet Answers
- Enzyme Worksheet Answers
- High School Biology Worksheets
- Cellular Respiration Worksheet High School
- Enzyme Practice Worksheet Answers
- Enzyme Reactions Worksheet Answer Key
- Computer Evidence Worksheet
- Restriction Enzyme Worksheet Answers
- Digestive System Lesson Plans
- Food for Thought the Digestive System Worksheet
- Homeostasis Printable Worksheets
More Other Worksheets
Kindergarten Worksheet My RoomSpanish Verb Worksheets
Cooking Vocabulary Worksheet
My Shadow Worksheet
Large Printable Blank Pyramid Worksheet
Relationship Circles Worksheet
DNA Code Worksheet
Meiosis Worksheet Answer Key
Art Handouts and Worksheets
7 Elements of Art Worksheets
What are enzymes?
Enzymes are biological molecules that act as catalysts to speed up chemical reactions in living organisms, while also being highly specific in their functions. They play a crucial role in metabolism by facilitating various biochemical reactions, such as breaking down food molecules for energy or building new molecules for growth and repair. Essentially, enzymes help cells perform their functions more efficiently by lowering the activation energy required for a reaction to occur.
Describe the role of enzymes in biological reactions.
Enzymes are biological catalysts that increase the speed of chemical reactions by lowering the activation energy required for the reaction to occur. They do this by binding to specific substrates and facilitating the conversion of the substrates into products. Enzymes are highly specific, with each enzyme catalyzing a particular reaction. They are crucial in various biological processes, including metabolism, digestion, and cellular signaling, ultimately enabling organisms to efficiently carry out essential functions for survival and growth.
How do enzymes lower the activation energy of a reaction?
Enzymes lower the activation energy of a reaction by providing an alternative pathway with a lower activation energy for the reaction to occur. This alternative pathway involves stabilizing the transition state of the reaction, making it easier for the reactants to reach the transition state and proceed to form products. Essentially, enzymes facilitate reactions by reducing the energy needed for the reaction to occur, thus increasing the reaction rate.
Explain why enzymes are specific in their substrate recognition.
Enzymes are specific in their substrate recognition due to the unique structure of their active sites. The active site is a region on the enzyme where the substrate binds and the chemical reaction takes place. The active site is precisely shaped and lined with specific amino acids that interact with the substrate in a lock-and-key manner, ensuring that only the correct substrate with a complementary shape and chemical properties can bind. This specificity is critical for enzymes to catalyze specific reactions with high efficiency and accuracy. Any changes in the active site structure or the substrate itself can impact enzyme-substrate interactions and the overall catalytic efficiency of the enzyme.
What is an active site, and how does it contribute to enzyme function?
An active site is a specific region on an enzyme where substrates bind and undergo a chemical reaction. It plays a crucial role in enzyme function by providing a unique microenvironment that facilitates the chemical reaction between the enzyme and its substrate. The active site has a precise three-dimensional structure that is complementary to the shape and chemical properties of the substrate, allowing for specific interactions to occur, such as bonding and positioning of atoms for the reaction to take place efficiently. Additionally, the active site may also undergo conformational changes upon substrate binding, further enhancing the enzyme's catalytic activity.
Describe the induced fit model of enzyme-substrate interaction.
The induced fit model of enzyme-substrate interaction states that enzymes undergo a conformational change upon binding to their substrate. This change in enzyme shape allows for a more snug and complementary fit of the substrate within the enzyme's active site, facilitating the catalytic action of the enzyme on the substrate. The binding of the substrate induces a change in the enzyme's structure, leading to optimal positioning of catalytic groups and promoting the chemical reaction. This model highlights the dynamic nature of enzyme-substrate interactions, emphasizing that both the enzyme and substrate can adjust their shapes to better interact with each other.
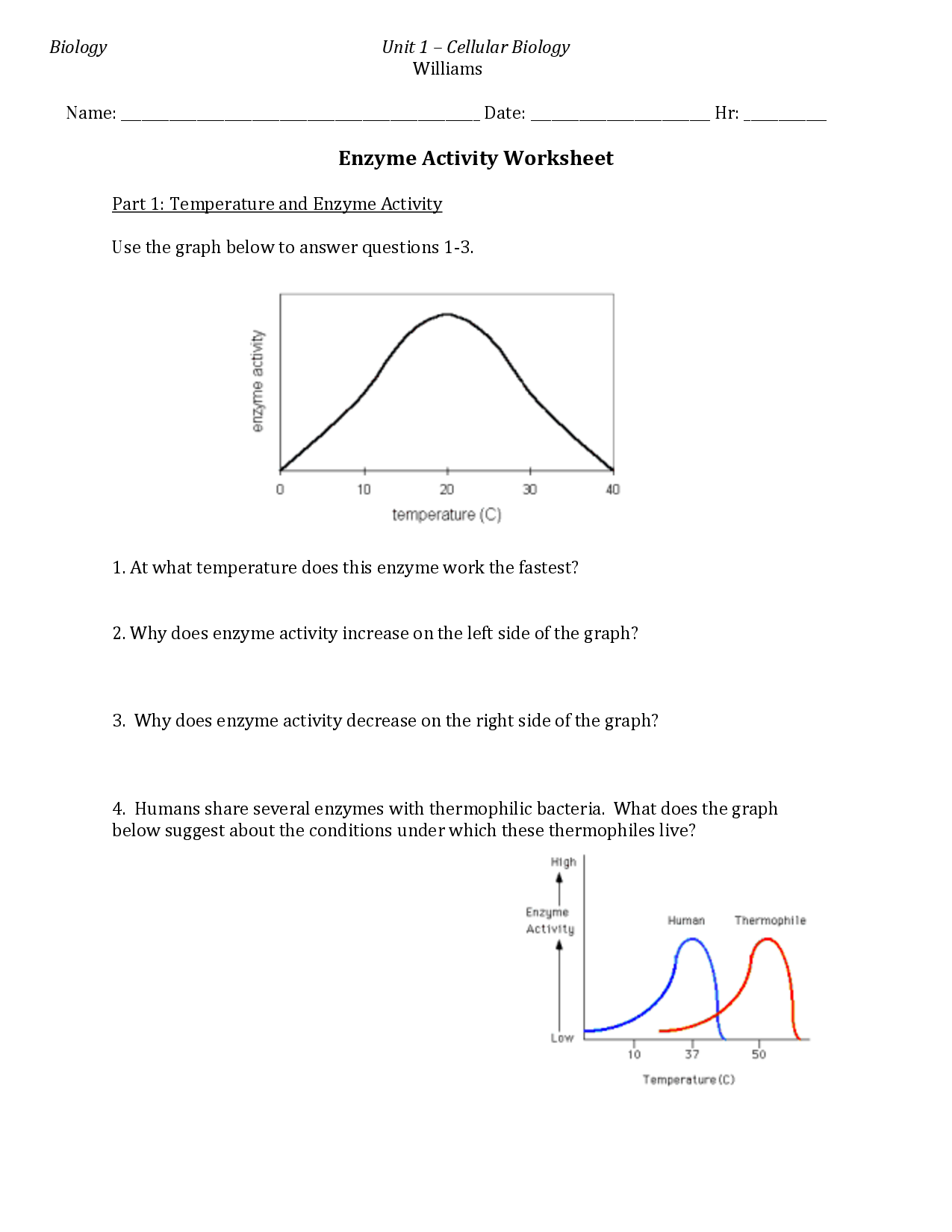
Explain the effect of temperature and pH on enzyme activity.
Temperature and pH have significant effects on enzyme activity. In general, enzymes function optimally within a specific range of temperature and pH. As temperature increases, enzyme activity also increases due to more frequent collisions between enzyme and substrate molecules. However, extreme temperatures can denature enzymes, causing them to lose their shape and thus their function. Similarly, changes in pH can disrupt the chemical interactions that maintain the enzyme's shape and active site, leading to a loss of activity. Enzymes have an optimal pH at which they function best, and deviations from this pH can inhibit their activity. Overall, maintaining appropriate temperature and pH conditions is crucial for maximizing enzyme activity and overall biological processes.
How do competitive inhibitors affect enzyme function?
Competitive inhibitors interfere with enzyme function by binding to the active site of the enzyme, preventing the substrate from binding and inhibiting the catalytic activity of the enzyme. This inhibition is reversible, as the inhibitor can be displaced by increasing the concentration of the substrate, ultimately allowing the enzyme to function normally.
What is allosteric regulation and how does it influence enzyme activity?
Allosteric regulation is when a molecule binds to a site on an enzyme that is not the active site, causing a change in the enzyme's shape and functioning. This regulation can either enhance or inhibit enzyme activity, depending on the specific molecule and its effect on the enzyme. By binding to allosteric sites, molecules can alter the enzyme's affinity for its substrate, effectively influencing the enzyme's activity levels. This type of regulation allows for precise control over metabolic pathways and enzymatic reactions in cells.
Describe the concept of enzyme kinetics and the significance of Michaelis-Menten equation.
Enzyme kinetics is the study of the rates at which enzymes catalyze chemical reactions. The Michaelis-Menten equation is a fundamental model that describes the relationship between the rate of an enzyme-catalyzed reaction and the concentration of substrate. This equation provides crucial information about the efficiency and specificity of an enzyme, as well as its maximum catalytic rate (Vmax) and the substrate concentration at which the reaction rate is half of Vmax (Km). Understanding enzyme kinetics and utilizing the Michaelis-Menten equation is essential in fields such as biochemistry, pharmacology, and biotechnology for optimizing enzyme reactions, designing drugs, and studying enzyme mechanisms.
Have something to share?
Who is Worksheeto?
At Worksheeto, we are committed to delivering an extensive and varied portfolio of superior quality worksheets, designed to address the educational demands of students, educators, and parents.



























Comments