High School DNA Structure Worksheet Answer Key
A DNA Structure Worksheet Answer Key is a useful tool for high school students learning about genetics and molecular biology. This resource provides a comprehensive guide to understanding the concept of DNA structure, which is essential for studying its role in inheritance and genetic composition. By providing a clear and concise answer key, this worksheet helps students solidify their understanding of DNA and its components, making it a valuable resource for biology classrooms.
Table of Images 👆
- DNA Structure and Replication Answer Key POGIL
- DNA Structure Worksheet Answer Key
- DNA Structure Worksheet Answer Key
- DNA Replication Worksheet
- DNA Structure Worksheet High School
- DNA Structure and Replication Worksheet
- Chapter 11 DNA and Genes Worksheet Answers
- DNA Replication Worksheet Answer Key
- DNA Replication Worksheet Key
- Chapter 11 DNA and Genes Worksheet Answers
- DNA Structure Worksheet Answers
- DNA Structure and Replication Worksheet Answer Key
- DNA Replication Worksheet Answer Key
- DNA Replication Worksheet Answer Key
- DNA Replication Worksheet Answer Key
- DNA Protein Synthesis Worksheet Answers
- DNA and Protein Synthesis Worksheet Answers
- DNA the Molecule of Heredity Worksheet Answer Key
More Other Worksheets
Kindergarten Worksheet My RoomSpanish Verb Worksheets
Cooking Vocabulary Worksheet
My Shadow Worksheet
Large Printable Blank Pyramid Worksheet
Relationship Circles Worksheet
DNA Code Worksheet
Meiosis Worksheet Answer Key
Art Handouts and Worksheets
7 Elements of Art Worksheets
What is DNA?
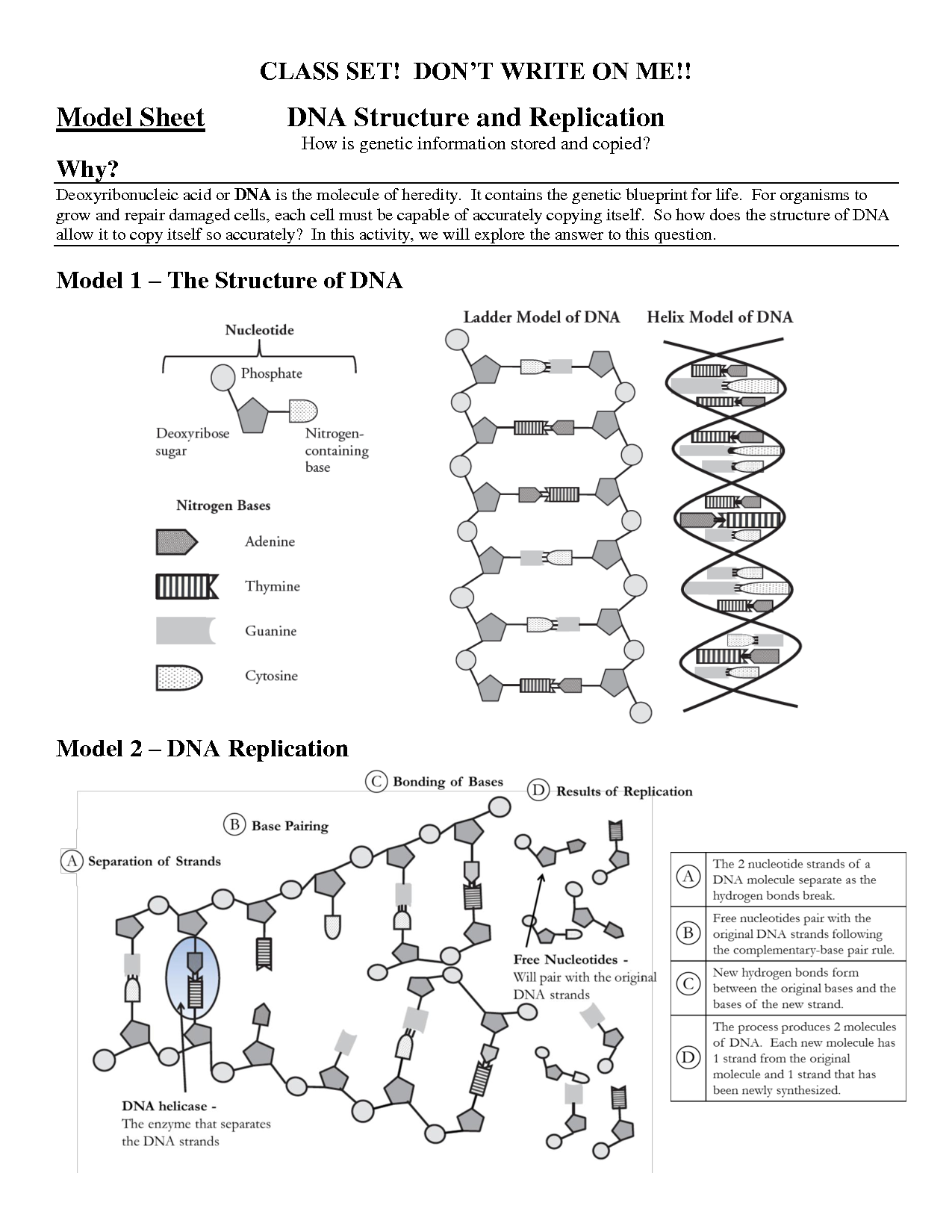
DNA, or deoxyribonucleic acid, is a molecule that encodes the genetic instructions used in the development and functioning of all living organisms. It consists of a long sequence of nucleotides that provide the blueprint for an organism's structure and function by controlling the synthesis of proteins within cells. DNA is found in the nucleus of eukaryotic cells and in the cytoplasm of prokaryotic cells, and its unique double-helix structure allows for the accurate replication and transmission of genetic information from one generation to the next.
What is the structure of DNA?
DNA, or deoxyribonucleic acid, has a double helix structure composed of two long strands of nucleotides that are twisted around each other. Each nucleotide consists of a sugar molecule, a phosphate group, and a nitrogenous base (adenine, thymine, cytosine, or guanine). The nitrogenous bases on each strand pair up in a specific way (A with T, C with G) to form base pairs that hold the two strands together. This structure allows DNA to store and transmit genetic information in living organisms.
What are the components of a DNA nucleotide?
A DNA nucleotide consists of three main components: a deoxyribose sugar molecule, a phosphate group, and a nitrogenous base. The nitrogenous base can be adenine (A), guanine (G), cytosine (C), or thymine (T), which determines the nucleotide's specific identity and function within the DNA molecule. The combination of these three components forms the basic building blocks of DNA that encode genetic information.
How is DNA organized in cells?
DNA in cells is organized into structures called chromosomes. Chromosomes are long strands of DNA that are tightly coiled and condensed to fit inside the cell nucleus. Humans have 46 chromosomes, which are typically present in pairs. Each chromosome contains many genes, which are specific segments of DNA that encode for proteins and play a role in determining an individual's traits and characteristics. The organization of DNA into chromosomes helps to regulate gene expression and ensure that genetic information is properly replicated and passed on to the next generation.
What is the role of DNA in heredity?
DNA, or deoxyribonucleic acid, is the molecule that carries the genetic instructions for all living organisms. In heredity, DNA is responsible for passing on genetic information from one generation to the next. It contains the instructions to produce proteins and determine traits, such as eye color, height, and susceptibility to certain diseases, that are inherited from parents to offspring. DNA is passed down through the process of reproduction, ensuring that offspring inherit a unique combination of genetic traits from their parents.
How does DNA replication occur?
DNA replication occurs in a semi-conservative manner, where the double-stranded DNA molecule unzips into two single strands. Enzymes then add complementary nucleotides to each strand using the original DNA as a template, creating two identical DNA molecules. The end result is two identical daughter DNA molecules that each consist of one original strand and one newly synthesized strand.
What is the significance of DNA mutations?
DNA mutations are significant as they are the driving force behind genetic diversity, evolution, and the development of various inherited genetic disorders and diseases. Mutations can lead to new traits and adaptations in organisms, contributing to biodiversity and evolutionary processes. On the other hand, mutations can also result in genetic diseases such as cancer or genetic disorders by disrupting normal cellular functions. Understanding DNA mutations is crucial in various fields including biotechnology, medicine, and evolutionary biology.
What are the different types of DNA mutations?
There are several types of DNA mutations, including point mutations (substitution, insertion, deletion), frameshift mutations (insertion or deletion of nucleotides that shifts the reading frame), silent mutations (no change in amino acid sequence), missense mutations (change in amino acid sequence), nonsense mutations (premature stop codon), and chromosomal mutations (involving changes in the structure or number of chromosomes).
How are DNA mutations related to genetic disorders?
DNA mutations are related to genetic disorders because mutations can alter the normal functioning of genes, leading to changes in protein structure or quantity. These changes can disrupt essential biological processes, resulting in genetic disorders. Some mutations may directly cause a disorder, while others may increase an individual's susceptibility to developing a disorder when combined with other genetic or environmental factors. Overall, DNA mutations play a critical role in the development of genetic disorders by affecting gene expression and protein production in cells.
How has our understanding of DNA structure impacted scientific and medical advancements?
Our understanding of DNA structure has revolutionized scientific and medical advancements by providing insights into the genetic basis of diseases and traits, allowing for the development of genetic testing, personalized medicine, and gene therapies. It has also led to breakthroughs in areas such as forensics, evolutionary biology, and biotechnology. By unraveling the complex code of DNA, researchers have been able to make significant strides in understanding and treating various health conditions, ultimately improving diagnostic accuracy, treatment efficacy, and overall patient outcomes.
Have something to share?
Who is Worksheeto?
At Worksheeto, we are committed to delivering an extensive and varied portfolio of superior quality worksheets, designed to address the educational demands of students, educators, and parents.


































Comments