Hand Anatomy and Physiology Worksheets
Understanding the intricacies of hand anatomy and physiology is crucial for healthcare professionals, anatomy students, and anyone interested in learning more about the human body. These hand anatomy and physiology worksheets provide a comprehensive yet accessible way to delve into the complexities of this fascinating subject matter.
Table of Images 👆
- Hand Bones Worksheet
- Circulatory System Heart Diagram Worksheet
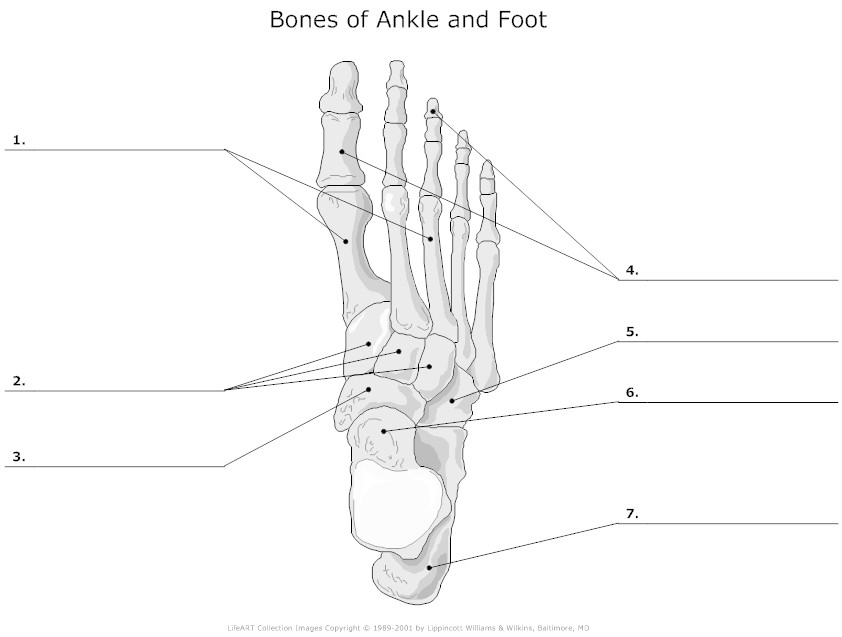
- Foot Bone Diagram Unlabeled
- Excretory System Labeled
- Anatomy and Physiology Bone Worksheets
- Body Movement Terms
- Anatomy Muscle Coloring Worksheet
- Blank Foot Bone Anatomy
- Hand and Wrist Bones Diagram
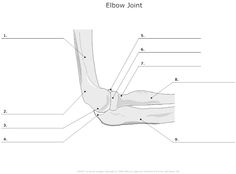
- Elbow Joint Articulations
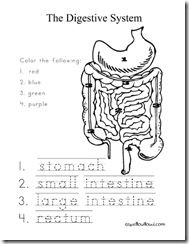
- Digestive System Coloring Worksheet
- Foot Bone Diagram Unlabeled
More Other Worksheets
Kindergarten Worksheet My RoomSpanish Verb Worksheets
Cooking Vocabulary Worksheet
My Shadow Worksheet
Large Printable Blank Pyramid Worksheet
Relationship Circles Worksheet
DNA Code Worksheet
Meiosis Worksheet Answer Key
Art Handouts and Worksheets
7 Elements of Art Worksheets
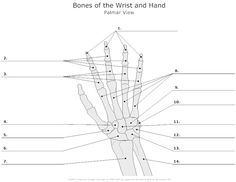
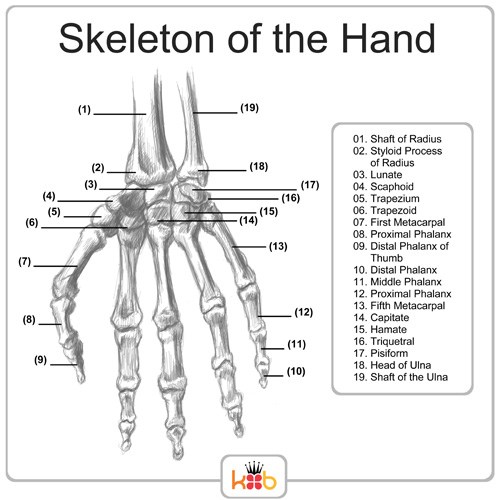
What are the bones in the hand called?
The bones in the hand are called metacarpal bones and phalanges. The metacarpal bones are the five long bones in the palm of the hand, while the phalanges are the fourteen small bones that make up the fingers and thumb.
How many phalanges are there in each finger?
Each finger typically has three phalanges, except for the thumb, which has two phalanges.
What is the purpose of the carpal bones in the hand?
The carpal bones in the hand provide structure, stability, and flexibility to the wrist and hand. They form the wrist joint, allowing for a wide range of motion while also supporting the weight and activities performed by the hand. Additionally, these bones help protect the nerves and blood vessels that pass through the wrist to the hand, ensuring proper function and sensation in the hand.
How many metacarpal bones are present in the hand?
There are five metacarpal bones present in the hand, one for each digit.
What are the two main types of joints found in the hand?
The two main types of joints found in the hand are the hinge joints and the saddle joints. Hinge joints, like those found in the fingers, allow movement in one direction, such as bending and straightening. Saddle joints, like the joint at the base of the thumb, allow for a wider range of motion, including bending, straightening, and rotating.
What is the function of the flexor tendons in the hand?
The function of the flexor tendons in the hand is to help flex or bend the fingers and thumb. These tendons run along the underside of the hand and connect the muscles in the forearm to the bones in the fingers, allowing for movements such as gripping objects or making a fist. They are vital for tasks that require fine motor control and strength in the hand.
What is the role of the extensor tendons in hand movement?
The extensor tendons in the hand are responsible for extending or straightening the fingers and thumb. These tendons run along the back of the hand and are attached to the muscles in the forearm. When the forearm muscles contract, they pull on the extensor tendons, causing the fingers and thumb to straighten and move away from the palm. This action enables us to grasp objects, release them, and perform various hand movements with precision and control.
What are the thenar muscles and what is their function?
The thenar muscles are a group of three intrinsic muscles located in the palm of the hand near the base of the thumb. These muscles include the abductor pollicis brevis, the flexor pollicis brevis, and the opponens pollicis. Their main function is to control the movements of the thumb, including abducting, flexing, and opposing it. These muscles play a crucial role in fine motor skills, gripping, and manipulating objects with the thumb and fingers.
How many intrinsic muscles are there in the hand, and what do they control?
There are approximately 35 intrinsic muscles in the hand. These muscles control fine motor movements, grip strength, coordination, and dexterity in activities such as writing, grasping objects, and typing. They play a crucial role in hand function and overall hand agility.
What is the purpose of the palmar aponeurosis in the hand?
The palmar aponeurosis is a thick layer of connective tissue in the palm of the hand that acts like a protective sheath for the underlying structures such as nerves and blood vessels. It helps to provide support and structure to the palm, allowing for grasping and movement while also protecting the soft tissues beneath it. Additionally, the palmar aponeurosis plays a role in distributing forces and pressures across the palm during various activities.
Have something to share?
Who is Worksheeto?
At Worksheeto, we are committed to delivering an extensive and varied portfolio of superior quality worksheets, designed to address the educational demands of students, educators, and parents.






















Comments